【算法竞赛入门经典】树形DP的状态转移方程优化 例题9-14 UVa1218
例题UVa1218
A network is composed of N computers connected by N −1 communication links such that any two computers can be communicated via a unique route. Two computers are said to be adjacent if there is a communication link between them. The neighbors of a computer is the set of computers which are adjacent to it. In order to quickly access and retrieve large amounts of information, we need to select some computers acting as servers to provide resources to their neighbors. Note that a server can serve all its neighbors. A set of servers in the network forms a perfect service if every client (non-server) is served by exactly one server. The problem is to find a minimum number of servers which forms a perfect service, and we call this number perfect service number.
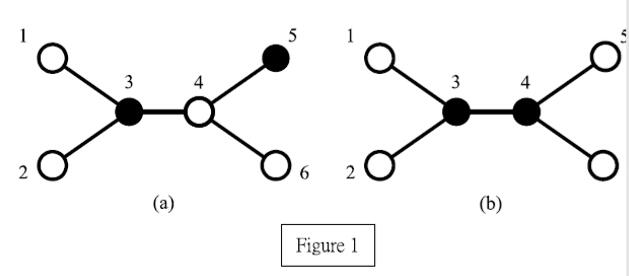
We assume that N (≤ 10000) is a positive integer and these N computers are numbered from 1 toN . For example, Figure 1 illustrates a network comprised of six computers, where black nodes represent servers and white nodes represent clients. In Figure 1(a), servers 3 and 5 do not form a perfect service because client 4 is adjacent to both servers 3 and 5 and thus it is served by two servers which contradicts the assumption. Conversely, servers 3 and 4 form a perfect service as shown in Figure 1(b). This set also has the minimum cardinality. Therefore, the perfect service number of this example equals two.
Your task is to write a program to compute the perfect service number.
Input
The input consists of a number of test cases. The format of each test case is as follows: The first line contains one positive integer, N, which represents the number of computers in the network. The next N −1 lines contain all of the communication links and one line for each link. Each line is represented by two positive integers separated by a single space. Finally, a ‘0’ at the (N + 1)-th line indicates the end of the first test case.
The next test case starts after the previous ending symbol ‘0’. A ‘-1’ indicates the end of the whole inputs
Output
The output contains one line for each test case. Each line contains a positive integer, which is the perfect service number.
Sample Input
6
1 3
2 3
3 4
4 5
4 6
0
2
1 2
-1
Sample Output
2
1
分析
鉴于本题顺序无关,而有根树操作起来较为方便,我们先建树。
【建树的过程中按顺序存储每个节点出现的顺序,这样后面操作的时候就可以从底层向上递推了】具体对比本站上一篇文章
利用d存储以u节点为根的子树最少需要多少服务器
那么可以定义如下三种状态:
d[u][0]第u个节点是服务器:这样每个子节点是不是服务器都可以
d[u][1]第u个节点不是服务器,u节点的父节点是服务器,这样每个节点必须不是服务器
d[u][2]第u个节点不是服务器,u节点的父节点不是服务器,这样u的所有节点中有且仅有一个服务器
下面开始考虑状态转移方程:
d[u][0]=sum(min(d[v][0],d[v][1]))+1
d[u][1]=sum(d[v][2]) **注意不是d[v][1],定义上不同,之后也会用到它的性质。
d[u[2]就比较复杂了,d[u][2]的组成是,枚举每一种:选出子节点v’,则加和所有非v’的d[v][2]再加上d[v][0]。这样非常的耗时间:本题的优化就在这里了:注意到所有d[v][2]的加和是d[u][1],那么d[u][1]-d[v’][2]就是所有非v’的d[v][2]和。因此d[u][2]=min(d[u][2],d[u][1]-d[v][2]+d[v][0]);
由于之前存储了节点顺序,我们便可以采用递推的方式来做。
如果要使用递归的话也可以,参照本站上一篇文章,只是会耗费更多时间,不值得。
样例实现代码
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define maxn 10000+5
#define INF 1000000000
using namespace std;
vector<int>G[maxn],vertices;
int pa[maxn],d[maxn][3];
void dfs(int u,int fa){
vertices.push_back(u);
pa[u]=fa;
for(int i=0;i<G[u].size();i++){
int v=G[u][i];
if(v!=fa)
dfs(v,u);
}
}
int main(){
int n;
while(cin>>n){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
G[i].clear();
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
u--;
v--;
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
vertices.clear();
dfs(0,-1);
for(int i=vertices.size()-1;i>=0;i--){
int u=vertices[i];
d[u][0]=1;
d[u][1]=0;
for(int j=0;j<G[u].size();j++){
int v=G[u][j];
if(v==pa[u])
continue;
d[u][0]+=min(d[v][1],d[v][0]);
d[u][1]+=d[v][2];
if(d[u][0] > INF) d[u][0] = INF; // avoid overflow!
if(d[u][1] > INF) d[u][1] = INF;
}
d[u][2]=INF;
for(int j=0;j<G[u].size();j++){
int v=G[u][j];
if(v==pa[u])
continue;
d[u][2]=min(d[u][2],d[u][1]-d[v][2]+d[v][0]);
}
}
cout<<min(d[0][0],d[0][2])<<endl;
cin>>n;
}
return 0;
} 






















 391
391

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








