1.编写一个程序,不断要求用户输入两个数,直到其中一个为0。对于每两个数,程序将使用一个函数来计算它们的 调和平均数,并将结果返回给main(),而后者将报告结果。调和平均数指的是倒数平均值的倒数,计算公式如下: 调和平均数 = 2.0 * x * y / (x + y)!
2.编写一个程序,要求用户输入最多10个高尔夫成绩,并将其存储在一个数组中。程序允许用户提早结束输入,并在 一行上显示所有成绩,然后报告平均成绩。请使用3个数组处理函数来分别进行输入、显示和计算平均成绩。请使用3个数组 处理函数来分别。
struct box
{
char maker[40];
float height;
float width;
float length;
float volume;
};
a.编写一个函数,按值传递box结构,并显示每个成员的值
b.编写一个函数,传递box结构的地址,并将volume成员设置为其他三维长度的乘积。
c.编写一个使用这两个函数的简单程序

5.定义一个递归函数,接受一个整型参数,并返回该参数的阶乘。前面讲过,3的阶乘写作3!,等于3 * 2!,以此类推: 而0!
被定义为1.通用的计算公式是,如果n大于零 , 则n! = n * (n - 1)!。
在程序中对该函数进行测试,程序使用循环让用户 输入不同的值,程序将报告这些值的阶乘。

6.编写一个程序,它使用下列函数: Fill_array()将一个double数组的名称和长度作为参数。
它提示用户输入double值,并将这些值存储到数组中。
当数组被填满或 用户输入了非数字时,输入将停止,并返回实际输入了多少个数字。
Show_array()将一个double数组的名称和长度作为参数,并显示该数组的内容。
Reverse-array()将一个double数组的名称和长度作为参数,并将存储在数组中的值的顺序反转。
程序将使用这些函数来填充数组,然后显示数组;反转数组,然后显示数组;

7.修改程序清单7.7中的3个数组处理函数,使之使用两个指针参数来表示区间。file_array()函数不返回实际读取了多少个 数字,而是返回一个指针,
8.在不使用array类的情况下完成程序清单7.15所做的工作。编写两个这样的版本:
a.使用const char *数组存储表示季度名称的字符串,并使用double数组存储开支。
b.使用const char *数组存储表示季度名称的字符串,并使用一个结构,该结构只有一个成员——一个用于存储开支的double数组。
这种设计与使用array类的基本设计类似
b.
double q = calculate(2.5,10.4,add);
将导致calculate()把2.5和10.4传递给add()函数,并返回add()的返回值(12.9).请编写一个程序,它调用上述两个函数和至少另一个与add()类似的数。
如果读者爱冒险,可以尝试创建一个指针数组,其中的指针指向add()样式的函数,并编写一个循环,使用这些指针连续让calculate()调用这些函数。
提示:下面是声明这种指针数组的方式,其中包含3个指针:double (*pf[3]) (double,double);
#include <iostream>
double average ( double x, double y )
{
return 2 * x * y / ( x + y );
}
int main()
{
using namespace std;
double x, y;
while ( cin >> x >> y )
{
if ( x == 0 || y == 0 )
break;
else
cout << average ( x, y ) << endl;
cin.sync();
}
return 0;
}
2.编写一个程序,要求用户输入最多10个高尔夫成绩,并将其存储在一个数组中。程序允许用户提早结束输入,并在 一行上显示所有成绩,然后报告平均成绩。请使用3个数组处理函数来分别进行输入、显示和计算平均成绩。请使用3个数组 处理函数来分别。
/* note:输入时,显示第几个的语句要放对地方,不然输入完10个不是直接显示score,而是显示11 :
我之前就是把
std::cout << i + 1 << " : ";
放到了
i++;if(i==10) break;
前面,导致显示这样;
这题用while很简单,只要不是输入数字输入别的都会,退出。*/
#include <iostream>
const int ArSize = 10;
static int k = 0;
void input ( double *a, int n )
{
int i = 0;
std::cout << "Please enter the number, enter any number other than the character to exit" << std::endl;
std::cout << i + 1 << " : ";
while ( std::cin >> a[i] && i < n )
{
i++;
if(i==10) break;
std::cout << i + 1 << " : ";
}
k = i;
}
void display ( double *a )
{
int i;
std::cout << "score : ";
for ( i = 0; i < k; i++ )
std::cout << a[i] << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
double average ( double *a )
{
int i;
double sum = 0;
for ( i = 0; i < k; i++ )
sum += a[i];
return sum/k;
}
int main()
{
using namespace std;
double score[ArSize];
input ( score, ArSize );
display ( score );
cout << "Average : " << average ( score ) << endl;
return 0;
}
struct box
{
char maker[40];
float height;
float width;
float length;
float volume;
};
a.编写一个函数,按值传递box结构,并显示每个成员的值
b.编写一个函数,传递box结构的地址,并将volume成员设置为其他三维长度的乘积。
c.编写一个使用这两个函数的简单程序
#include <iostream>
struct box
{
char maker[40];
float height;
float width;
float length;
float volume;
};
void adisplay(box cube)
{
std::cin>>cube.maker>>cube.height>>cube.width>>cube.length;
cube.volume=cube.height*cube.length*cube.width;
std::cout<<"Value :"<<std::endl<<cube.maker<<" "<<cube.height<<" "<<cube.width<<" "<<cube.length<<" "<<cube.volume<<std::endl<<std::endl;
}
void bdisplay(box *cube)
{
std::cin>>cube->maker>>cube->height>>cube->width>>cube->length;
cube->volume=cube->height*cube->length*cube->width;
std::cout<<"Pointer :"<<std::endl<<cube->maker<<" "<<cube->height<<" "<<cube->width<<" "<<cube->length<<" "<<cube->volume<<std::endl;
}
int main()
{
box cube;
adisplay(cube);
bdisplay(&cube);
return 0;
}

