进程间通讯的方式有:
- 管道
- 消息队列
- 共享内存
信号量
在这里面管道是最古老的进程间通讯方式,管道又分为匿名管道和命名管道。
匿名管道
局限性:- 只能够在具有亲缘关系的进程里面使用
- 管道提供流式服务
- 管道的生命周期随进程
- 内核会对管道操作进行互斥和同步
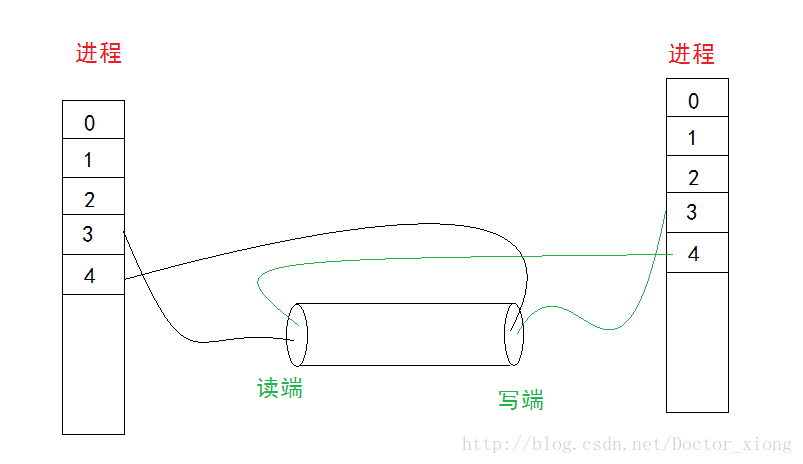
管道数据只能单向传递
在匿名管道里面使用到的函数是int pipo(int fd[2]);
fd[0]表示的是读端
fd[1]表示的是写端
当需要两个进程之间进行通信的时候就可以将一个进程的读或写端的文件关闭,那么剩下的就是一个进程掌握的写,一个进程掌握着读,那么这样就可以在进程间进行通信了。
实例:实现两个进程间的通讯
#include<stdio.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){
int fd[2];
char* buf = "nihao!\n";
pid_t pid;
if(pipe(fd) < 0){
perror("pipe");
exit(2);
}
if((pid = fork()) < 0){
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
if(pid == 0){
int i = 5;
close(fd[0]);
while(i--){
sleep(1);
write(fd[1],buf,strlen(buf));
}
close(fd[1]);
exit(0);
}
else{
char* output[1024] = {0};
int r = 0;
while(1){
if(read(fd[0],output,1024) > 0){
printf("%s",output);
}
else {
exit(0);
}
}
close(fd[1]);
}
return 0;
}
命名管道
在匿名管道里面最大的局限性就是进程间的通讯只能具有亲缘关系的进程间才可以进行。但是在实际的应用中进程间的通信往往并不只是在亲缘进程间,这时候就需要使用命名管道来进行进程间的通讯。
原理:在启动一个进程的时候就会在进程里面打开有相应的文件,而每个进程里面的打开的文件是独立的,命名管道是通过管道文件实现的,这里的管道文件是一个所有进程都共享的文件,那么这样进程通过文件的读写操作就可以进行进程间的通信了。
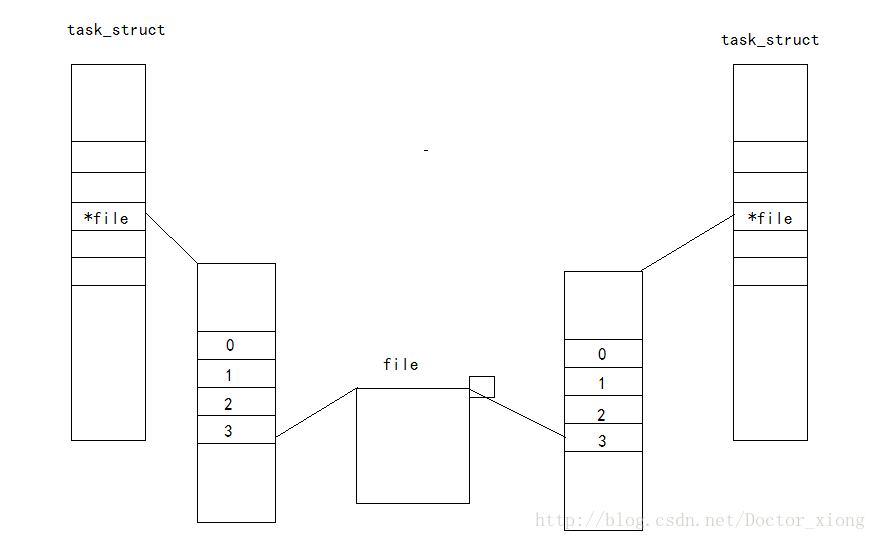
注:这里的不同进程的文件描述符不一定一样
在创建命名管道文件的时候可以使用mkfifo命令创建,同时如果实在程序里面也可以使用函数创建
创建命名管道文件的函数是int mkfifo(const char *pathname,int mode);
实例:实现两个不相干程序间的通信
1_exe.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
int main()
{
char buf[1024] = {0};
int fd = open("fifo",O_WRONLY);
if(fd < 0){
perror("open");
return 1;
}
while(1){
printf("Please Inter :>");
fflush(stdout);
ssize_t r = read(0,buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
if(r < 0){
perror("read");
return 2;
}
else{
write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));
}
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
2_exe.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
int main(){
int fd;
if(mkfifo("./fifo",0644) < 0)
{
perror("mkfifo");
return 1;
}
fd = open("fifo",O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0){
perror("open");
return 1;
}
else{
char buf[1024] = {0};
while(1){
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
ssize_t r = read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
if(r > 0){
printf("Msg->:%s",buf);
}
else if(r == 0){
printf("child is close!\n");
return 0;
}
else{
perror("read");
return 1;
}
}
}
close(fd);
}






















 954
954











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








