Vue框架的虚拟DOM部分是基于snabbdom优化的,我们接下来就通过snabbdom分析一下diff算法的原理是什么,为什么要使用diff算法。
安装snabbdom
我本地使用了webpack打包工具安装了dev-server插件方便调试。配置文件如下:
//webpack.config.js
const path = require('path')
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
filename: 'main.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist')
},
devServer: {
static: {
directory: './dist'
},
compress: true,
port: 8090
}
}
之后我们直接安装snabbdom即可
npm install snabbdom
核心方法介绍
snabbdom对外暴露了两个核心方法init和h
init函数会根据配置返回patch方法
patch方法用于对比新老Vnode,并且将新的虚拟DOM渲染成真实DOM,是我们研究的重点。
h方法用于创建Vnode
h函数
h函数用来创建一个虚拟节点,函数声明如下:

我们打印一下虚拟节点,如下
patch函数
path函数用来对比新老vnode并把最新内容渲染到页面上。
我们通过一个简单的例子实现向页面渲染内容
port {init,h,styleModule} from 'snabbdom'
const patch = init([styleModule])
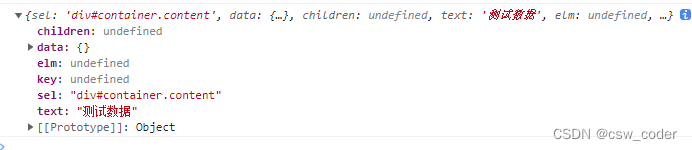
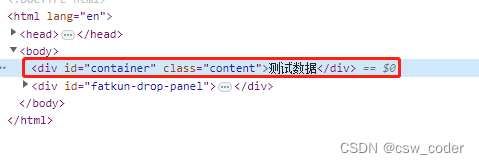
const vnode = h("div.content#container", '测试数据');
const oldVnode = patch(document.getElementById('app'),vnode)
patch函数的第一个参数如果是dom元素,会用vnode来代替该内容
patch函数同样会返回一个vnode,作为老的虚拟dom。我们可以新建一个vnode然后通过patch函数对比渲染出新的dom
import { init, h, styleModule } from 'snabbdom'
const patch = init([styleModule])
const vnode = h('div#container.content', '测试数据')
const oldVnode = patch(document.getElementById('app'), vnode)
const newVnode = h('div', 'hello world')
patch(oldVnode, newVnode)
diff算法
既然新老vnode对比发生在patch函数内,那patch函数自然是重点研究对象,diff算法也是在此发生。
同级比较
Diff算法的核心就是针对具有相同父节点的同层新旧子节点进行比较,而不是使用逐层搜索递归遍历的方式。时间复杂度为O(n)。
patch
patch函数负责判断两个节点是否相同,如果相同则调用patchNode继续比较,否则直接将老节点替换成新节点。

源码如下
return function patch(
oldVnode: VNode | Element | DocumentFragment,
vnode: VNode
): VNode {
let i: number, elm: Node, parent: Node;
const insertedVnodeQueue: VNodeQueue = [];
for (i = 0; i < cbs.pre.length; ++i) cbs.pre[i]();
if (isElement(api, oldVnode)) {
oldVnode = emptyNodeAt(oldVnode);
} else if (isDocumentFragment(api, oldVnode)) {
oldVnode = emptyDocumentFragmentAt(oldVnode);
}
//相同节点
if (sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
//调用patchNode进一步比较
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
} else {
//不同节点
elm = oldVnode.elm!;
parent = api.parentNode(elm) as Node;
createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
if (parent !== null) {
