2种形式参数类型
形式参数:
引用类型:
形式参数:
基本类型(太简单)
引用类型
类名:(匿名对象的时候其实我们已经讲过了)需要的是该类的对象 <StudentTest >
抽象类:需要的是该抽象的类子类对象 <PersonTest>
接口:需要的是该接口实现类对象 <TeacherTest>
类名作为形式参数-代码块
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
抽象类作为形式参数-代码块
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
接口作为形式参数-代码块
-------------------------------------------------Java返回值-类、抽象类、接口
返回值类型
返回值类型
基本类型:(基本类型太简单,我不准备讲解)
引用类型:
类:返回的是该类的对象
抽象类:返回的是该抽象类的子类对象
接口:返回的是该接口的实现类的对象
类名作为返回值-代码块
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
抽象类作为返回值-代码块
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
接口作为返回值-代码块
--------------------------------------------------------
链式编程。
每次调用完毕方法后,返回的是一个对象。
链式连接-代码块
-----------------类及其组成可以用的修饰符
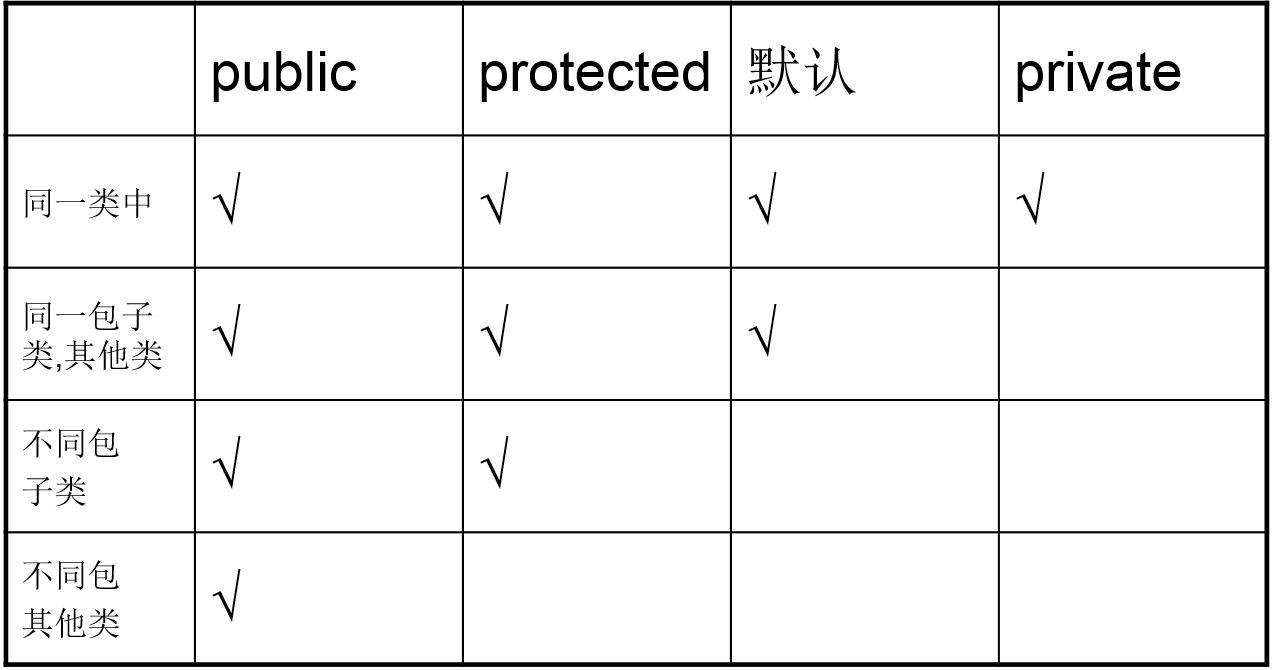
权限修饰符
Java 类及其组成可以用的修饰符
修饰符:
权限修饰符:private,默认的,protected,public
状态修饰符:static,final
抽象修饰符:abstract
类:
权限修饰符:默认修饰符,public
状态修饰符:final
抽象修饰符:abstract
用的最多的就是:public
成员变量:
权限修饰符:private,默认的,protected,public
状态修饰符:static,final
用的最多的就是:private
构造方法:
权限修饰符:private,默认的,protected,public
用的最多的就是:public
成员方法:
权限修饰符:private,默认的,protected,public
状态修饰符:static,final
抽象修饰符:abstract
用的最多的就是:public
除此以外的组合规则:
成员变量:public static final
成员方法:public static
public abstract
public final
代码块
---------------------------------------------------------------------成员内部类
成员内部类:
<1>外部类名.内部类名 对象名 = 外部类对象.内部类对象;
Outer.Inner oi = new Outer().new Inner();
<2>成员内部类被静态修饰后的访问方式是:
//格式:外部类名.内部类名 对象名 = new 外部类名.内部类名();
Outer.Inner oi = new Outer.Inner();
成员内部类的代码块1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
成员内部类(被静态修饰)的代码块2
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
练习题
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------






















 4057
4057

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








