自定义容器
Stack
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Stack {
private int[] data;
private int size;
private int capacity = 10;
public Stack(){
this.data = new int[capacity];
}
public Stack(int capacity){
this.capacity = capacity;
this.data = new int[capacity];
}
//进栈一个元素
public void push(int e){
if (isFull()){
int length = this.capacity + this.capacity / 2;
this.resize(length);
}else {
this.data[size++] = e;
}
}
//判断栈是否满了
private boolean isFull(){
return this.capacity == this.size;
}
//出栈一个元素
public int pop(){
if (this.isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,无法弹栈元素");
}
return this.data[--this.size];
}
//查看栈顶元素
public int peek(){
if (this.isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,没有栈顶元素");
}
return this.data[this.size - 1];
}
//扩容或缩容容器的大小
private void resize(int len){
this.data = Arrays.copyOf(this.data, len);
this.capacity = len;
}
//栈中的元素个数
public int size(){
return this.size;
}
//判断栈是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.size == 0;
}
//清空栈
public void clear(){
this.size = 0;
}
//返回栈的字符串形式
public String toString(){
return Arrays.toString(Arrays.copyOf(this.data, this.size));
// if (isEmpty()){
// return "[]";
// }
// String s = "[";
// for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++){
// s += data[i];
// if (i == data.length - 1){
// s += "]";
// }else {
// s += ",";
// }
// }
// return s;
}
//对比两个栈是否相等
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
Stack stack = (Stack) o;
if (this.size != stack.size()) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < stack.size; i++){
if (data[i] != stack.data[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
测试:
public class TestStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty());
stack.push(123);
stack.push(456);
stack.push(789);
System.out.println(stack);
System.out.println(stack.size());
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty());
System.out.println(stack.peek());
}
}

Queue
public class Queue {
private Stack stackA;
private Stack stackB;
//创建默认的队列对象
public Queue(){
this.stackA = new Stack();
this.stackB = new Stack();
}
//进队一个元素
public void offer(int e){
this.stackA.push(e);
}
//出队一个元素
public int poll(){
remove();
return stackB.pop();
}
private void remove() {
if (this.stackB.size() == 0){
while (this.stackA.size() != 0){
this.stackB.push(this.stackA.pop());
}
}
}
//查看队首元素
public int element(){
remove();
return this.stackB.peek();
}
//获取队列中元素的个数
public int size(){
remove();
return this.stackB.size();
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
remove();
return this.stackB.size() == 0 && this.stackA.size() == 0;
}
//清空队列
public void clear(){
this.stackA.clear();
this.stackB.clear();
}
//返回队列的字符串形式
public String toString(){
return this.stackB.toString();
}
//对比两个队列是否相等
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
Queue queue = (Queue) o;
if (this.size() != queue.size()) {
return false;
}
if (this.stackA.equals(queue.stackA) && this.stackB.equals(queue.stackB)){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
}
测试:
class QueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new Queue();
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());
queue.offer(123);
queue.offer(456);
queue.offer(789);
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.element());
System.out.println(queue.toString());
Queue queue1 = new Queue();
queue1.offer(456);
queue1.offer(789);
System.out.println(queue.equals(queue1));
}
}

LinkedList
public class LinkedList {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int size;
public LinkedList() {
}
public void add(Object obj) {
// 向尾部添加一个新的节点
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.value = obj;
// 判断是否是第一次添加
if (first == null) {
this.first = newNode;
this.last = newNode;
} else {
newNode.prev = last;
last.next = newNode;
last = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
//从前面删除
public void removeHead() {
if(first == null){ // 链表为空
return;
}
first.value = null;
Node p = first.next;
first.next = null;
if(first == last){ // 当前链表只有一个结点
first = null;
last = null;
}else{
first = p;// 更新头
}
}
//从后面删除
public void removeTail() {
if(first == null){
return;
}
if(first == last){
first = null;
last = null;
}else {
last.value = null;
Node prev = searchPrev(last);
prev.next = null;// prev 新尾巴
last = prev;// 更新新尾巴
}
}
private Node searchPrev(Node node){
for(Node p = first; p != null; p = p.next){
if(p.next == node){
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
public void show() {
for (Node p = first; p != null; p = p.next) {
System.out.print(p.value + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
//通过下标获取值
public Object get(int index) {
if (index >= this.size || index < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("对不起,不存在这个下标");
}
Node temp = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp.value;
}
//节点(内部类)
class Node {
Node prev;
Node next;
Object value;
public Node() {
}
public Node(Node prev, Object value, Node next) {
this.prev = prev;
this.next = next;
this.value = value;
}
}
}
测试:
public class TestLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.add(123);
list.add(456);
list.add(789);
list.show();
System.out.println(list.get(1));
list.removeHead();
list.show();
list.removeTail();
list.show();
}
}