//替换成新节点
api.insertBefore(parent, vnode.elm!, api.nextSibling(elm));
removeVnodes(parent, [oldVnode], 0, 0);
}
}
for (i = 0; i < insertedVnodeQueue.length; ++i) {
insertedVnodeQueue[i].data!.hook!.insert!(insertedVnodeQueue[i]);
}
for (i = 0; i < cbs.post.length; ++i) cbs.post[i]();
return vnode;
};
patchNode
接下来该pathNode登场了,这是diff算法发生的地方。
新老节点都可能有text属性或者children属性,需要覆盖所有情况。
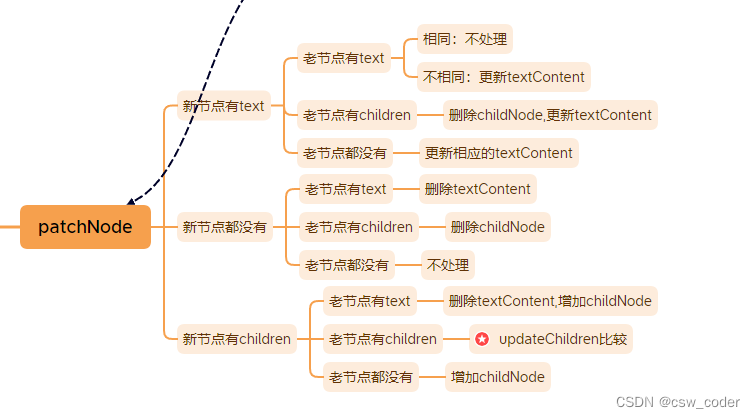
代码实现上肯定要比上图简洁,如下
function patchVnode(
oldVnode: VNode,
vnode: VNode,
insertedVnodeQueue: VNodeQueue
) {
const hook = vnode.data?.hook;
hook?.prepatch?.(oldVnode, vnode);
const elm = (vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm)!;
if (oldVnode === vnode) return;
if (
vnode.data !== undefined ||
(isDef(vnode.text) && vnode.text !== oldVnode.text)
) {
vnode.data ??= {};
oldVnode.data ??= {};
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.update.length; ++i)
cbs.update[i](oldVnode, vnode);
vnode.data?.hook?.update?.(oldVnode, vnode);
}
const oldCh = oldVnode.children as VNode[];
const ch = vnode.children as VNode[];
if (isUndef(vnode.text)) {
if (isDef(oldCh) && isDef(ch)) {
if (oldCh !== ch) updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch, insertedVnodeQueue);
} else if (isDef(ch)) {
if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) api.setTextContent(elm, "");
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1, insertedVnodeQueue);
} else if (isDef(oldCh)) {
removeVnodes(elm, oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1);
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) {
api.setTextContent(elm, "");
}
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
if (isDef(oldCh)) {
removeVnodes(elm, oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1);
}
api.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text!);
}
hook?.postpatch?.(oldVnode, vnode);
}
updateChildren
接下来是对子节点的比较
暴力对比
我们先不考虑算法,给定两个children,我们使用暴力方式对比会有什么问题呢?
假定给出:老children: [A,B,C,D] 新children:[D,A,B,C]
用暴力对比会将所有的节点全部替换掉,这显然是不可取的,我们明明只需要把D移动到A前面即可。
实际上的dom操作大部分都是有规律的,比如说插入,排序,删除,只会有一部分节点需要变动,所以引入了首尾指针算法来对children进行对比
首尾指针
首尾指针能让我们以更小的成本来更新dom,减小开销。
我们假定旧节点有头指针oldStartIndex, 尾指针olcEndIndex