5.定义一个递归函数,接受一个整型参数,并返回该参数的阶乘。前面讲过,3的阶乘写作3!,等于3 * 2!,以此类推: 而0!
被定义为1.通用的计算公式是,如果n大于零 , 则n! = n * (n - 1)!。
在程序中对该函数进行测试,程序使用循环让用户 输入不同的值,程序将报告这些值的阶乘。
#include <iostream>
long long factorial ( long long n )
{
if ( n == 1 || n == 0 )
return 1;
else
n *= factorial ( n - 1 );
return n;
}
int main()
{
int n, i = 0;
std::cout << i + 1 << " : " ;
while ( std::cin >> n )
{
std::cout << "n!=" << factorial ( n ) << std::endl;
std::cout << ++i + 1 << " : " ;
}
return 0;
}
6.编写一个程序,它使用下列函数: Fill_array()将一个double数组的名称和长度作为参数。
它提示用户输入double值,并将这些值存储到数组中。
当数组被填满或 用户输入了非数字时,输入将停止,并返回实际输入了多少个数字。
Show_array()将一个double数组的名称和长度作为参数,并显示该数组的内容。
Reverse-array()将一个double数组的名称和长度作为参数,并将存储在数组中的值的顺序反转。
程序将使用这些函数来填充数组,然后显示数组;反转数组,然后显示数组;
反转数组中除第一个和最后一个元素之外的所有元素, 然后显示数组
#include <iostream>
const int ArSize = 10;
void fill_array ( double *a, int& n )
{
int i = 0;
std::cout << "fill_array : " << std::endl;
std::cout << "Please enter double numbers : " << std::endl;
std::cout << "#" << i + 1 << " : " ;
while ( std::cin >> a[i] )
{
if ( i == 10 ) break;
i++;
std::cout << "#" << i + 1 << " : " ;
}
n = i;
std::cout << "return numbers : " << i << std::endl << std::endl;
}
void show_array ( double *a, int n )
{
int i = 0;
std::cout << "show_array :" << std:: endl;
for ( ; i < n; i++ )
std::cout << a[i] << " ";
std::cout << std::endl << std::endl;
}
void reverse_array ( double *a, int n )
{
int i,j;
double t;
j=n;
for ( i = 0; i < (n/2); i++, j-- )
{
t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j - 1];
a[j - 1] = t;
}
std::cout << "reverse_array :" << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
double ar[ArSize];
int len=ArSize;
fill_array ( ar, len );
show_array ( ar, len );
reverse_array ( ar, len );
show_array ( ar, len );
std::cin.clear();
std::cin.sync();
return 0;
}

