文章目录
前置知识
参考前文
参考文章:
LeetCode刷题笔记【9】:二叉树专题-1(分别用递归遍历、迭代遍历、标记遍历实现前、中、后序遍历)
LeetCode刷题笔记【10】:二叉树专题-2(二叉树的层序遍历、翻转二叉树、对称二叉树)
LeetCode刷题笔记【10.5】:二叉树专题-2.5(二叉树的层序遍历 - 10道题)
104. 二叉树的最大深度
题目描述
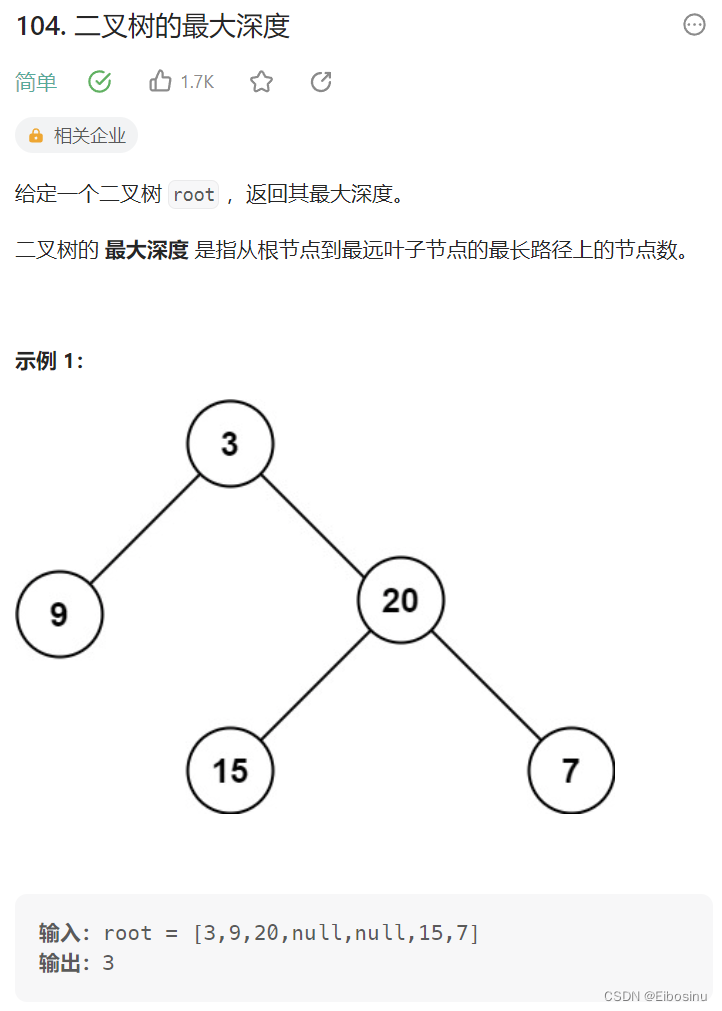
LeetCode链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/description/
层次遍历法
思路1: 层次遍历(广度优先遍历), 统计层数
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
int ans=0;
if(root==NULL)
return ans;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
ans++;
int size = que.size();
for(int i=0; i<size; ++i){
TreeNode* cur = que.front();
que.pop();
if(cur->left)
que.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right)
que.push(cur->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
递归法
思路2: 递归深度优先遍历, 在递归函数中加index+1, 求max
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