新节点有头指针newStartIndex,尾指针newEndIndex
比较顺序是 旧首新首,旧尾新尾,旧首新尾,旧尾新首。
前面的规则没有命中时,才会继续下面的规则,如果都没有命中,则从旧节点中查找,找得到用旧节点,找不到创建新节点。
我们拿一个例子:
初始如下
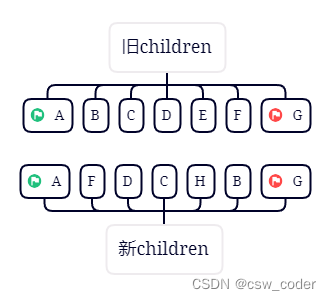
1.首先对比旧首新首,新旧都是A,则直接patchVnode,新旧 首指针向后移动
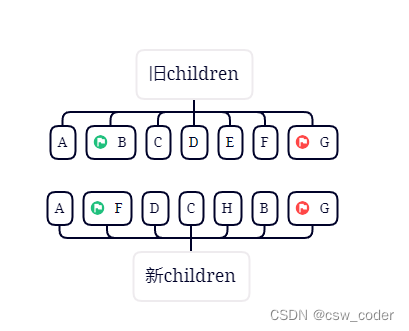
2.对比旧首新首,发现一个是B一个是A,则比较旧尾新尾,发现一样,则直接pathVnode,新旧尾指针前移
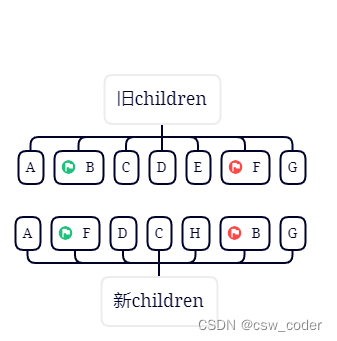
3.对比旧首新首,旧尾新尾,都不一样,再对比旧首新尾,发现一样,patchVnode之后,将B移动到旧尾指针下一个节点,
新尾指针前移,旧首指针后移。
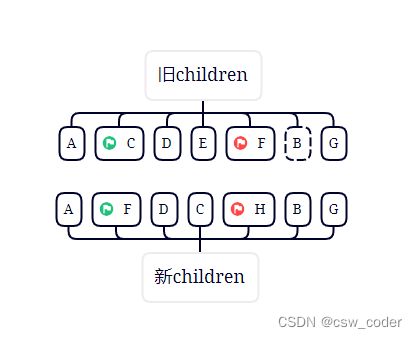
4.对比旧首新首,旧尾新尾,旧首新尾都不一样,但是旧尾新尾一样,parchVnode之后,将F移动到旧首指针的上一个节点。
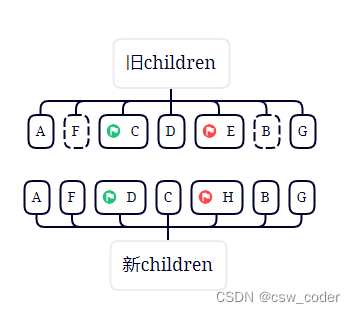
5.重新走上述规则,发现都没有命中,则从旧节点中查找D,找到之后patchVnode并移动D,并将D原来的索引位置置为undefined
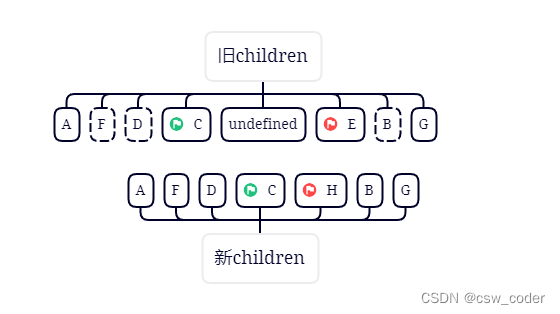
6.好的,接下来C旧首新首相同
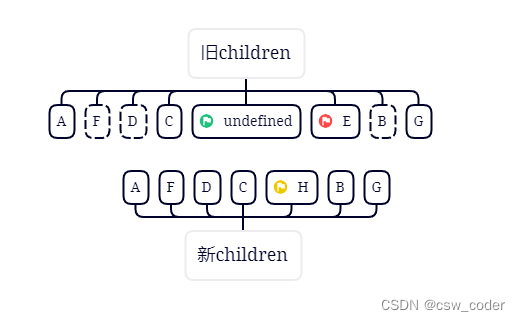
7.这时候旧首再undefined,直接跳过,新首新尾重合,用黄色标记
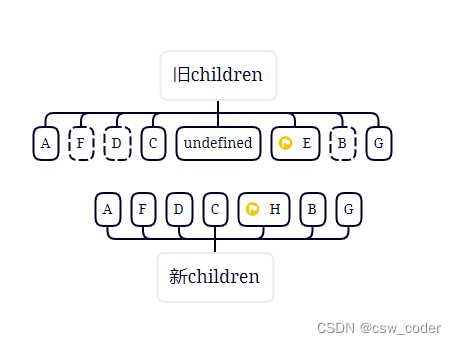
8.ok,再走所有规则发现都未命中,旧节点中不包含H,则创建H
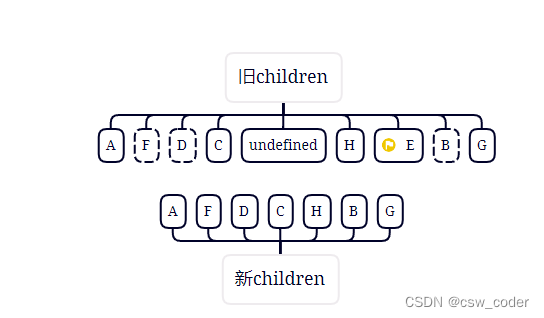
9.这时候新节点已经走完了,发现老节点还有剩余则直接删除掉E,那如果新节点有剩余呢,则将剩余节点插入到dom中。
源代码如下
function updateChildren(
parentElm: Node,
oldCh: VNode[],
newCh: VNode[],
insertedVnodeQueue: VNodeQueue
) {
let oldStartIdx = 0;
let newStartIdx = 0;
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1;
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0];
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx];
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1;
let newStartVnode = newCh[0];
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx];
let oldKeyToIdx: KeyToIndexMap | undefined;
let idxInOld: number;
let elmToMove: VNode;
let before: any;
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
if (oldStartVnode == null) {
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]; // Vnode might have been moved left
} else if (oldEndVnode == null) {
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
} else if (newStartVnode == null) {
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
} else if (newEndVnode == null) {
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) {
// Vnode moved right
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
api.insertBefore(
parentElm,
oldStartVnode.elm!,
api.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm!)