7.修改程序清单7.7中的3个数组处理函数,使之使用两个指针参数来表示区间。file_array()函数不返回实际读取了多少个 数字,而是返回一个指针,
该指针指向最后被填充的位置:其他的函数可以将该指针作为第二个参数,以标识数据结尾。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int Max = 5;
// function prototypes
double *fill_array ( double *begin, double *end );
void show_array ( double *begin, double *end );
void revalue (double r, double *begin, double *end );
int main()
{
double properties[Max];
double *size = fill_array ( properties, properties + Max );
show_array ( properties, size );
cout << "Enter revaluation factor: ";
double factor;
cin >> factor;
revalue (factor, properties, size );
show_array ( properties, size );
cout << "Done.\n";
return 0;
}
double* fill_array ( double *begin, double *end )
{
double temp,*i = begin;
int j=0 ;
for ( ; i < end; i++ )
{
cout << "Enter value #" << ( j++ + 1 ) << ": ";
cin >> temp;
if ( !cin ) // bad input
{
cin.clear();
while ( cin.get() != '\n' )
continue;
cout << "Bad input; input process terminated.\n";
break;
}
else if ( temp < 0 ) // signal to terminate
break;
*i = temp;
}
return i;
}
// the following function can use, but not alter,
// the array whose address is ar
void show_array ( double *begin, double *end )
{
int j=0;
double* i = begin;
for ( ; i < end; i++ )
{
cout << "Property #" << ( j++ + 1 ) << ": $";
cout << *i << "\n";
}
}
// multiplies each element of ar[] by r
void revalue ( double r,double *begin, double *end )
{
double* i = begin;
for ( ; i < end; i++ )
*i *= r;
}
8.在不使用array类的情况下完成程序清单7.15所做的工作。编写两个这样的版本:
a.使用const char *数组存储表示季度名称的字符串,并使用double数组存储开支。
b.使用const char *数组存储表示季度名称的字符串,并使用一个结构,该结构只有一个成员——一个用于存储开支的double数组。
这种设计与使用array类的基本设计类似
a.
#include <iostream>
const int seasons = 4;
const char* snames[seasons] = {"spring", "summer", "fall", "winter"};
void fill ( double e[] );
void show ( double e[] );
int main()
{
double expenses[seasons];
fill ( expenses );
show ( expenses );
return 0;
}
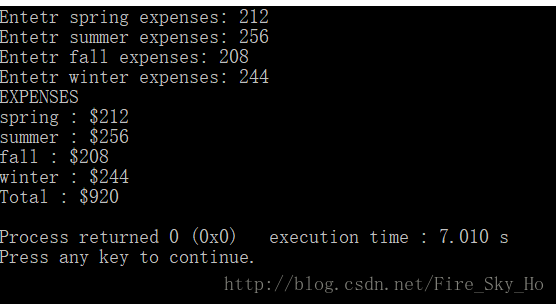
void fill ( double e[] )
{
for ( int i = 0; i < seasons; i++ )
{
std::cout << "Entetr " << snames[i] << " expenses: ";
std::cin >> e[i];
}
}
void show ( double e[] )
{
std::cout << "EXPENSES" << std::endl;
int i = 0, sum = 0;
for ( ; i < seasons; i++ )
{
std::cout << snames[i] << " : $" << e[i] << std::endl;
sum += e[i];
}
std::cout << "Total : $" << sum << std::endl;
}b.
#include <iostream>
const int seasons = 4;
const char* snames[seasons] = {"spring", "summer", "fall", "winter"};
struct pay
{
double expenses[seasons];
};
void fill ( pay *e );
void show ( pay *e );
int main()
{
pay e;
fill ( &e );
show ( &e );
return 0;
}
void fill ( pay *e )
{
for ( int i = 0; i < seasons; i++ )
{
std::cout << "Entetr " << snames[i] << " expenses: ";
std::cin >> e->expenses[i];
}
}
void show ( pay *e )
{
std::cout << "EXPENSES" << std::endl;
int i = 0, sum = 0;
for ( ; i < seasons; i++ )
{
std::cout << snames[i] << " : $" << e->expenses[i] << std::endl;
sum += e->expenses[i];
}
std::cout << "Total : $" << sum << std::endl;
}
10.设计一个名为calculate()的函数,它接受两个double值和一个指向函数的指针,而被指向的函数接受两个double参数,并返回一个double值、calculate()函数的类型也是double,并返回被指向的函数使用calculate()的两个double参数计算得到的值。例如,假如add()函数的定义如下:
double add(double x,double y)
{
return x + y;
}
double q = calculate(2.5,10.4,add);
将导致calculate()把2.5和10.4传递给add()函数,并返回add()的返回值(12.9).请编写一个程序,它调用上述两个函数和至少另一个与add()类似的数。
如果读者爱冒险,可以尝试创建一个指针数组,其中的指针指向add()样式的函数,并编写一个循环,使用这些指针连续让calculate()调用这些函数。
提示:下面是声明这种指针数组的方式,其中包含3个指针:double (*pf[3]) (double,double);
可以采用数组初始化句法,并将函数名作为地址来初始化这样的数组。
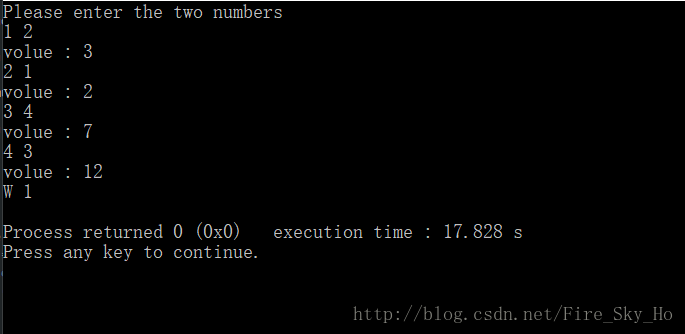
#include <iostream>
double calculate ( double x, double y, const double ( *pf ) ( double, double ) )
{
return ( *pf ) ( x, y );
}
const double add ( double a, double b )
{
return a + b;
}
const double mul ( double a, double b )
{
return a * b;
}
const double ( *pf[2] ) ( double x, double y ) = {add, mul};
int main()
{
double x, y;
int i = 0;
std::cout << "Please enter the two numbers" << std::endl;
while ( std::cin >> x >> y&&i<2 )
{
std::cout << "volume : " << calculate ( x, y, pf[i] ) << std::endl;
i++;
if(i==2)
i=0;
}
std:: cin.clear();
std::cin.sync();
return 0;
}


























 1752
1752

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








