改文章发表于2021年九月份的GRS,一作是中南大学的大佬。
小白第一次写文章阅读,纯粹记录下自己的所得,希望大家一起来交流讨论~~
摘要
- To comprehensively evaluate the impact of adversarial examples on the remote sensing image(RSI) scene classification, this study tests eight state-of-art classification DNNs on six RSI benchmarks. These data sets include both optical and synthetic-aperture radar(SAR) images of different spectral and spatial resolutions.
- the authors create 48 classification scenarious and use four cutting-edge attack algorithms to investigate the influence of the adversarial example on the classification of RSIs.
- By analyzing the distribution of these adversarial examples, we find that the class distribution of the misclassifications is not affected by the types of models and attack algorithms-----adversarial examples of RSIs of the same class cluster on fixed several classes.The analysis of class of adversarial examples not only helps us explore the relationships between data set classes but also provides insights for further designing defensive algorithms.
- 为了全面评估对抗性示例对遥感图像 (RSI) 场景分类的影响,本研究在六个 RSI 基准上测试了八个最先进的分类 DNN。这些数据集包括不同光谱和空间分辨率的光学和合成孔径雷达 (SAR) 图像。在实验中,我们创建了 48 个分类场景,并使用四种前沿的攻击算法来研究对抗样本对 RSI 分类的影响。实验结果表明,在 48 个场景中,攻击的愚弄率均在 98% 以上。我们还发现,对于光学数据,对抗性问题的严重程度与特征信息的丰富度呈负相关。此外,从 SAR 图像生成的对抗样本很容易被用来欺骗模型,平均欺骗率为 76.01%。通过分析这些对抗样本的类分布,我们发现错误分类的分布不受模型类型和攻击算法的影响——同一类集群的 RSI 在固定的几个类上的对抗样本。对抗性示例类别的分析不仅有助于我们探索数据集类别之间的关系,还可以为进一步设计防御算法提供见解。
个人见解,这篇文章最大的特色,似乎也是GRS喜欢的点,非常充分的实验,作者在六个RSI数据集(光学4种:AID、UCM、NWPU、EuroSAT-MS; SAR图像两种:MSTAR、SEN1-1(SAR-summer))上测试了8种网络,并且使用了FGSM,BIM,DeepFool,CW四种攻击方法分别对48种不同的场景做以对比分析,我要是编辑我也喜欢啊!满满的图,透露着作者对该问题的透彻理解与分析,人见人爱!
数据集的介绍
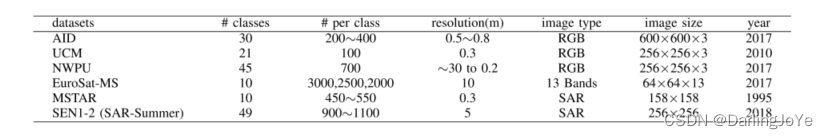
The AID data set [33] is a large-scale aerial image data set from Google Earth imagery. It has several 10 000 images within 30 classes from the original optical aerial images, and all images are collocated from different remote imaging sensors.
The UC Merced Land Use Data set (UCM) [34] has 21 classes for various urban areas around the country. Each class has 100 images with 256 × 256, which are extracted from large images from the USGS National Map Urban Area
Imagery collection.
The NWPU-RESISC45 (NWPU) data set [35] is created by Northwestern Polytechnical University and used for RSI scene classification. It covers 45 classes with 700 images in each class.
The EuroSAT-MS data set [36] has ten classes. The Sentinel-2 satellite system collects these images with 13 spectral bands ranging from 550 to 1342 nm. The dimension of the image is 64 × 64.
The MSTAR data set [37] is a SAR data set with a resolution of 0.3 m. This data set is used for the detection of vehicles, including 2S1 (self-propelled howitzer), BRDM2(armored reconnaissance vehicle), T62 (tank), and D7 (bull-dozer). In this study, we select ten classes from the data set for model evaluation.
