1.制树,由权重得到树
//节点的定义
struct Hnode {
char value; //值
int weight; //权重
Hnode* leftC;
Hnode* rightC;
Hnode(char ch,int weight):value(ch),weight(weight),leftC(NULL),rightC(NULL){}
Hnode(int weight):Hnode('/0',weight) {}
};
重载operator,利用优先队列生成哈夫曼树
//重载operator,使得队首元素始终是最轻的
struct comp {
bool operator()(const Hnode* n1,const Hnode* n2) {
return n1->weight > n2->weight;
}
};
/*
构建哈夫曼树
用户传入值和权重的映射
*/
Hnode* buildTree(map<char,int> &nodes ) {
priority_queue<Hnode*, vector<Hnode*>, comp> pq;
for (auto &p : nodes) {
pq.push(new Hnode(p.first,p.second));
}
//队列中的最后一个节点就是根节点,直接返回
while (pq.size()>1) {
Hnode* left = pq.top();
pq.pop();
Hnode* right = pq.top();
pq.pop();
Hnode* father = new Hnode(left->weight+right->weight);
father->leftC = left;
father->rightC = right;
pq.push(father);
}
return pq.top();
}测试
/*
先序遍历
*/
void preOrder(Hnode* root) {
if (root != NULL) {
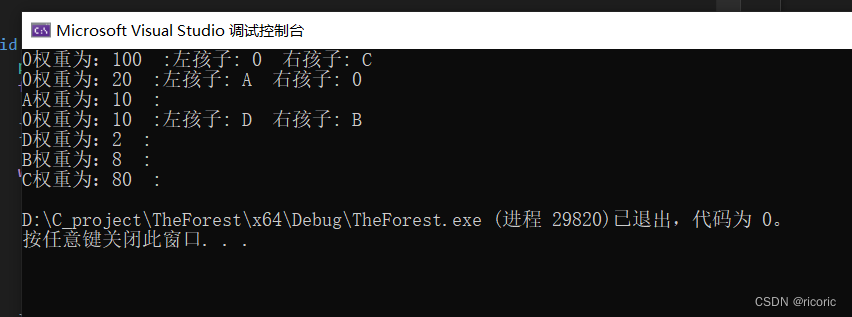
cout << root->value << "权重为:" << root->weight<<" :";
if (root->leftC != NULL) {
cout << "左孩子: " << root->leftC->value << " ";
}
if (root->rightC != NULL) {
cout << "右孩子: " << root->rightC->value << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
preOrder(root->leftC);
preOrder(root->rightC);
}
}
int main() {
map<char, int> nodes = {
{'A',10},
{'B',8},
{'C',80},
{'D',2}
};
Hnode* tree = buildTree(nodes);
preOrder(tree);
//测试;
map<char, string> codemap;
coding(tree,codemap);
cout << endl;
for (auto n:codemap) {
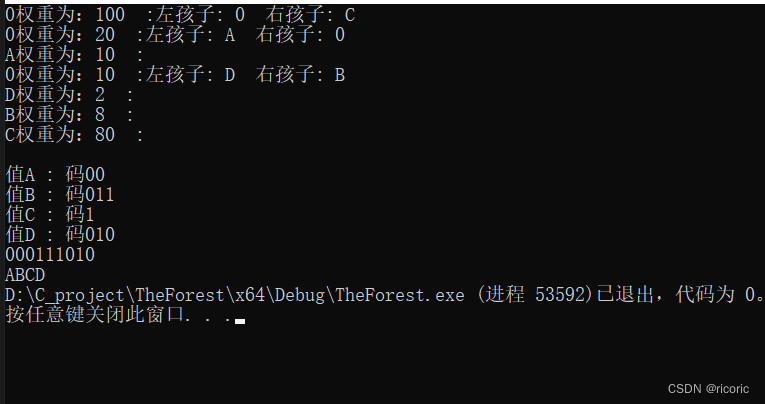
cout <<"值" << n.first << " : " <<"码" << n.second<<endl;
}
}
2.编码,更具得到的树进行编码
根据先序遍历的路径,往左走为1,往右走为0,递归实现
/*
由哈夫曼树进行编码:
*/
void coding(Hnode* tree,map<char,string> &resultMap,string code="") {
//按照先序遍历的顺序,如果到达叶子节点,就将code的值和叶子节点的value建立映射并返回
if (tree->leftC == NULL && tree->rightC == NULL) {
resultMap[tree->value] = code;
return;
}
//按照先序遍历的路径,向左就添0,向右则添1 ;
coding(tree->leftC,resultMap,code+"0");
coding(tree->rightC, resultMap, code + "1");
}
测试
int main() {
map<char, int> nodes = {
{'A',10},
{'B',8},
{'C',80},
{'D',2}
};
Hnode* tree = buildTree(nodes);
//eOrder(tree);
//测试;
map<char, string> codemap;
coding(tree,codemap);
cout << endl;
for (auto n:codemap) {
cout <<"值" << n.first << " : " <<"码" << n.second<<endl;
}
} 3.对一具体字段进行编码
3.对一具体字段进行编码
/*
根据具体字段得出该字段的哈夫曼编码
*/
string encry(string code, map<char,string> &codemap) {
string mystery="";
//遍历找到对应的映射并加到结果后面
for (char ch:code) {
mystery += codemap[ch];
}
return mystery;
}
3.解码,由一串哈夫曼编码得到具体表达的意思
如果要解码我们就必须要知道每个编码所代表的具体的值是多少,就相当于我们知道了哈夫曼树长啥样,虽然根据同一套编码集生成的哈夫曼树可能权重一样,但是树的结构可能不同,导致相同值有不同的编码,所以要解码就要知道树长啥样或者是知道编码代表的具体意思。
/*
有哈夫曼树进行解码操作
按照先序序列的顺序解码
根据编码的序列沿着根节点一直向下,遇到1就往右,遇到0就向左,直到到达叶子节点
*/
string decoding(string mystery,Hnode* tree) {
string password = "";
Hnode* root = tree;
for (char ch : mystery) {
if (ch == '0') {
root = root->leftC;
}
if (ch=='1') {
root = root->rightC;
}
if (root->leftC == NULL && root->rightC == NULL) {
password += root->value; //读取叶子节点,并将roo重新指向根节点
root = tree;
}
}
return password;
}测试
int main() {
map<char, int> nodes = {
{'A',10},
{'B',8},
{'C',80},
{'D',2}
};
Hnode* tree = buildTree(nodes);
//eOrder(tree);
//测试;
map<char, string> codemap;
coding(tree,codemap);
cout << endl;
for (auto n:codemap) {
cout <<"值" << n.first << " : " <<"码" << n.second<<endl;
}
string s1 = "ABCD";
string mystery = encry(s1,codemap);
cout << mystery;
cout << endl;
string s2 = "000111010";
string passward = decoding(s2,tree);
cout << passward;
}





















 5945
5945











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