111. 二叉树的最小深度
题目描述
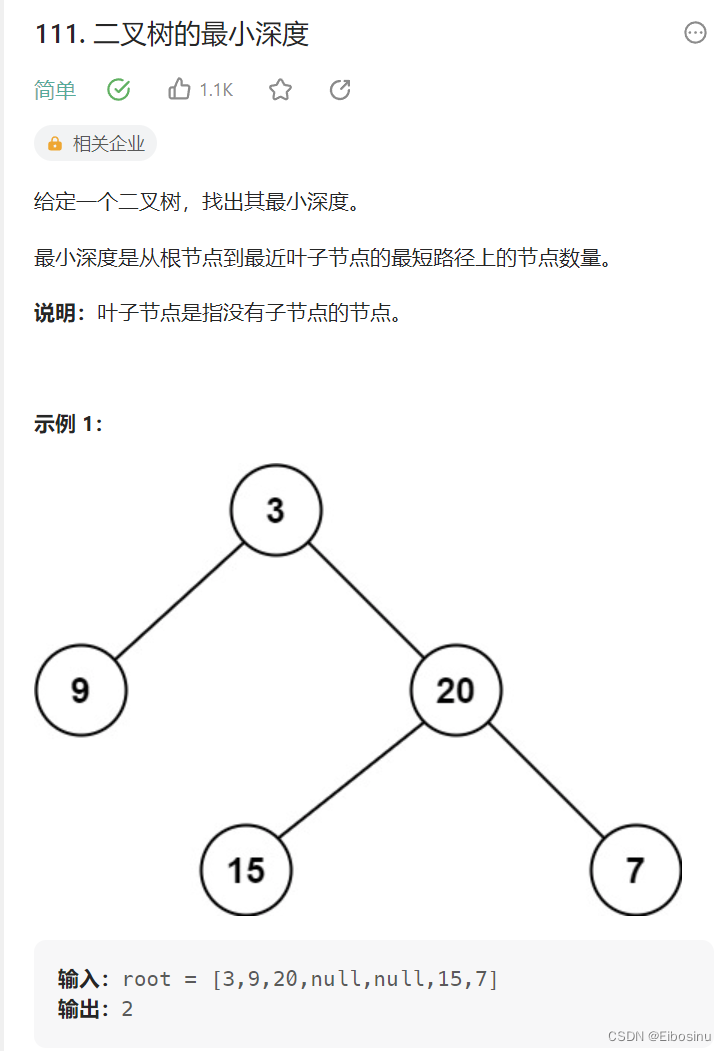
LeetCode链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/description/
层序遍历
思路1: 层次遍历(广度优先遍历), 统计层数
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
int ans=0;
if(root==NULL)
return ans;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
ans++;
int size = que.size();
for(int i=0; i<size; ++i){
TreeNode* cur = que.front();
if(cur->left==NULL && cur->right==NULL)// 在这里检查一下cur是不是叶节点, 只要发现叶子节点就返回
return ans;
que.pop();
if(cur->left)
que.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right)
que.push(cur->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
递归
思路2: 递归深度优先遍历, 在递归函数中加index+1, 求max
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
if(root->left==NULL && root->right==NULL)
return 1;
if(root->left!=NULL && root->right!=NULL)
