在中大型企业开发以及国资项目中,企业为防止市面上的框架出现bug等问题,一般选择自设框架,而反射就是框架设计的灵魂。
什么是反射
一个java文件从字节码加载到jvm内存中的过程就是:源码—javac—字节码文件—JAVA命令—可执行文件。我们通过类加载器ClassLoader把字节码文件加载到内存中,加载完毕后,在jvm中以Class的形式存在。如图所示:
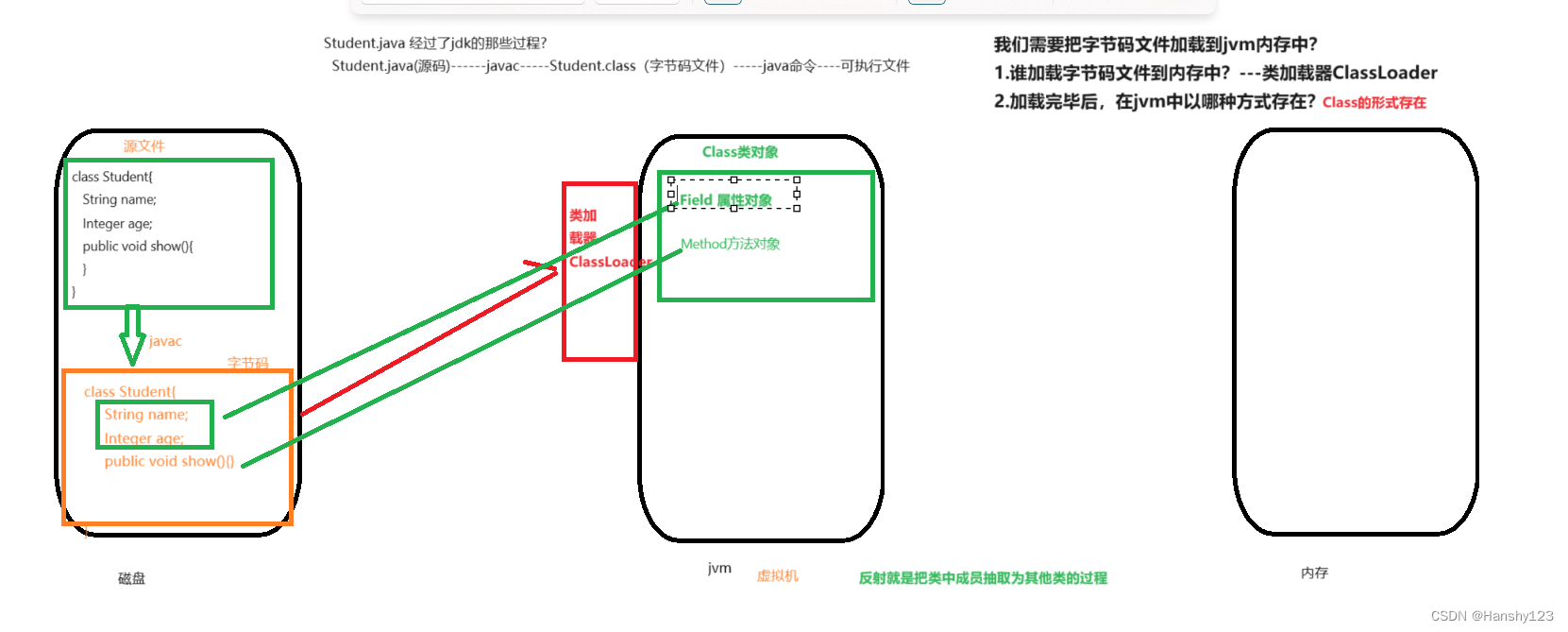
所以反射其实就是在类的运行期间,把类中的成员抽取为其他类。这个抽取的过程就是反射。
反射的意义
反射存在的意义就是为了解决在运行期间,我们对某个实例一无所知的情况下,想要来调用他的方法或者是属性。例如:我们在使用Spring框架时,只需要传入类的路径,spring框架就会帮我们创建类的对象。
获取Class反射类的方法
//第一种方法:通过类名的class属性
Class<Main> aClass = Main.class;
//第二种方法:通过类的路径
Class<?> aClass1 = Class.forName("com.aaa.Main");
//第三种方法:通过对象名获取反射类型
Main main= new Main();
Class aClass2 = main.getClass();Class类中常用的方法
1.根据反射类得到实例对象 new Instance()
2.得到反射类上的注解对象 getAnnotation()
//获取Class反射类对象
Class<Main> aClass = Main.class;
//通过反射类创建类对象
Main main= aClass.newInstance();
//获取反射类上的注解对象---反射是在运行时得到
MyAnnotation annotation = aClass.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(annotation.value());获取Method方法类对象
getDeclaredMethods(): 得到本类中所有的方法。
getDeclaredMethod("方法名",参数类型):获取本类中指定的方法对象
getMethods():获取本类以及父辈类中public修饰的方法。
getMethod("方法名",参数类型):获取本类以及父辈类中指定public修饰的方法。
Class<Main> aClass = Main.class;
//得到本类中定义的所有Method类对象
Method[] declaredMethods = aClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m :declaredMethods){
System.out.println(m);
}
//获取本类中指定的方法对象
Method fun = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("fun",Integer.class);
//获取本类以及父类中所以public方法对象
Method[] methods = aClass.getMethods();
for (Method m :methods){
System.out.println(m);
}
//获取本类以及父类中指定的public方法对象
Method method = aClass.getMethod("equals", Object.class);Method类对象中常用的方法
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//泛型通配符
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.aaa.test.People");
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
Method method = aClass.getMethod("print");
//执行该方法 返回该方法执行的结果.
//第一个参数表示执行方法的对象
Object result = method.invoke(o);
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~间隔线~~~~~~~~~~~");
Method method1 = aClass.getMethod("hehe", int.class);
Object result1 = method1.invoke(o, 25);
System.out.println(result1);
Method print02 = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("print02");
//IllegalAccessException:该异常表示 private私有方法不能被反射调用-->强力反射
print02.setAccessible(true);//设置允许访问私有成员
Object ressult2 = print02.invoke(o);
System.out.println(ressult2);
}获取Field属性对象的方式
getDeclaredFields(): 得到本类中所有的属性对象。
getDeclaredField("方法名",参数类型):获取本类中指定的属性对象
getFields():获取本类以及父辈类中public修饰的属性。
getField("方法名",参数类型):获取本类以及父辈类中指定public修饰的属性。
Class<Main> aClass = Main.class;
Main main= aClass.newInstance();
Field name = aClass.getDeclaredField("name");
System.out.println(name);Field类中的常用方法
//获取属性名
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
System.out.println(declaredField.getName());
//获取每个属性对象上的注解对象
MyAnnotation annotation = declaredField.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
String value = annotation.value();
System.out.println(value);
}





















 468
468











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








