day day18 二叉树 part05
day18-1 513.找树左下角的值
如何找到左下角
最后一行 + 最靠左侧的节点(注意:最靠左侧的节点不一定是左孩子)
迭代法要比递归法简单一些
深度最大的叶子节点
代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
/**
* 迭代法
*/
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int res = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
TreeNode tempNode = queue.poll();
if(i == 0){
res = tempNode.val;
}
if(tempNode.left != null){
queue.offer(tempNode.left);
}
if(tempNode.right != null){
queue.offer(tempNode.right);
}
}
}
return res;
}
/**
* 递归法
*/
private int maxDepth = -1;
private int resValue = 0;
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
resValue = root.val;
findLeftValue(root,0);
return resValue;
}
private void findLeftValue(TreeNode root, int depth){
if(root == null){
return;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
if(depth > maxDepth){
resValue = root.val;
maxDepth = depth;
}
}
// 左
if(root.left != null){
depth++;
findLeftValue(root.left, depth);
depth--;
// 简化版 depth的值没变,但是传入函数的值+1了满足回溯的含义
// findLeftValue(root.left, depth + 1);
}
// 右
if(root.right != null){
depth++;
findLeftValue(root.right, depth);
depth--;
}
}
}
总结
为啥没有中的处理逻辑,是因为本题没有处理中的逻辑,所有本题前中后序都可以
day18-2 112. 路径总和 113.路径总和ii
大体思路
递归和迭代都可以,但是递归更简单
代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
/**
* 递归法(详细版) 精简版可以简化回溯部分的代码
*/
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null){
return false;
}
return traversal(root, targetSum - root.val);
}
private boolean traversal(TreeNode root, int targetSum){
if(root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum == 0 ){
return true;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
return false;
}
// 左
if(root.left != null){
targetSum -= root.left.val;
boolean left = traversal(root.left, targetSum);
if(left){
return true;
}
// 回溯
targetSum += root.left.val;
}
// 右
if(root.right != null){
targetSum -= root.right.val;
boolean right = traversal(root.right, targetSum);
if(right){
return true;
}
// 回溯
targetSum += root.right.val;
}
return false;
}
}
day18-3 113.路径总和ii
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) {
return res;
}
List<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
preorderdfs(root, targetSum, res, path);
return res;
}
private void preorderdfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path){
path.add(root.val);
// 遇到叶子节点
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
// 找到了和为 targetSum 的路径
if(targetSum - root.val == 0){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));// LinkedList放ArrayList中需要转化一下
}
// 如果和不为 targetSumm,直接返回
return;
}
if(root.left != null){
preorderdfs(root.left, targetSum - root.val, res, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
if(root.right != null){
preorderdfs(root.right, targetSum - root.val, res, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
day18-4 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
构造二叉树的流程
以 后序数组的最后一个元素为切割点,先切中序数组,根据中序数组,反过来再切后序数组。
流程:
- 后序数组为0,说明是空节点
- 后序数组最后一个元素为节点元素
- 寻找中序数组位置的切割点
- 切中序数组为左中序+右中序
- 切后序数组为左后序+右后序
- 递归处理左区间后区间
代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 方便根据数值查找位置
Map<Integer, Integer> map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
// 用 map 保存中序序列的数值对应的位置
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++){
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return findNode(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder, 0, postorder.length);
}
public TreeNode findNode(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd){
// 参数里的范围都是前闭右开
if(inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd){// 不满足左闭右开,说明没有元素,返回空数
return null;
}
// 找到后序遍历的最后一个元素在中序遍历中的位置
int rootIndex = map.get(postorder[postEnd -1]);
// 构造结点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]);
// 保存中序左子树个数,用于确定后序数列的个数
int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin;
root.left = findNode(inorder, inBegin, rootIndex,
postorder, postBegin, postBegin + lenOfLeft);
root.right = findNode(inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd,
postorder, postBegin + lenOfLeft, postEnd - 1);
return root;
}
}
注意细节
- 保证循环不变量,即切割中序数组和后序数组的时候要注意区间,左闭右开?左闭右闭?
- 先切中序然后再切后序,不然不知道中间的节点(中序里面的左区间和后序里面的左区间相同)
前序和后序构造二叉树?
否,因为只有前序和后序就找不到左右的分割点
图例 :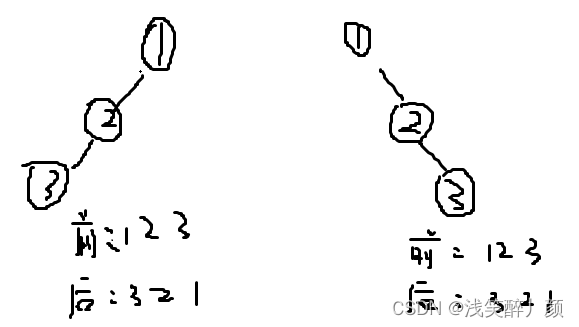
总结
打流程日志容易排错
day18-5 105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 方便根据数组查找位置
Map<Integer, Integer> map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
// 用 map 保存中序序列的数值对应的位置
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++){
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return findNode(inorder, 0, inorder.length, preorder, 0, preorder.length);
}
private TreeNode findNode(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int[] preorder, int preBegin, int preEnd){
// 参数里面的范围都是左闭右开
if(inBegin >= inEnd || preBegin >= preEnd){
return null;
}
// 找到前序遍历的第一个元素在中序遍历中的位置
int rootIndex = map.get(preorder[preBegin]);
// 构造结点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]);
// 保存中序遍历的左子树用于确定前序数列的个数
int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin;
root.left = findNode(inorder, inBegin, rootIndex,
preorder, preBegin + 1, preBegin + 1 + lenOfLeft);
root.right = findNode(inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd, preorder, preBegin + 1 + lenOfLeft, preEnd);
return root;
}
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








