Computer
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 5805 Accepted Submission(s): 2909
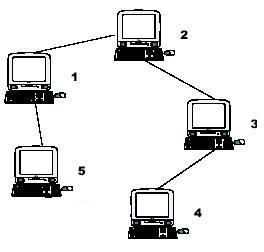
Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
5 1 1 2 1 3 1 1 1
3 2 3 4 4
题意,给一棵树,对于每一个结点,到离他最远的一个点的距离是多少。
输入是从点2开始的,i是起点,只输入了v和w。相当于是一条i->v,边权为w 的边。
有两种解法。
第一种,利用树的直径,我们知道求树的直径的时候,是任意找一个点,dfs寻找它的最远距离的点u,再用u相同dfs一遍找到一个v。u->v就是树的直径。证明:点击打开链接。重点就是任意,意思就是任意一个点在树上最远距离的点是树的直径两个端点中的一个。取max就行了。
三遍dfs,第一遍寻找直径的一个端点
第二遍端点出发更新每一个点的距离值,顺便找到另一个端点。
第三遍从另一个端点出发,再更新取大就行了。
由于这三个dfs基本上一毛一样,所以只写一个就行了。
CODE
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 1e9+10;
const int N = 1e4+10;
struct node
{
int en,val,next;
}E[N*2];
int n;
int uu; ///树的直径端点
int max_dis; ///某个点能走到的最远距离,用来寻找树的直径端点
int top; ///邻接表边的编号
int head[N]; ///邻接表头结点
int ans[N]; ///存答案
void Init() ///初始化
{
top = max_dis = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < N;i++){
head[i] = -1;
ans[i] = 0;
}
}
void add(int u,int v,int w){
E[top].en = v;
E[top].val = w;
E[top].next = head[u];
head[u] = top++;
}
void dfs(int u,int fa,int dis){
if(dis >= max_dis){ ///找到距离更大的点就需要更新,max_dis不需要每次都初始化为0
max_dis = dis;
uu = u;
}
if(ans[u] < dis) ans[u] = dis; ///每个点距离值取大
for(int i = head[u];i != -1;i = E[i].next){
int v = E[i].en;
if(v == fa) continue;
dfs(v,u,dis+E[i].val);
}
}
int main(void)
{
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
Init();
for(int i = 2;i <= n;i++){
int v,w;
scanf("%d %d",&v,&w);
add(i,v,w);
add(v,i,w);
}
///需要注意的是,虽然三个都采用同一个dfs函数,但是作用却是不一样的
dfs(1,-1,0); ///第一遍寻找端点
dfs(uu,-1,0); ///第二遍第一个端点出发更新每个点距离,寻找另一个端点
dfs(uu,-1,0); ///第三遍另一个端点出发更新每个点距离
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
}
return 0;
}
第二种 :树形DP
第一次写树形DP,被我瞎yy出来用树的直径做,2333.
树形dp,从这道题来看,随便定义一个根节点,每个点距离的最大值可以是从这个点的子树来,也可以从它的父亲更新而来。
存在的问题就是如果某一个点的dis最大值是由它父亲更新而来,而它父亲的最大距离又是由这个点更新而来。那么这个点能被父亲更新而来,那一定是父亲的次长链加上它们连接的这条边的距离。这就是这道树形DP次长链的作用。
做法就是,第一遍任意找个点作为根节点,dfs求出每个点在它子树中距离的最大值的次大值。第二遍dfs从相同根节点开始更新每个点从父亲结点过来是否能更新最大值。就是注意处理由父亲节点更新过来的最长链是本身结点的问题。记录每个点的id就行了,每个点最长链和次长链由哪一个点的更新来的,记录它的坐标。第二次dfs判断处理就行了。
CODE
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+10;
struct node{
int en,val,next;
}E[N*2];
int n;
int top; ///邻接表边的编号
int maxnid[N]; ///最长距离链的子节点编号
int smaxnid[N]; ///次长距离链的子节点编号
int head[N]; ///邻接表头结点
int maxn[N]; ///最长距离链长度
int smaxn[N]; ///次长距离链长度,secondmaxn
void Init(){ ///初始化
top = 0;
for(int i = 0;i <= n;i++){
head[i] = -1;
maxn[i] = smaxn[i] = 0;
maxnid[i] = smaxnid[i] = i;
}
}
void add(int u,int v,int w){
E[top].en = v;
E[top].val = w;
E[top].next = head[u];
head[u] = top++;
}
void dfs1(int u,int fa){ ///第一次更新子树中的最长距离链和次长距离链
for(int i = head[u];i != -1;i = E[i].next){
int v = E[i].en;
if(v == fa) continue;
dfs1(v,u);
if(maxn[v]+E[i].val > smaxn[u]){
smaxn[u] = maxn[v]+E[i].val;
smaxnid[u] = v;
if(smaxn[u] > maxn[u]){
swap(smaxn[u],maxn[u]);
swap(smaxnid[u],maxnid[u]);
}
}
}
}
void dfs2(int u,int fa){ ///第二次更新由父亲结点更新来的最长链
for(int i = head[u];i != -1;i = E[i].next){
int v = E[i].en;
if(v == fa) continue;
if(maxnid[u] == v){ ///当前节点的父亲最长链是它本身就用父亲结点的次长链来更新
if(smaxn[u]+E[i].val > smaxn[v]){
smaxn[v] = smaxn[u]+E[i].val;
smaxnid[v] = u;
if(smaxn[v] > maxn[v]){
swap(smaxn[v],maxn[v]);
swap(smaxnid[v],maxnid[v]);
}
}
}
else{ ///否则就直接用父亲结点的最长链来更新就行了
if(maxn[u]+E[i].val > smaxn[v]){
smaxn[v] = maxn[u]+E[i].val;
smaxnid[v] = u;
if(smaxn[v] > maxn[v]){
swap(smaxn[v],maxn[v]);
swap(smaxnid[v],maxnid[v]);
}
}
}
dfs2(v,u);
}
}
int main(void)
{
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
Init();
for(int i = 2;i <= n;i++){
int v,w;
scanf("%d%d",&v,&w);
add(i,v,w);
add(v,i,w);
}
dfs1(1,-1);
dfs2(1,-1);
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) printf("%d\n",maxn[i]);
}
}






















 87
87











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








