单例模式定义:
某一个类只有这个一个实例且自行实例化并向系统提供这个实例
uml类图
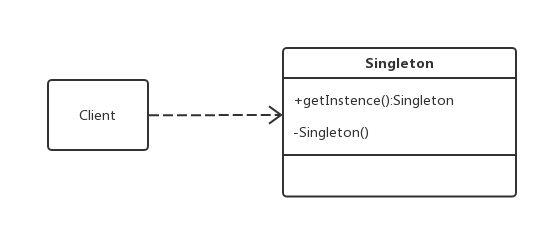
饿汉式单例
在类创建的同时就已经创建好一个静态的对象供系统使用,以后不再改变,所以天生是线程安全的。
public
class
SingletonCommon {
private
static
final
SingletonCommon
single
=
new
SingletonCommon();
private
SingletonCommon() {
}
public
static
SingletonCommon getSingleCommon() {
return
single
;
}
}
线程安全的懒加载DoubleCheck
public
class
SingleDoubleCheck {
// private static SingleDoubleCheck single = null; //高并发时可能破坏单例的唯一性
private
volatile
static
SingleDoubleCheck
single
=
null
;
//JVM保证volatile从内存中读取,跳过
cpu
的cache
private
SingleDoubleCheck() {
}
public
static
SingleDoubleCheck getInstance() {
if
(
null
==
single
) {
synchronized
(SingleDoubleCheck.
class
) {
if
(
null
==
single
) {
single
=
new
SingleDoubleCheck();
}
}
}
return
single
;
}
}
懒汉单例的classLoader实现
public
class
SingleClassLoader {
private
static
class
SingleHolder {
static
final
SingleClassLoader
SINGLE
=
new
SingleClassLoader();
}
private
SingleClassLoader() {
}
public
SingleClassLoader getInstance() {
return
SingleHolder.
SINGLE
;
}
}
利用了classloader的机制来保证初始化instance时只有一个线程,所以也是线程安全的,同时没有性能损耗,所以倾向于使用这一种。
使用场景
单例模式只允许创建一个对象,因此节省内存,加快对象访问速度,因此对象需要被公用的场合适合使用,如多个模块使用同一个数据源连接对象等等。如:
1.需要频繁实例化然后销毁的对象。
2.创建对象时耗时过多或者耗资源过多,但又经常用到的对象。
3.有状态的工具类对象。 (也可以使用static修饰)
4.频繁访问数据库或文件的对象。
举例:
1.Windows的Task Manager(任务管理器)
2. windows的Recycle Bin(回收站)也是典型的单例应用。
3. 网站的计数器
4. 应用程序的日志应用
5. 数据库连接池的设计
优点:
(1)资源共享的情况下,避免由于资源操作时导致的性能或损耗等。如上述中的日志文件,应用配置。
(2)控制资源的情况下,方便资源之间的互相通信。如线程池等。
jdk的应用:
Runtime类, 饿汉式单利,保证Runtime的唯一性
public class Runtime {
private static Runtime currentRuntime = new Runtime(); //声明私有的静态类成员变量currentRuntime ,当类加载完成时,构造Runtime实例对象。
/**
* Returns the runtime object associated with the current Java application.
* Most of the methods of class <code>Runtime</code> are instance
* methods and must be invoked with respect to the current runtime object.
*
* @return the <code>Runtime</code> object associated with the current
* Java application.
*/
public static Runtime getRuntime() { //通过公有的静态方法获取唯一实例对象
return currentRuntime;
}
/** Don't let anyone else instantiate this class */
private Runtime() {} //构造函数私有化,保证类外不可创建该类对象
......






















 1585
1585

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








