深度学习笔记
学习视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ZX4y1c7Sw/?p=3&spm_id_from=pageDriver&vd_source=75dce036dc8244310435eaf03de4e330
多尺度目标检测
%matplotlib inline
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
img = d2l.plt.imread('../img/catdog1.jpg')
h, w = img.shape[:2]
h,w
(450, 640)
特征图:某个卷积层上的输出
在特征图 (fmap) 上生成锚框 (anchors),每个单位(像素)作为锚框的中心
def display_anchors(fmap_w, fmap_h, s):
d2l.set_figsize()
# 10 通道数
fmap = torch.zeros((1,10, fmap_h, fmap_w))
# 生成锚框(ratios锚框在整个图片的大小)
anchors = d2l.multibox_prior(fmap, sizes=s,
ratios=[1,2,0.5])
bbox_scale = torch.tensor((w, h, w,h))
# 画出锚框 anchors【0】 : batch_size =1 所以拿出那个锚框
# 乘以 bbox_scale 还原成真正大小图片上的锚框
d2l.show_bboxes(d2l.plt.imshow(img).axes, anchors[0]*bbox_scale)
探测小目标
display_anchors(fmap_w=4, fmap_h=4, s=[0.15]) # 锚框排列 4 * 4
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-KDr4k7pG-1675150702256)(output_5_0.svg)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/296512def8ee4749b66f481669b75afb.png)
将特征图的高度和宽度减小一半,然后使用较大的锚框来检测较大的目标
display_anchors(fmap_w=2, fmap_h=2, s=[0.4])
将特征图的高度和宽度减小一半,然后将锚框的尺度增加到0.8
display_anchors(fmap_w=1, fmap_h=1, s=[0.8]) # 将锚框缩成一个像素
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-2EQLamGX-1675150702257)(output_9_0.svg)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8aa8552bd6274efdbe014e9834bff0b4.png)
后面层做大的锚框,对全局看得更好;下层取小的锚框,去尝试框住小的物体。
单发多框检测(SSD 实现)
类别预测层
%matplotlib inline
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from d2l import torch as d2l
# 预测类别
def cls_predictor(num_inputs, num_anchors, num_classes):
# num_inputs 输入通道数 num_anchors + 1 加的是背景类, 对每一个锚框都要去预测它的类
# 通道数是 每个像素生成的多个锚框的预测
return nn.Conv2d(num_inputs, num_anchors * (num_classes + 1),
kernel_size=3, padding=1)
边界框预测层
# 预测与真实锚框的偏移
def bbox_predictor(num_inputs, num_anchors):
# 通道数:num_anchors * 4 输入和输出高宽一致
return nn.Conv2d(num_inputs, num_anchors * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
连接多尺度的预测
def forward(x, block):
return block(x)
Y1 = forward(torch.zeros((2,8,20,20)), cls_predictor(8, 5, 10))
Y2 = forward(torch.zeros((2, 16, 10, 10)), cls_predictor(16, 3, 10))
Y1.shape, Y2.shape
(torch.Size([2, 55, 20, 20]), torch.Size([2, 33, 10, 10]))
def flatten_pred(pred):
# 1 :通道数挪到最后(为了每个预测后面是个连续值) flatten 后面维度拉成向量变成2D
return torch.flatten(pred.permute(0, 2, 3, 1), start_dim=1)
def concat_preds(preds):
# 拉成2D后在框上 concat起来(目的是后面的代码会简单点)
return torch.cat([flatten_pred(p) for p in preds], dim=1)
concat_preds([Y1, Y2]).shape
torch.Size([2, 25300])
高和宽减半块
# 网络块定义(前面学过的任何一个网络都行,通常使用pretune好的模型)
# 最简单的CNN网络做演示,主要干的事:每次把高宽减半
def down_sample_blk(in_channels, out_channels):
blk = []
# 一个卷积+ bn + relu(重复两次) + maxPool2d(高宽减半)
for _ in range(2):
blk.append(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
blk.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels))
blk.append(nn.ReLU())
in_channels = out_channels
blk.append(nn.MaxPool2d(2))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
# 高宽20 通道数3 的输入,输出通道数变成10 高宽减半10 2 批量大小
forward(torch.zeros((2, 3, 20, 20)), down_sample_blk(3, 10)).shape
torch.Size([2, 10, 10, 10])
基本网络块
# 从原始图片抽特征,一直到第一次对featuremap做锚框,中间部分为base_net
# 给一张图片,有三个 down_sample_blk 放在一起
def base_net():
blk = []
# 通道数,输入3 ,然后不断从16变成32, 64
num_filters = [3, 16, 32, 64]
# 构造三个 down_sample_blk ,通道数变化如上,最后输出64
for i in range(len(num_filters) - 1):
blk.append(down_sample_blk(num_filters[i], num_filters[i + 1]))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
