day11复习

一、static关键字
可以修饰成员变量和成员方法,被修饰的成员可以被类的所有对象所共享

1.1 静态的特点
1. 随着类的加载而加载
2. 优先于对象而存在
3. 被类的所有对象共享
4. 被静态修饰的变量可以通过 对象名.变量名 访问,但更建议使用 类名.变量名 访问
/*
手机类
*/
public class Phone {
//成员变量
String brand; //品牌
String color;
int price;
static String location; //产地
//构造方法
public Phone(){
}
public Phone(String brand, String color, int price){
this.brand = brand;
this.color = color;
this.price = price;
}
public Phone(String brand, String color, int price, String location){
this.brand = brand;
this.color = color;
this.price = price;
this.location = location;
}
//getXxx和setXxx
public void setBrand(String brand){
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getBrand(){
return brand;
}
public void setColor(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor(){
return color;
}
public void setPrice(int price){
this.price = price;
}
public int getPrice(){
return price;
}
public void setLocation(String location){
this.location = location;
}
public String getLocation(){
return location;
}
//show方法
public void show(){
System.out.println(brand + "---" + color + "---" + price + "---" + location);
}
}
/*
测试类
下方的代码:每部手机有不同的品牌、颜色、价格,它们在堆上占用相应的空间我们是可以接受,
但是产地都为中国(也就是一样)的话,我们还需要在堆上再开一个空间分别存放它们,这样我们就接受不了。
(因为这样造成了空间的浪费、管理维护也比较麻烦)
我们应该单独建立一个空间,来统一存放这个静态的变量即可。
Java中有static关键字可以修饰成员变量,然后被修饰的成员变量被类的所有对象所共享
*/
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建对象
Phone p = new Phone();
// 通过set方法赋值
p.setBrand("xiaomi");
p.setColor("black");
p.setPrice(3999);
// p.setLocation("中国");
Phone.location = "HongKong";
//-------------------
Phone p2 = new Phone("huawei", "black", 6999);
Phone p3 = new Phone("iphone", "gold", 10999 );
Phone p4 = new Phone("samsung", "yellow", 9999);
Phone p5 = new Phone();
//展示数据
p.show();
p2.show();
p3.show();
p4.show();
p5.show();
}
}
1.2 静态的注意事项
静态方法:就是被static修饰的方法
格式:
public static 返回值类型 方法名(参数列表){}
1. 静态方法可以访问非静态的变量吗?
不能访问。因为非静态的变量是随着对象的创建而存在,而静态的变量是跟着类加载的而存在,(类要先加载,才能创建对象,也就是有先后)。如果静态的方法可以访问非静态的变量,那就造成了逻辑上的错误。
2. 静态的方法可以访问非静态的方法吗?
不能访问。因为非静态方法可以访问到非静态的变量,如果静态方法可以访问到非静态方法的话,那么也就间接的访问了非静态的变量,还是错误的。
总结:静态只能访问静态
class Car {
//普通的变量
String brand;
//静态的变量
static String color;
//普通的方法
public void test(){
System.out.println(brand);
System.out.println(color); //非静态方法可以访问静态变量
a(); //非静态方法可以访问静态方法
}
//静态的方法
public static void show(){
System.out.println(color); //静态的方法可以访问静态的变量
// System.out.println(brand); //静态的方法不能访问非静态的变量
// test(); //静态的方法不能访问非静态的方法
a();
}
public static void a(){
}
}
1.3 静态变量和成员变量的区别
1. 所属不同
静态变量:跟着类
成员变量:跟着对象
2. 内存中的位置不同:
静态变量:方法区
成员变量:堆上
3. 生命周期不同:
静态变量:随着类的加载而存在,随着类的销毁而消失
成员变量:随着对象的创建而存在,随着对象的回收而消失
4. 调用方式不同:
静态变量:既可以通过 对象名.变量名 也可以通过 类名.变量名【推荐】 访问
成员变量:只能通过 对象名.变量名 访问
二、main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public:是权限修饰符,表示公开的,最大的权限
static:被static修饰的内容,可以直接通过类名访问,可以很方便的被jvm虚拟机调用
void: 没有返回值,因为虚拟机不需要返回值
main: 大部分语言程序的入口方法,都被叫做main
String[] args:之前被用来作为键盘录入
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(args.length);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
