###JAVA 设计模式之策略模式
1、初步认识:
定义一组算法,将每个算法都封装起来,使得它们之间可以相互替换。策略模式让算法独立于调用它的客户端而独立变化。
为了更好的理解这个模式,我们举个例子,我们出行的时候有很多种选择(自驾、高铁、大巴、飞机等),需要我们做出选择,根据我们的选择然后执行出行的方式。
传统的方式比如 if-else 语句来实现,也就时用户可以根据自己的需求选择A、选择B这样的一种情况。这种情况耦合性太高了,而且代码臃肿,有了策略模式就可以避免这种现象。
2、策略模式的结构图
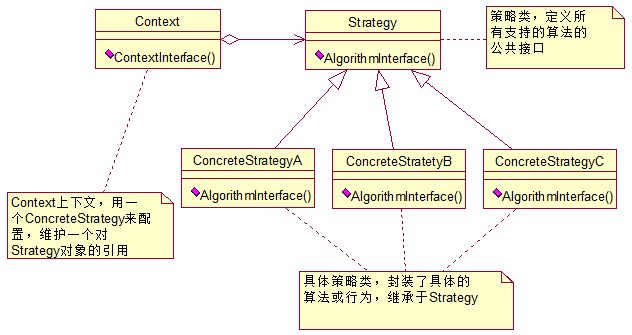
3、包含了三个角色
-
抽象策略(StrategyService):通常由接口或抽象类实现。定义了多个具体策略的公共接口,具体策略类中各种不同的算法以不同的方式实现这个接口;Context使用这些接口调用不同实现的算法。
-
具体策略(StrategyServiceImpl):实现StrategyService接口或继承于抽象类StrategyService,封装了具体的算法和行为。
-
环境类(Context):持有一个公共策略接口的引用,直接给客户端调用。
4、使用场景
说实话,对于设计模式来说,使用场景仅仅只是举一两个例子。如果你能够理解我们出去旅游的这个案例,基本上你也就能在自己遇到这种情况的时候自动的去选择它。这里就不说了。
5、策略模式的具体实现
(1) 策略对象 定义一个公共接口
public interface StrategyService {
// 具体执行的策略方法
void doHandler(Object param);
// 策略对应的类型
String getType();
}
(2) 具体的策略 实现上面的接口
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class StrategyServiceA implements StrategyService{
@Override
public void doHandler(Object param) {
System.out.println("do something...A");
}
// 该策略类型根据实际情况定义,后面传参选择对应的策略
@Override
public String getType() {
return "A";
}
}
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class StrategyServiceB implements StrategyService{
@Override
public void doHandler(Object param) {
System.out.println("do something...B");
}
// 该策略类型根据实际情况定义,后面传参选择对应的策略
@Override
public String getType() {
return "B";
}
}
(3) 环境
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public class ApplicationContextHelper implements ApplicationContextAware {
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public <T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(Class<T> clazz) {
return applicationContext.getBeansOfType(clazz);
}
}
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
@Service
public class ClientServiceImpl implements InitializingBean,ClientService{
@Autowired
private ApplicationContextHelper applicationContextHelper;
private ConcurrentHashMap<String,StrategyService> strategyServiceHandler = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 服务启动时 将所有策略实现缓存
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
Map<String, StrategyService> beans = applicationContextHelper.getBeansOfType(StrategyService.class);
for (Map.Entry<String, StrategyService> serviceEntry : beans.entrySet()) {
strategyServiceHandler.put(serviceEntry.getValue().getType(),serviceEntry.getValue());
}
}
// 根据参数选择对应的策略
// 执行实现类型
@Override
public void doHandler(Object param,String type) {
strategyServiceHandler.get(type).doHandler(param);
}
}
(4) 对外提供调用入口
public interface ClientService {
void doHandler(Object param,String type);
}
(5) 最后客户端调用策略
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/strategy")
public class StrategyController {
@Autowired
ClientService clientService;
@GetMapping("/doHandler")
public void doHandler(@RequestParam String param,@RequestParam String type){
clientService.doHandler(param,type);
}
}
输出结果为 根据 参数type=A\B 执行对应的策略
6、策略模式,小结一下:
-
重点在于:给对象传入什么样的策略,就执行什么样的动作。
-
优点在于:可以轻易的扩展与改变策略,可以动态改变对象的行为。
-
缺点在于:客户端必须知道所有的策略类,并自行决定使用哪一种。每个具体的策略都会产生一个新类,这样会造成很多策略类。
最后希望我的笔记对你有帮助






















 192
192











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