# 32, 32 : 减少了8倍, 通道数变成64
forward(torch.zeros((2, 3, 256, 256)), base_net()).shape
torch.Size([2, 64, 32, 32])
完整的单发多框检测模型由五个模块组成
# 整个网络 5个stage(一个手动构造的完整的SDD)
# base_net 之后也是三个 down_sample_blk 最后 AdaptiveMaxPool2d
def get_blk(i):
if i == 0:
# 通道数变成64
blk = base_net()
elif i == 1:
# 通道数变成128
blk = down_sample_blk(64, 128)
elif i == 4:
# 最后 featuremap压到一个 1*1
blk = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d((1, 1))
else:
# 2,3 通道数不变(因为图片比较小,没必要在增加了)
blk = down_sample_blk(128, 128)
return blk
为每个块定义前向计算
# 对每个stage 做前向计算
# 与之前不一样,因为要处理锚框
# blk 当前网络 size 、 ratio 这个分辨率下的锚框构造参数
def blk_forward(X, blk, size, ratio, cls_predictor, bbox_predictor):
# Y 当前卷积层的输出
Y = blk(X)
# 输入锚框的超参数,生成锚框
anchors = d2l.multibox_prior(Y, sizes=size, ratios=ratio)
# 对每个Y 算每个锚框的类别(并不需要把锚框传进去,在构造时已经传进去,
# 看到的是整个Y, 而不是单独的锚框,之后算LOSS的时候才会尽量去看锚框内的东西)
cls_preds = cls_predictor(Y)
# 到真实锚框的偏移预测
bbox_preds = bbox_predictor(Y)
# 输出,生成的锚框,锚框类别预测, 到真实锚框的偏移预测
return (Y, anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds)
超参数
# 5 个stage , 每个stage要设置锚框的size(在整个图片的占比)和ratio(高宽比)
# 均匀的往上加
sizes = [[0.2, 0.272], [0.37, 0.447], [0.54, 0.619], [0.71, 0.79],
[0.88, 0.961]]
# 一般固定住,这个常用的组合
ratios = [[1, 2, 0.5]] * 5
# 每个像素为中心,生成的锚框数
num_anchors = len(sizes[0]) + len(ratios[0]) - 1
定义完整的模型
# 完整的网络,简单一点的一个SSD
class TinySSD(nn.Module):
# num_classes 类别
def __init__(self, num_classes, **kwargs):
super(TinySSD, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.num_classes = num_classes
# 每个stage的输出
idx_to_in_channels = [64, 128, 128, 128, 128]
# 在 5个尺度上做 5 次预测
for i in range(5):
setattr(self, f'blk_{i}', get_blk(i))
setattr(
self, f'cls_{i}',
cls_predictor(idx_to_in_channels[i], num_anchors,
num_classes))
setattr(self, f'bbox_{i}',
bbox_predictor(idx_to_in_channels[i], num_anchors))
# 完整的forward函数
def forward(self, X):
anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds = [None] * 5, [None] * 5, [None] * 5
# 对每个stage run blk_forward
for i in range(5):
# 拿出一些参数
X, anchors[i], cls_preds[i], bbox_preds[i] = blk_forward(
X, getattr(self, f'blk_{i}'), sizes[i], ratios[i],
getattr(self, f'cls_{i}'), getattr(self, f'bbox_{i}'))
# 将所有的anchor并在一起
anchors = torch.cat(anchors, dim=1)
# 所有的预测并在一次
cls_preds = concat_preds(cls_preds)
# reshape为3D, 做softmax方便,最后将类别的预测值拿出来
cls_preds = cls_preds.reshape(cls_preds.shape[0], -1,
self.num_classes + 1)
bbox_preds = concat_preds(bbox_preds)
# 所有东西concat在一起之后,输出回去(每一层跑出的东西,然后合并到一起)
return anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds
创建一个模型实例,然后使用它 执行前向计算
# 创建net
net = TinySSD(num_classes=1)
# 32 批量大小
X = torch.zeros((32, 3, 256, 256))
# 算 5444 个锚框 2 num_classes+1(1 是背景) 21776 = 5444*4 (每个锚框要预测4次)
anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds = net(X)
print('output anchors:', anchors.shape)
print('output class preds:', cls_preds.shape)
print('output bbox preds:', bbox_preds.shape)
output anchors: torch.Size([1, 5444, 4])
output class preds: torch.Size([32, 5444, 2])
output bbox preds: torch.Size([32, 21776])
读取 香蕉检测数据集
batch_size = 32
# 每个图片可能有多个对应的边缘框
train_iter, _ = d2l.load_data_bananas(batch_size)
read 1000 training examples
read 100 validation examples
初始化其参数并定义优化算法
device, net = d2l.try_gpu(), TinySSD(num_classes=1)
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.2, weight_decay=5e-4)
定义损失函数和评价函数
# reduction : 不要将所有的加起来 (分类loss)
cls_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