System.out.println(args[i]);
}
}
}
三、帮助文档
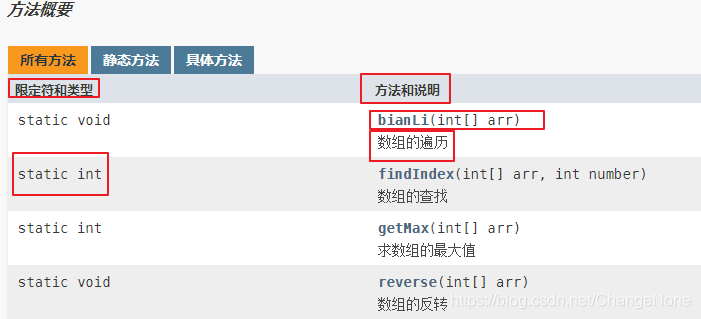
新建一个ArrayTools工具类,在类中定义数组遍历、求最大值、反转、查找4个方法,并写上相应的注释。最后在Demo中进行测试
/**
这是一个关于数组的工具类ArrayTools,
其中包含了数组遍历、求最大值、反转、查找等方法
@author NEO
@version 1.1
@since 1.0
*/
public class ArrayTools {
/**
数组的遍历
@param arr 要被遍历的数组
*/
public static void bianLi(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
/**
求数组的最大值
@param arr 要求最值的数组
@return 求得的最大值
*/
public static int getMax(int[] arr) {
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i] > max){
max = arr[i];
}
}
return max;
}
/**
* 数组的反转
* @param arr 要被反转的数组
*/
public static void reverse(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length / 2; i++) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[arr.length-1-i];
arr[arr.length-1-i] = temp;
}
}
/**
数组的查找
@param arr 要被查找的数组
@param number 待查找的数
@return 对应的索引(如果找不到则返回-1)
*/
public static int findIndex(int[] arr, int number) {
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i] == number) {
index = i;
}
}
return index;
}
}
/*
测试类
*/
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55};
System.out.println(ArrayTools.getMax(arr));
ArrayTools.reverse(arr);
ArrayTools.bianLi(arr);
System.out.println(ArrayTools.findIndex(arr, 33));
}
}
如何使用帮助文档
1. 先在左侧的index搜索框处搜索类、接口等
2. 看类、接口等的简介,及从什么版本开始支持的
3. 看有无构造构造方法(有构造方法了,就可以创建对象了;没有构造方法,要么方法全是静态的,要么可以通过其它方式获取对象)
4. 看方法
看右边
方法名一定要正确
参数列表一定要确定好
看左边
返回值类型
看是否被static修饰
练习:
猜数字的大小:键盘录入一个数,然后判断是否和随机生成的数(1-100)相同,如果大了,那就提示“大了”,如果小了,那就提示”小了“,如果相同,那就提示”正确“。
/*
猜数字的大小:键盘录入一个数,然后判断是否和随机生成的数(1-100)相同,
如果大了,那就提示“大了”,如果小了,那就提示”小了“,如果相同,那就提示”正确“。
*/
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 生成一个随机数(1-100)
int number = (int)(Math.random()*100 + 1);
System.out.println(number);
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//2. 多次猜,所以需要放在循环中
while(true) {
System.out.println("请输入您猜的数:");
int guessNumber = sc.nextInt();
//3. 判断是否相等
if(guessNumber > number) {
System.out.println("Big!");
}else if(guessNumber < number) {
System.out.println("Small!");
}else {
System.out.println("Bingo!");
break; //猜对之后就退出循环
}
}
}
}
四、继承
将一些类中共同的内容提取到一个公共的类中,然后这些类通过固定的格式和这个公共的类产生关联性,产生关联性之后就可以使用这个公共类中所有的内容了,这样极大简化代码书写和管理的行为被我们称为继承。
4.1 格式
关键字:extends
格式:
class 子类 extends 父类 {
}
注意:
父类又被称为基类、超类
子类又被称为派生类
/*
公共的类:
在此类中可以提取定义一些内容,方便其他类使用
*/
public class Person {
String name;
int age;
public void eat(){
System.out.println("吃饭");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("睡觉");
}
}
/*
护士类
*/
public class Nurse extends Person {
}
/*
医生类
*/
public class Doctor extends Person {
}
/*
测试类
*/
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Nurse n = new Nurse();
n.sleep();
Doctor d = new Doctor();
d.eat();
}
}





 该博客主要复习Java知识,涵盖static关键字,其可修饰成员变量和方法,被修饰成员可被类的所有对象共享;还介绍了main方法、帮助文档的使用,新建ArrayTools工具类进行测试;最后讲解继承,将公共内容提取到公共类,通过固定格式关联以简化代码。
该博客主要复习Java知识,涵盖static关键字,其可修饰成员变量和方法,被修饰成员可被类的所有对象共享;还介绍了main方法、帮助文档的使用,新建ArrayTools工具类进行测试;最后讲解继承,将公共内容提取到公共类,通过固定格式关联以简化代码。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