return min(minDepth(root->left), minDepth(root->right)) + 1;
if(root->left==NULL && root->right!=NULL)
return minDepth(root->right) + 1;
if(root->left!=NULL && root->right==NULL)
return minDepth(root->left) + 1;
return 0;
}
};
递归的优化
感觉题解中的深度遍历优雅很多, 模仿一下
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
if(root->left==NULL && root->right==NULL)
return 1;
int ans = INT_MAX;
if(root->right!=NULL)
ans = min(ans, minDepth(root->right)+1);
if(root->left!=NULL)
ans = min(ans, minDepth(root->left)+1);
return ans;
}
};
完全二叉树的节点个数
题目描述
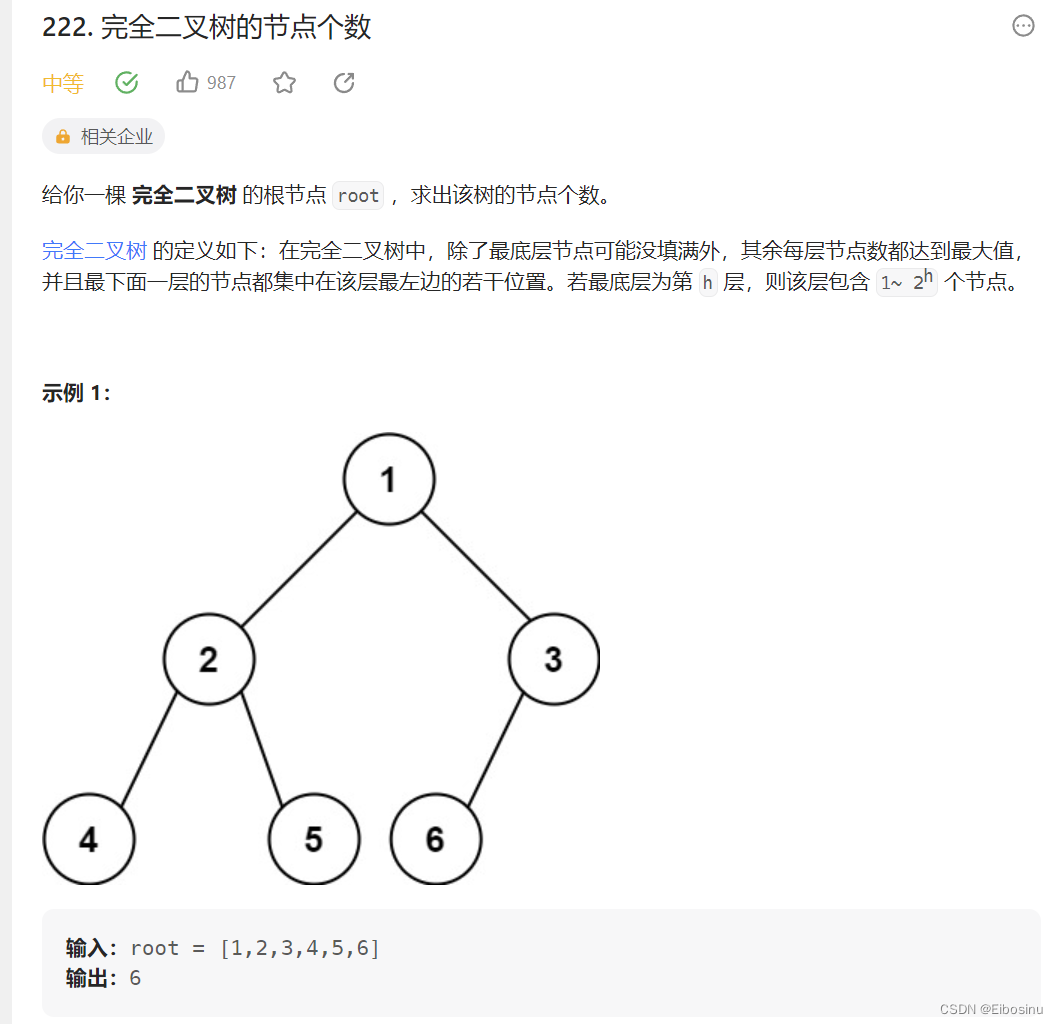
LeetCode链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/description/
解题思路
思路1: 用递归或者迭代法, 遍历所有节点, 进行统计数量
思路2: 利用完全二叉树的性质, 查到最后一层的节点有多少, 就可以算出来
如上所示, 一方面可以完全忽略题目中的"完全二叉树"这一提示, 就当做普通的二叉树来挨个遍历, 求节点数量;
另一方面可以利用完全二叉树的性质, 进行求解.