ArrayList
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayList {
private Object[] objs;
private int size;
private int capacity = 10;
public ArrayList() {
this.objs = new Object[this.capacity];
}
public ArrayList(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.objs = new Object[this.capacity];
}
//添加一个元素
public void add(Object obj) {
// 如果满了就扩容
if (this.isFull()) {
this.grow();
}
this.objs[size++] = obj;
}
//判断是否满了
private boolean isFull() {
return this.size == this.capacity;
}
//扩容
private void grow() {
// 扩 1.5 倍
int newCapaCity = this.capacity + (this.capacity >> 1);
this.objs = Arrays.copyOf(this.objs, newCapaCity);
this.capacity = newCapaCity;
}
//在指定位置添加元素
public void add(int index, Object obj) {
if (this.isFull()) {
this.grow();
}
for (int i = size; i > index ; i--) {
this.objs[i] = this.objs[i - 1];
}
this.objs[index] = obj;
this.size++;
}
//删除指定位置的元素
public void remove(int index) {
for (int i = index; i < this.size - 1; i++) {
this.objs[index] = this.objs[index + 1];
}
this.size--;
}
//删除指定元素
public void remove(Object obj) {
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++){
if (objs[i] == obj){
index = i;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("没有该元素");
}
}
remove(index);
}
//替换指定位置的元素
public void update(int index, Object obj) {
this.objs[index] = obj;
}
//获取指定位置的元素
public Object get(int index) {
if (index < size) {
return null;
}
return this.objs[index];
}
//元素个数
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
public Object[] list() {
return Arrays.copyOf(this.objs, size);
}
public void clear() {
this.size = 0;
}
public String toString() {
return "ObjectMangerImpl [objs=" + Arrays.toString(objs) + ", size=" + size + ", capacity=" + capacity + "]";
}
}
测试:
import org.oracle.test.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add(123);
list.add(456);
list.add(789);
list.add(369);
list.add("hello world");
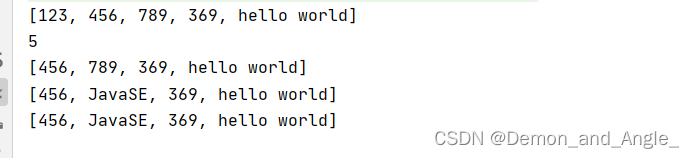
System.out.println(list.toString());
System.out.println(list.size());
list.remove(0);
System.out.println(list.toString());
list.update(1, "JavaSE");
System.out.println(list.toString());
}
}
ArrayList源码解析
ArrayList实现了List接口,是顺序容器,即元素存放的数据与放进去的顺序相同,允许放入null元素,底层通过数组实现。
ArrayList根据调用不同的构造函数,初始化容器不同。
如果使用无参的构造,默认容量是0,节约内存,一旦添加元素,会发生第一次扩容,默认容量为10;如果有参的构造,则传递为多少,默认就是多少。
ArrayList alist = new ArrayList(); // 默认容量0,第一次扩容后,默认容量为10
ArrayList alist = new ArrayList(8); // 默认容量8
注意: 如果在开发过程中,数据大小基本确定,建议使用有参的构造函数,减少频繁扩容,提高性能当然如果不能确定的话,可以使用无参的构造。
为追求效率,ArrayList没有实现同步(synchronized),是不安全的;如果需要多个线程并发访问,用户可以手动同步,也可使用Vector替代,Vector是线程安全的容器,操作方法都加了同步锁。
源码解读
实现的接口:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
// 实现RandomAccess接口,支持随机访问(也就是根据下标访问)
// 实现Cloneable接口, 可以进浅拷贝
// 实现Serializable接口,可以进行序列化和反序列化
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
属性:
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
//默认的初始容量
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
// 空数组,如果传入的容量为0时使用
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
//空数组,在第一次add也就是第一次插入数据的时候进行初始化容量(10)
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
//ArrayList的存储数据数组,根据传入的容量来根据设置
// transient 表示不进行序列化
transient Object[] elementData;
// 数组的元素个数
private int size;
// 用来计算和限制容量
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
构造方法:
// 传入容量的初始化
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
// 如果传入的数据大于0,数组初始化使用传入的数据
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
// 如果传入的数据为0,则初始化为空数组
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
// 如果不传入,设置为空数组,在第一次add的时候进行初始化,默认容量为10
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
//传入一个集合,进行初始化
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
//转化为数组
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// 检查c.toArray()返回的是不是Object[]类型,如果不是,重新拷贝成Object[].class类型
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
// 进行复制
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// 如果长度为0, 设置为空数组
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
方法:
// 添加元素
public boolean add(E e) {
// 确保容量够,看是否需要扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
// 添加到指定索引的位置
public void add(int index, E element) {
// 检查索引是否合法
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
// 确保容量够
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
// 移动index之后的元素