The SEN1-2 data set [38] is a data set collected by the Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 for global observation in all seasons. In this study, we select the Sentinel-1 SAR images from the
summer data set with 49 classes.
(附上数据集相关的引用文章)
[33] G.-S. Xia et al., “AID: A benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification,” IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens.,vol. 55, no. 7, pp. 3965–3981, Jul. 2017.
[34] Y . Y ang and S. Newsam, “Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification,” in Proc. 18th SIGSPATIAL Int. Conf. Adv. Geographic Inf. Syst., 2010, pp. 270–279.
[35] G. Cheng, J. Han, and X. Lu, “Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art,” Proc. IEEE, vol. 105, no. 10,pp. 1865–1883, Oct. 2017. Authorized licensed use limited to: National Univ of Defense Tech. Downloaded on August 22,2022 at 07:17:36 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply. 7432 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 59, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2021
[36] P. Helber, B. Bischke, A. Dengel, and D. Borth, “EuroSA T: A novel dataset and deep learning benchmark for land use and land cover classification,” IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens., vol. 12, no. 7, pp. 2217–2226, Jul. 2019.
[37] T. D. Ross, S. W. Worrell, V . J. V elten, J. C. Mossing, and M. L. Bryant, “Standard SAR A TR evaluation experiments using the MSTAR public release data set,” Proc. SPIE, vol. 3370, pp. 566–573, Sep. 1998.
[38] M. Schmitt, L. H. Hughes, and X. Xiang Zhu, “The SEN1-2 dataset for deep learning in SAR-optical data fusion,” 2018, arXiv:1807.01569. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1807.01569
8种网络的介绍
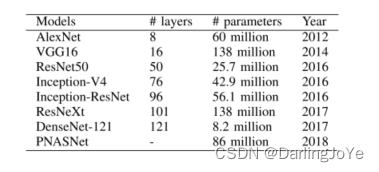
接下来就是8种网络、四种攻击方法、6种数据集轮番交替测试(所以说,有时候提不出创新的大点,咱们就把目前能搜集到的算法来一个大荟萃,对比分析,所谓,背会唐诗三百首,不会诗歌也会吟~) 。但不得不说,得出的结论有意思,可以作为之后研究的点。
但交替轰炸测试也有策略和分类可言,本文作者主要从:
- class benchmarks(我的理解是网络类型和数据类型)
- are adversarial examples universal in RSIscene classification(四种攻击方法在48种场景的数据集下,分别在8种网络中的fooling rate,即创建不同的分类场景来比较攻击算法的欺骗率,想说明对抗样本 is a severe and universal problem of RSI scene classification)
- characteristic of adversarial examples of RSIs(correlation between the feature information and L2 perturbation distance,探讨研究特征信息和L2范数扰动距离之间的关系,并且用皮尔逊系数来量化相关性,并且发现光学比较一致为负相关,SAR数据集有正有负,作者分析原因可能是特征信息定义不严谨,我猜测,会不会和SAR本身的成像机理有关?)
- transferability benchmark(迁移性,这块用混淆矩阵来放图分析是最合适不过的!可视化非常清楚,不仅能看出方法本身的迁移性,并且还揭示了对抗样本的迁移性是否对称。)
- class distributions of adversarial examples(对抗样本的类型分布,作者采用饼状图的形式来可视化对抗样本的分布,发现尽管模型和攻击算法不同,但对抗样本在错误分类中具有很高的相似性)
实验中发现的有趣的点
- 同一模型在不同类型的数据集上有不同的表现,在同一数据集上,最新的模型可能反而无法获得最优的表现。目前在模型分类性能上没有同一的标准,the relationship betweem model archiecture and data is still a black box,需要进一步研究。
- 文章采用L2范数来约束扰动,同时 A high L2 perturbation distance indicates either a weaker attack algorithms or a more robust DNN model
- 对抗样本的类型在很多情况下不会受到对抗算法和DNN架构模型的影响,原因可是是1)训练数据中图像的数量和质量 the quantity and quality of images in the training data set, for example, if the dataset has only two classes, adversarial examples can only be the other class, regardless of whether the two classes have a strong correlation ;2)类之间的同质性和异质性homogeneity and heterogeneity between classes.