递归遍历求解
// ① 递归法
class Solution {
private:
int counter=0;
public:
void helper(TreeNode* root){
if(root==nullptr)
return;
counter++;
helper(root->left);
helper(root->right);
return;
}
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
helper(root);
return counter;
}
};
层序遍历求解
// ② 迭代法(层序遍历)
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
int ans=0;
if(root==nullptr)
return ans;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
TreeNode* cur = que.front();
que.pop();
ans++;
if(cur->left) que.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) que.push(cur->right);
}
return ans;
}
};
利用完全二叉树性质求解
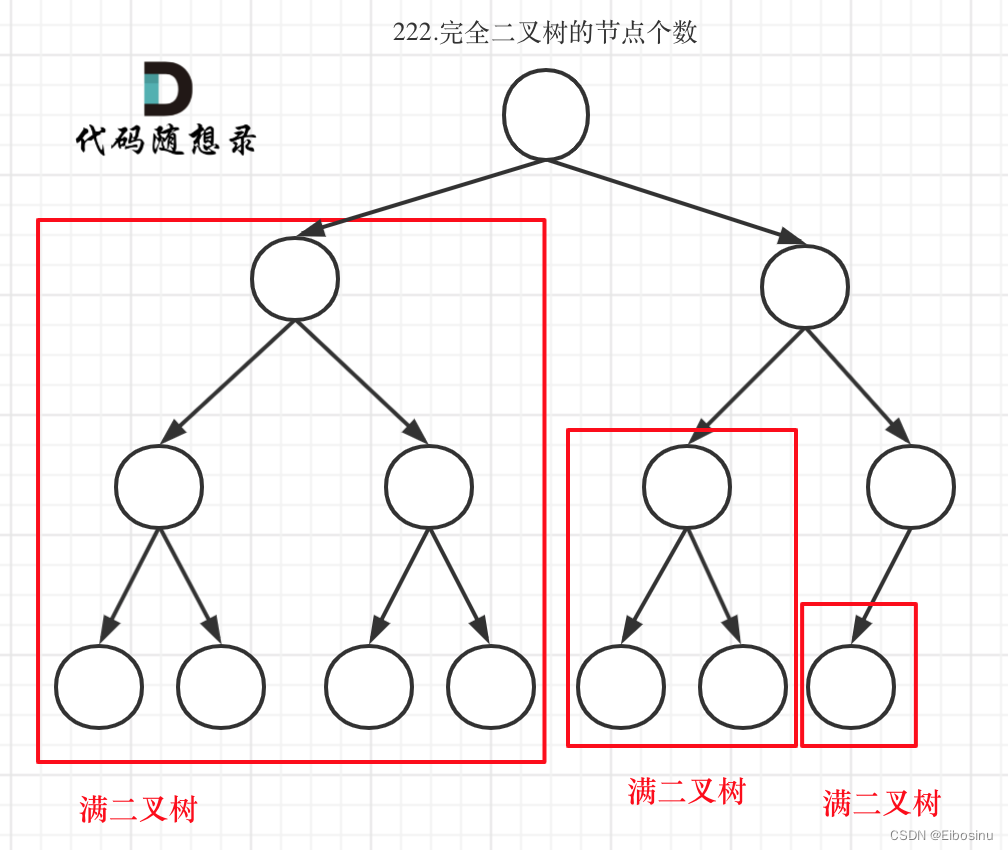
对于一个满二叉树, 如果其有n层, 它就有2^n-1个节点.
那么如上图所示, 我们分别从根节点一路left和一路right, 得到depthLeft和depthRight;
如果二者相等, 那么就是满二叉树;
如果不相等, 那么递归调用处理其左右子树.
// ③ 利用完全二叉树性质
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr)
return 0;
int leftDepth=0, rightDepth=0;
TreeNode *leftNode=root, *rightNode=root;
while(leftNode){
leftDepth++;
leftNode = leftNode->left;
}
while(rightNode){
rightDepth++;
rightNode = rightNode->right;
}
if(leftDepth==rightDepth)
return (1<<leftDepth)-1;
return countNodes(root->left)+countNodes(root->right)+1;
}
};
总结
很多题目是掌握了基础方法就可以一通百通的, 但是也有很多题目, 出题人很明显地给出了提示, 那么就对于你使用这些提示并给出简便的解法有所期待.






















 1511
1511











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








