[Linux - C] 自主Shell
[Linux - C语言] 自主Shell
逻辑策划 main()
先打印命令行,然后再获取用户字符串,并且判断字符串是否有效,在进行重定向检查,然后再切割字符串。将整行的命令切割为命令与命令选项,在判断是否为内键命令,如果是内建命令则不需要利用子进程替换,如果不是内建命令则利用子进程替换执行命令。
main函数代码如下:
int main()
{
while(1)
{
//命令行
MakeCommandLineAndPrint();
//获取用户字符串
int n = GetUserCommand();
if(n<=0) continue;
//检查重定向
CheckRedir();
//切割字符
SplitCommand();
//内建命令
n = CheckBuildin();
if(n) continue;
//执行命令
ExecuteCommand();
filename = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
打印命令行 void MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
在Linux系统中的命令行中,包括了用户名USER,主机名HOSTNAME,当前目录PWD,还有身份标识符,如下图所示:
下面就让我们来一一实现吧!
用户名 USER
获取用户名,我们需要从环境变量中获取USER,这里需要使用char* getenv(const char* name)函数,参数name代表我们要查询的变量,查询后,如果成功找到了返回该环境变量,否则返回NULL。
代码参考如下:
const char* GetUserName()
{
const char* UserName = getenv("USER");
if(UserName == NULL) return "None";
return UserName;
}
主机名 HOSTNAME
同理。
const char* GetHostName()
{
const char* name = getenv("HOSTNAME");
if(name==NULL) return "None";
return name;
}
当前目录 PWD
const char* GetCwd()
{
const char* cwd = getenv("PWD");
if(cwd==NULL) return "None";
return cwd;
}
SkipPath 切割目录
因为我们PWD获取的环境变量,是由用户的家目录到当前目录的绝对地址,而命令行中只是当前目录,所以我们需要对目录进行切割。
因为代码量较小,所以我们利用宏函数,用do - while结构对函数内部进行封装,利用尾指针向右移的方法切割。
#define SkipPath(p) do{ p+=strlen(p)-1,while(*p != '/') p++; }while(0)
例如:”/home/Ang/Test“ 切割后为 “/Test”
打印命令行
利用前面的函数再将其组合即可。
需要注意的是用户标识符,在bash进程的命令行中 ‘$’ 代表普通用户,'#'代表超级用户。
