MarkDown It is my first time
运算符号结构分类图
运算符号解释
标示符的表示方法
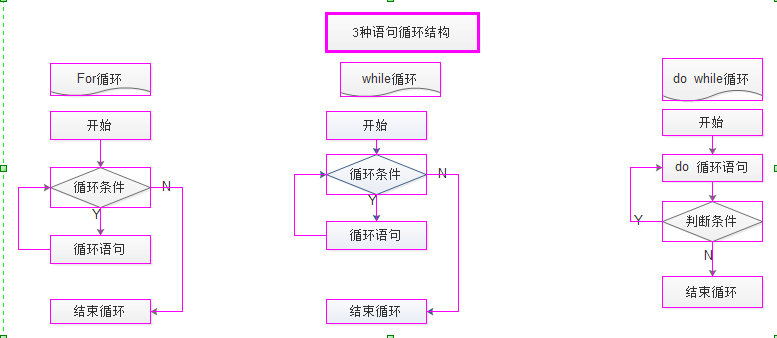
三种循环结构
几个重要的知识点
java程序输入方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("你好世界");
}运算符号
算术运算符
+- * / %(取模(余)运算)
浮点数取模运算公式 a%b=a-(b*q) q=int(a/b)
整数取模运算公式 a%b=a-(a/b)*b
递增递减运算符
++ j++先运算后加1 ++j先加1在运算
–
赋值运算符
= += -= *= /=
关系运算符
》> >= < <= ==(是否相等) !=(是否不等)
逻辑运算符
&& || 称为短路与(只要有一个为0则直接中断计算) 短路或(只要有一个1则直接中断计算)
位运算
& | ^ ~ 将十进制数转换为二进制数 按位进行与或运算 异或是相同为零不同为1 ~是单目运算
三目运算
三目运算在规范中不允许使用 ? :
位移运算
分为左移后右移运算
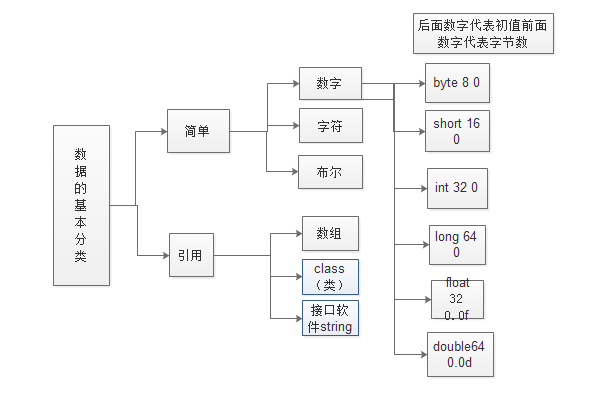
浮点类型数据float和double型数据的关系
double型数据可以转换为float型数据,但是float型数据不可以转换为double型数据
标示符的表示规则
变量名必须为名词,通常第一个单词首字母是小写,其后面单词的首字母大写
首字母必须以 下划线_
字母,开头后面可跟任意多的数字,字母
符号,下划线。
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 80;
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
score=scanner.nextInt();
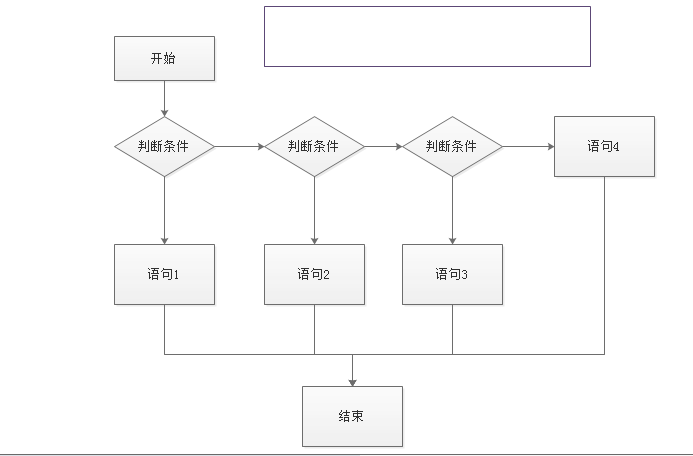
if (score > 98) {
System.out.println("优秀");
if(score==100){
System.out.println("完美");
}
else {
System.out.println("其他");
}
} else if (score > 80) {
System.out.println("良好");
} else if (score > 60) {
System.out.println("及格");
} else {
System.out.println("不及格");
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 0;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
score = scanner.nextInt();
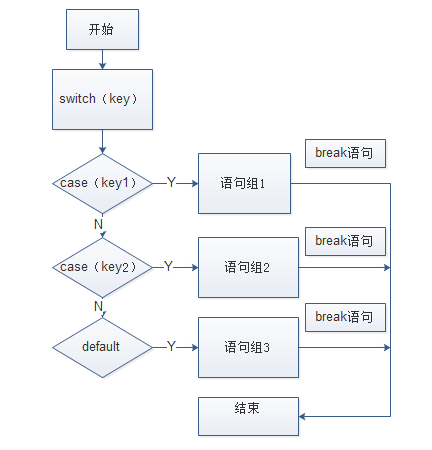
switch (score / 10) {
case 10:
System.out.println("5p分");
break;
case 9:
System.out.println("4p分");
break;
case 8:
System.out.println("3p分");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("2p分");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("1p分");
break;
default:
System.out.println("0p分");
break;
}
}
}
利用循环结构求一个整数在二进制的情况下1的个数有几个
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
// int i=scanner.nextInt();
// int count=0;
// for (int j = 0; j < 32; j++) {
// if(i%2==1){
// count++;
// }
// i=i>>1;
// }
// System.out.println(count);
int k=scanner.nextInt();
int count=0;
while(k!=0){
if(k%2==1){
count++;
}
k=k/2;
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
continue 与break的区别
continue是跳出本次循环,假如continue在循环次数位100次的循环语句中的第26次中出现,那么第26次就会被轮空,循环接着第27次进行,而break语句是跳出循环,不会再执行循环语句。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