# 回归loss
# 真实的offset 做减法然后取平均值,L1 当预测特别不准时也不会给你一个特别大的值
bbox_loss = nn.L1Loss(reduction='none')
def calc_loss(cls_preds, cls_labels, bbox_preds, bbox_labels, bbox_masks):
batch_size, num_classes = cls_preds.shape[0], cls_preds.shape[2]
# cls_preds 之前reshape成了3D,-1 将批量大小和锚框维放到一起
cls = cls_loss(cls_preds.reshape(-1, num_classes),
cls_labels.reshape(-1)).reshape(batch_size, -1).mean(dim=1)
# bbox_masks :作用是如果这个锚框是背景框的时候=0,使背景框不去做乘法
bbox = bbox_loss(bbox_preds * bbox_masks,
bbox_labels * bbox_masks).mean(dim=1)
return cls + bbox
# 分类精度
def cls_eval(cls_preds, cls_labels):
return float(
(cls_preds.argmax(dim=-1).type(cls_labels.dtype) == cls_labels).sum())
# 非背景锚框的预测错误
def bbox_eval(bbox_preds, bbox_labels, bbox_masks):
return float((torch.abs((bbox_labels - bbox_preds) * bbox_masks)).sum())
训练模型
num_epochs, timer = 20, d2l.Timer()
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs],
legend=['class error', 'bbox mae'])
net = net.to(device)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
metric = d2l.Accumulator(4)
net.train()
for features, target in train_iter:
timer.start()
trainer.zero_grad()
X, Y = features.to(device), target.to(device)
anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds = net(X)
# multibox_target 把 anchors y 拿进去后,将锚框和真实的锚框对应起来
# 对每个锚框变成样本,拿到类别编号,是不是只有背景和对应的物体的类别,然后就可以算loss了
bbox_labels, bbox_masks, cls_labels = d2l.multibox_target(anchors, Y)
# 计算损失(分类误差+损失误差)
l = calc_loss(cls_preds, cls_labels, bbox_preds, bbox_labels,
bbox_masks)
# 然后在loss上回归
l.mean().backward()
trainer.step()
metric.add(cls_eval(cls_preds, cls_labels), cls_labels.numel(),
bbox_eval(bbox_preds, bbox_labels, bbox_masks),
bbox_labels.numel())
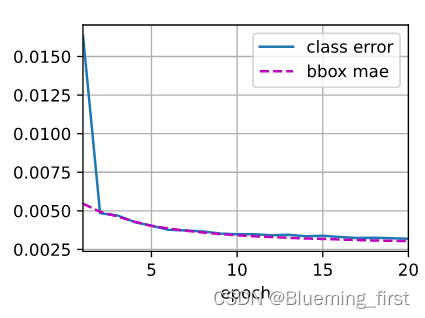
cls_err, bbox_mae = 1 - metric[0] / metric[1], metric[2] / metric[3]
animator.add(epoch + 1, (cls_err, bbox_mae))
print(f'class err {cls_err:.2e}, bbox mae {bbox_mae:.2e}')
print(f'{len(train_iter.dataset) / timer.stop():.1f} examples/sec on '
f'{str(device)}')
class err 3.19e-03, bbox mae 3.04e-03
4177.8 examples/sec on cuda:0
预测目标
X = torchvision.io.read_image('../img/banana.jpg').unsqueeze(0).float()
img = X.squeeze(0).permute(1, 2, 0).long()
def predict(X):
# 预测模式
net.eval()
anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds = net(X.to(device))
# predictions 变成概率
cls_probs = F.softmax(cls_preds, dim=2).permute(0, 2, 1)
# 根据每个类别的置信度,将锚框和类别置信度结合起来
output = d2l.multibox_detection(cls_probs, bbox_preds, anchors)
idx = [i for i, row in enumerate(output[0]) if row[0] != -1]
# 留下nms 去掉之后的锚框
return output[0, idx]
output = predict(X)
筛选所有置信度不低于 0.9 的边界框,做为最终输出
# threshold 输出的阈值
def display(img, output, threshold):
d2l.set_figsize((5, 5))
fig = d2l.plt.imshow(img)
for row in output:
score = float(row[1])
if score < threshold:
continue
h, w = img.shape[0:2]
bbox = [row[2:6] * torch.tensor((w, h, w, h), device=row.device)]
d2l.show_bboxes(fig.axes, bbox, '%.2f' % score, 'w')
display(img, output.cpu(), threshold=0.9)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-gEn2aPQH-1675150702258)(output_44_0.svg)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e6ee68f1a727436e81c5df66be150088.png)
总结:对每个不同尺度下面的锚框的预测和真实框的偏移,对每个像素预测,预测值在通道里面;一张图片输出锚框、锚框类别预测、偏移预测,每个输出结合在一起;loss时 类别预测时类别的预测, 偏移预测时L1LOSS,预测时加入了NMS。神经网络时没有只看一个锚框内的东西而是看的整个,在loss的时候才去关注锚框内的物体。
目标检测的代码尽量用c++ cuda去写会快,尽量去用别人成熟的包。






















 1619
1619











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