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
// 根据传入的集合,来添加元素
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 转换为数组
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
// 确保容量够,看是否需要扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
// 根据传入的集合和索引,来添加元素
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 检查索引是否合法
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
// 确保容量够,看是否需要扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
// 移动元素
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
/*扩容
每当向数组中添加元素时,都要去检查添加后元素的个数是否会超出当前数组的长度,如果超出,数组将会进行扩容,以满足添加数据的需求。
数组进行扩容时,会将老数组中的元素重新拷贝一份到新的数组中,每次数组容量的增长大约是其原容量的1.5倍。*/
// 确保空间够用
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
//如果数组不等于DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA则设置为0,否则设置为10,默认的初始容量
int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
// any size if not default element table
? 0
// larger than default for default empty table. It's already
// supposed to be at default size.
: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
// 如果要求的最小容量大于当前的数组的容量得调用方法进行扩容
if (minCapacity > minExpand) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
}
// 计算需要的最小容量
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
// 确保空间够用
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
// 确保空间够用
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
//操作数++
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
// 如果需要的最小容量大于当前数组的长度,调用扩容的方法
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
// 扩容方法
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 原来的容量右移一位加上原来的容量,相当于扩容为原来的1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
// 如果扩容完,还小于需要的最小容量,则新容量为当前需要的最小容量
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// 如果新容量大于AX_ARRAY_SIZE= Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8 防止OOM异常
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
// 防止容量超
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
//检查索引
//索引合法检查
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
//索引合法检查
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
// 根据索引获取元素
public E get(int index) {
// 检查索引是否合法
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
// 根据索引设置元素的值
public E set(int index, E element) {
// 检查索引是否合法
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
// 根据索引删掉元素
public E remove(int index) {
// 检查索引是否合法
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
// 移动index之后的元素
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//清除该位置的引用,让GC起作用
elementData[--size] = null;
return oldValue;
}
// 根据元素的值,删除元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 可以看到这个删除,跳过了检索引的边界,效率更高
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
// 移动index之后的元素
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//清除该位置的引用,让GC起作用
elementData[--size] = null;
}
//将底层数组的容量调整为当前列表保存的实际元素的大小的
public void trimToSize() {
//操作数用于快速失败
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
//如果数组为空,设置为空数组,否则复制数组
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
// 删除不在这个集合的其他元素
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
//判断是否为null
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return batchRemove(c, true);
}
private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {
final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
int r = 0, w = 0;
boolean modified = false;
try {
// 遍历整个数组,如果c中包含该元素,则把该元素放到写指针的位置(以complement为准)
for (; r < size; r++)
if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement)
elementData[w++] = elementData[r];
} finally {
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,
// 如果c.contains()抛出了异常,则把未读的元素都拷贝到写指针之后
if (r != size) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, r,
elementData, w,
size - r);
w += size - r;
}
if (w != size) {
// 将写指针之后的元素置为空,帮助GC
for (int i = w; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
modCount += size - w;
size = w;
modified = true;
}
}
return modified;
}
// 删除集合里面包含的元素
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
//判断是否为null
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return batchRemove(c, false);
}
// 根据元素查找索引的位置
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 返回元素最后一次出现的索引
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}





















 495
495











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