结论
1) Our result shows that all the DNN models can achieve an average fooling rate of 98% or above, which shows the universality and severity of adversarial example problems in RSI scene classification than we thought.
2) We find that adversarial examples have different impacts on different RSI data sets. For optical data sets, adversarial examples would divert little from the original images because they contain rich information in terms of spectral bands, spatial dimension, and high resolution. However, this rule doesn’t apply to SAR data sets.
3) Multiple DNNs can be easily fooled with an average fooling rate of 76.01% for the SAR data sets. Adversarial examples generated under SAR data sets pose a greater threat to other classification models.
4) We also find that the classes of adversarial examples are more affected by the class distribution of data than the attack algorithms or the model architectures
1)结果表明,所有的 DNN 模型都能达到 98% 或以上的平均欺骗率,这表明 RSI 场景分类中对抗性示例问题的普遍性和严重性超出了想象。 2)发现对抗样本对不同的 RSI 数据集有不同的影响。对于光学数据集,对抗样本几乎不会从原始图像中转移出来,因为它们在光谱带、空间维度和高分辨率方面包含丰富的信息。但是,此规则不适用于 SAR 数据集。 3) 多个 DNN 很容易被欺骗,SAR 数据集的平均欺骗率为 76.01%。在 SAR 数据集下生成的对抗性示例对其他分类模型构成更大的威胁。 4)还发现对抗样本的类别比攻击算法或模型架构更受数据类别分布的影响。
未来展望
1) The adversarial perturbation covering the whole image cannot be applied in the real scene with various sizes of ground objects because we use smaller RSI patches as the input. Thus, we need to develop a new strategy to fool the classification model in a real scene.
2) Errors in the RSIs might come from the sensors, and multiview distortions of ground objects might also be problematic since the object might have adversarial perturbations when the same ground object is misclassified in several views. In the future, we would like to explore the relationship between the classification objects and their environment to help defend adversarial examples. Besides, we would also focus on the explanation of adversarial examples from RSIs classification, detection, and segmentation tasks 1)覆盖整个图像的对抗性扰动不能应用于具有各种大小的地面物体的真实场景,因为我们使用较小的 RSI 补丁作为输入。因此,需要开发一种新的策略来欺骗真实场景中的分类模型。 2) RSI 中的错误可能来自传感器,并且地面物体的多视图失真也可能是有问题的,因为当同一地面物体在多个视图中被错误分类时,物体可能会产生对抗性扰动。未来,希望探索分类对象与其环境之间的关系,以帮助防御对抗样本。此外,还将重点解释 RSI 分类、检测和分割任务中的对抗性示例。





 该研究评估了对抗性示例对遥感图像(RSI)场景分类的影响,测试了8种DNN和4种攻击算法在6个RSI数据集上的性能。实验显示所有模型的平均欺骗率超过98%,表明对抗性问题的普遍性和严重性。光学数据对抗样本的影响小于SAR数据,后者平均欺骗率为76.01%。研究还发现,对抗样本的类别分布不受模型和算法影响,而与数据集类别的分布相关。
该研究评估了对抗性示例对遥感图像(RSI)场景分类的影响,测试了8种DNN和4种攻击算法在6个RSI数据集上的性能。实验显示所有模型的平均欺骗率超过98%,表明对抗性问题的普遍性和严重性。光学数据对抗样本的影响小于SAR数据,后者平均欺骗率为76.01%。研究还发现,对抗样本的类别分布不受模型和算法影响,而与数据集类别的分布相关。
















 4803
4803

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