我们这里为了和bash的命令行区分,我们就用 ‘>’ 代表普通用户,'->'代表超级用户。
如果返回的name,为root就表示为超级用户,所以在这进行判断即可。
还需要注意的是如果我们当前位置为根目录,即honstname = "/"的时候,
如果直接使用cwd+1,就没有字符可打印了,而在根目录下命令行的此时这个位置为"/",所以此时直接打印"/"。
void MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
{
const char* name = GetUsrName();
const char* hostname = GetHostName();
const char* cwd = GetCwd();
SkipPath(cwd);
const char* ManageSign = "->";
const char* CommonSign = ">";
printf("[%s@%s %s]%s ",name,hostname,cwd[1]=='\0'?"/":cwd+1,
!strcmp("root",name)?ManageSign:CommonSign);
fflush(stdout);
}
获取用户字符串 int GetUserCommand()
在定义这个函数之前,我们现在全局定义一个字符数组,用于储存我们输入的命令,如下:
#define NUM 500
char* command[NUM];
然后利用fgets函数获取用户的行输入,如果fgets读取失败返回NULL,所以这里要进行判断。
还需要注意的是'\n'也会被读取的command中,而此时的’\n’会影响后续的命令执行,所以要将尾部的'\n'改为'\0',再返回有效地输入个数。
而在main函数中根据读取的状态来确定是否继续执行下一步。
代码如下:
int GetUserCommand()
{
char* s = fgets(command,sizeof(command),stdin);
if(s == NULL) return -1;
int n = strlen(command);
command[n - 1]='\0';
return n - 1;
}
检查重定向 void CheckRedir()
重定向的本质:是在内核中改变文件描述符表特定下标的内容,如下:
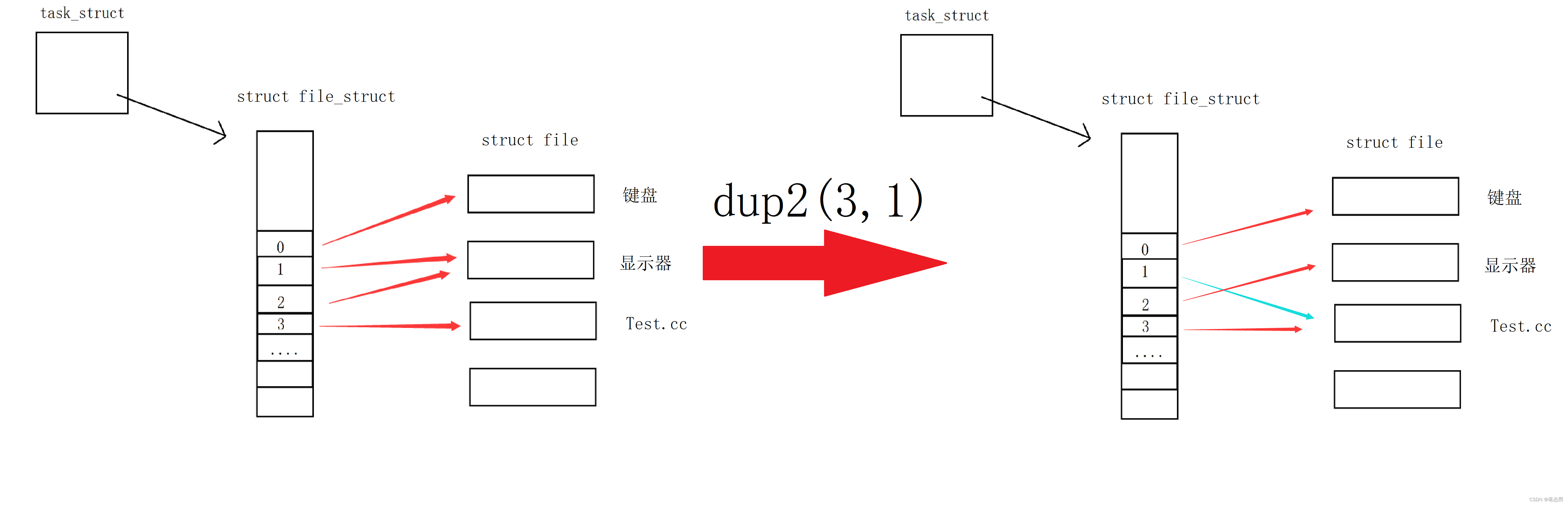
在定义这个函数之前,我们现在全局定义几个常量来表示重定向的状态,再定义一个全局的字符串指针用来指向command中的目标文件,再定义一个int变量来表示当前命令重定向的状态,如下:
#define None_Redir 0 //没有重定向
#define In_Redir 1 //输入重定向
#define Out_Refir 2 //输出重定向
#define App_Redir 3 //追加重定向
int redir_type = None_Redir;
char* filename = NULL;
在此之前,我们还需要写一个宏函数,功能是:当我们找到重定向符号后,让filename指向后面的文件名称.