);
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) {
// Vnode moved left
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
api.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm!, oldStartVnode.elm!);
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
} else {
if (oldKeyToIdx === undefined) {
oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
}
idxInOld = oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key as string];
if (isUndef(idxInOld)) {
// New element
api.insertBefore(
parentElm,
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue),
oldStartVnode.elm!
);
} else {
elmToMove = oldCh[idxInOld];
if (elmToMove.sel !== newStartVnode.sel) {
api.insertBefore(
parentElm,
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue),
oldStartVnode.elm!
);
} else {
patchVnode(elmToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined as any;
api.insertBefore(parentElm, elmToMove.elm!, oldStartVnode.elm!);
}
}
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
}
}
if (newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
before = newCh[newEndIdx + 1] == null ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm;
addVnodes(
parentElm,
before,
newCh,
newStartIdx,
newEndIdx,
insertedVnodeQueue
);
}
if (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
}
}
流程图如下
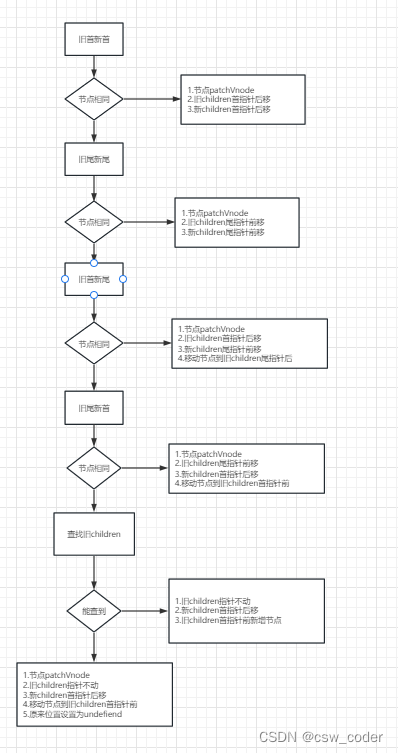
优化
其实上面的第5部说的不够准确,假如通过遍历的方式查找那每个节点的查找时间复杂度为O(n)。这是无法接受的,所以引入了key,
通过key,我们可以实现HashMap从而将时间复杂度降为O(1)·。这就说明了,为何指定key要唯一,不唯一会出现不符合预期的结果。
那如果不指定key呢,会按照找不到处理,直接插入,最终多的节点会被删除。
相关代码如下:
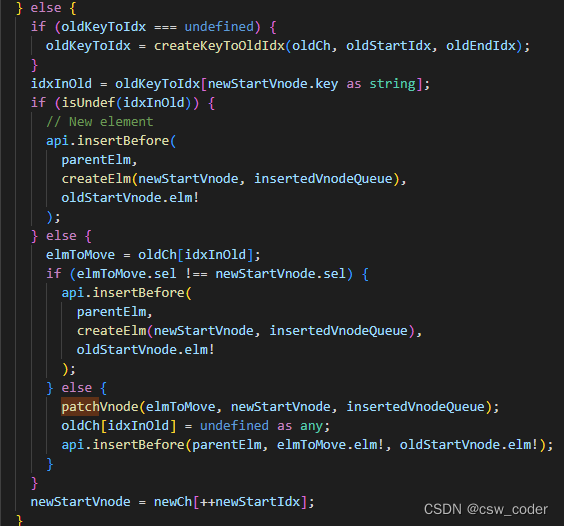

























 216
216











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