#define SkipSpace(cmd, pos) do{\
while(1)\
{\
if(isspace(cmd[pos])) pos++;\
else break;\
}\
}while(0)
在实现了上述功能之后,这个函数的编写变得异常简单了。只需要再确认重定向符号后,将filename指向正确的文件名,并且将redir_type变为正确的重定向状态即可,需要注意的是在检测到重定向符号后,要将其改为'\0',因为后边的内容已经不是指令了。
void CheckRedir()
{
int pos = 0;
int n = strlen(command);
while(pos < n)
{
if(command[pos]=='>')
{
if(command[pos+1]=='>')
{
redir_type = App_Redir;
command[pos++]='\0';
pos++;
SkipSpace(command,pos);
filename = command + pos;
}
else
{
command[pos++]='\0';
redir_type = Out_Redir;
SkipSpace(command,pos);
filename = command + pos;
}
}
else if(command[pos]=='<')
{
command[pos++]='\0';
redir_type = In_Redir;
SkipSpace(command,pos);
filename = command + pos;
}
else pos++;
}
}
切割字符 void SplitCommand()
因为我们输入的一行指令中间是由空格所分开的,在切割字符的时候,利用strtok函数进行切割,所以我们需要定义一个全局变量表示只有一个空格的字符串。
我们在后续利用execvp进行程序替换,所以我们需要一个全局的可以存放指令的参数。
#define SEP " "
char* gArgv[NUM];
利用strtok进行切割即可。
void SplitCommand()
{
int index = 0;
gArgv[index++] = strtok(command, SEP);
while(gArgv[index++] =strtok(NULL, SEP));
}
内建命令 bool CheckBuildin()
内建命令不需要子进程来执行,是由bash进程直接执行的命令,所以这一类的命令不能利用子进程替换,实现需要自己编写。
直接利用strcmp来判断是否为内建命令,如果是实现相应功能并返回1,表示为内建命令。
代码如下:
bool CheckBuildin()
{
int yes = 0;
if(strcmp("cd",gArgv[0]) == 0)
{
yes = 1;
Cd();
}
else if(!strcmp("echo",gArgv[0])&&!strcmp(gArgv[1],"$?"))
{
yes=1;
printf("%d",lastcode);
lastcode=0;
}
return yes;
}
Cd
利用chird函数来变换当前目录,再定义一个temp来存放当前目录(此时目录已经变了),再利用snprintf重写cwd,使其符合putenv的参数标准,再让putenv感谢环境变量即可。
代码如下:
void Cd()
{
const char* path = gArgv[1];
if(path == NULL) path = GetHome();
chdir(path);
char temp[SIZE*2];
getcwd(temp, sizeof(temp));
snprintf(cwd,sizeof(cwd),"PWD=%s",temp);
putenv(cwd);
}
执行命令 void ExecuteCommand()
利用fork创建子进程,利用返回值id判断进程,如果id<0,进程就可以直接去死了,如果id=0说明是子进程,如果id>0,说明是父进程。
在子进程中,我们先用filename判断命令是否使用了重定向,如果使用了则打开相关文件,利用dup2函数,更改相关文件操作符下标,然后再执行程序替换即可。如果替换失败,利用exit退出并报告错误。
在父进程中,我们需要用waitpid等待子进程。等待子进程结束后,利用waitpid的返回值判断等待是否成功,如果返回值为负数,说明waitpid调用失败,可能是子进程不存在。再利用输出型参数status。判断子进程的运行状态,用lastcode进行更新 ,如果lastcode不为零,说明子进程有异常,打印错误即可。
void ExecuteCommand()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id < 0) Die();
if(id == 0)
{
if(filename != NULL)
{
if(redir_type == In_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename,O_RDONLY);
dup2(fd,0);
}
else if(redir_type == Out_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0666);
dup2(fd,1);
}
else if(redir_type == App_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0666);
dup2(fd,1);
}
else {}
}
execvp(gArgv[0],gArgv);
exit(errno);
}
else
{
int status = 0;
pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);
if(rid > 0)
{
lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status);
if(lastcode != 0)
{
printf("%s:%s:%d\n",gArgv[0],strerror(lastcode),lastcode);
}
}
}
}
ps: lastcode是一个全局变量,用来记录子进程的退出状态,配合echo内建命令。
源代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define NUM 1000
#define SIZE 64
#define SkipPath(p) do{ p+=strlen(p)-1; while(*p!='/') p--; }while(0)
#define SkipSpace(cmd, pos) do {\
while(1)\
{\
if(isspace(cmd[pos]))\
pos++;\
else break;\
}\
}while(0)
#define None_Redir 0
#define In_Redir 1
#define Out_Redir 2
#define App_Redir 3
char cwd[SIZE*2];
char* gArgv[NUM];
char command[NUM];
char* filename = NULL;
const char* SEP =" ";
int redir_type = 0;
int lastcode = 0;
const char* GetCwd()
{
const char* cwd = getenv("PWD");
if(cwd==NULL) return "None";
return cwd;
}
const char* GetUsrName()
{
const char* name = getenv("USER");
if(name==NULL) return "None";
return name;
}
const char* GetHostName()
{
const char* name = getenv("HOSTNAME");
if(name==NULL) return "None";
return name;
}
void MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
{
const char* name = GetUsrName();
const char* hostname = GetHostName();
const char* cwd = GetCwd();
SkipPath(cwd);
const char* ManageSign = "->";
const char* CommonSign = ">";
printf("[%s@%s %s]%s ",name,hostname,cwd[1]=='\0'?"/":cwd+1,
!strcmp("root",name)?ManageSign:CommonSign);
fflush(stdout);
}
int GetUserCommand()
{
char* s = fgets(command,sizeof(command),stdin);
if(s == NULL) return -1;
int n = strlen(command);
command[n - 1]='\0';
return n - 1;
}
void SplitCommand()
{
int index = 0;
gArgv[index++] = strtok(command,SEP);
while(gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL,SEP));
}
void Die()
{
exit(1);
}
void ExecuteCommand()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id < 0) Die();
if(id == 0)
{
if(filename != NULL)
{
if(redir_type == In_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename,O_RDONLY);
dup2(fd,0);
}
else if(redir_type == Out_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0666);
dup2(fd,1);
}
else if(redir_type == App_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0666);
dup2(fd,1);
}
else {}
}
execvp(gArgv[0],gArgv);
exit(errno);
}
else
{
int status = 0;
pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);
if(rid > 0)
{
lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status);
if(lastcode != 0)
{
printf("%s:%s:%d\n",gArgv[0],strerror(lastcode),lastcode);
}
}
}
}
const char* GetHome()
{
const char* home = getenv("HOME");
if(home== NULL) return "/";
return home;
}
void Cd()
{
const char* path = gArgv[1];
if(path == NULL) path = GetHome();
chdir(path);
char temp[SIZE*2];
getcwd(temp, sizeof(temp));
snprintf(cwd,sizeof(cwd),"PWD=%s",temp);
putenv(cwd);
}
bool CheckBuildin()
{
int yes = 0;
if(strcmp("cd",gArgv[0]) == 0)
{
yes = 1;
Cd();
}
else if(!strcmp("echo",gArgv[0])&&!strcmp(gArgv[1],"$?"))
{
yes=1;
printf("%d",lastcode);
lastcode=0;
}
return yes;
}
void CheckRedir()
{
int pos = 0;
int n = strlen(command);
while(pos < n)
{
if(command[pos]=='>')
{
if(command[pos+1]=='>')
{
redir_type = App_Redir;
command[pos++]='\0';
pos++;
SkipSpace(command,pos);
filename = command + pos;
}
else
{
command[pos++]='\0';
redir_type = Out_Redir;
SkipSpace(command,pos);
filename = command + pos;
}
}
else if(command[pos]=='<')
{
command[pos++]='\0';
redir_type = In_Redir;
SkipSpace(command,pos);
filename = command + pos;
}
else pos++;
}
}
int main()
{
while(1)
{
//命令行
MakeCommandLineAndPrint();
//获取用户字符串
int n = GetUserCommand();
if(n<=0) continue;
//检查重定向
CheckRedir();
//切割字符
SplitCommand();
//内建命令
n = CheckBuildin();
if(n) continue;
//执行命令
ExecuteCommand();
filename = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
结语
以上就是本期的全部内容了,喜欢就多多关注吧!!!
下期会继续完善的捏!
























 2656
2656

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










