一、JDBC概述
1.1 JDBC概述
JDBC:Java Database Connectivity,它是代表一组独立于任何数据库管理系统(DBMS)的API,声明在java.sql与javax.sql包中,是SUN(现在的Oracle)提供的一组接口规范。由各个数据库厂商来提供实现类,这些实现类的集合构成了数据库驱动jar。
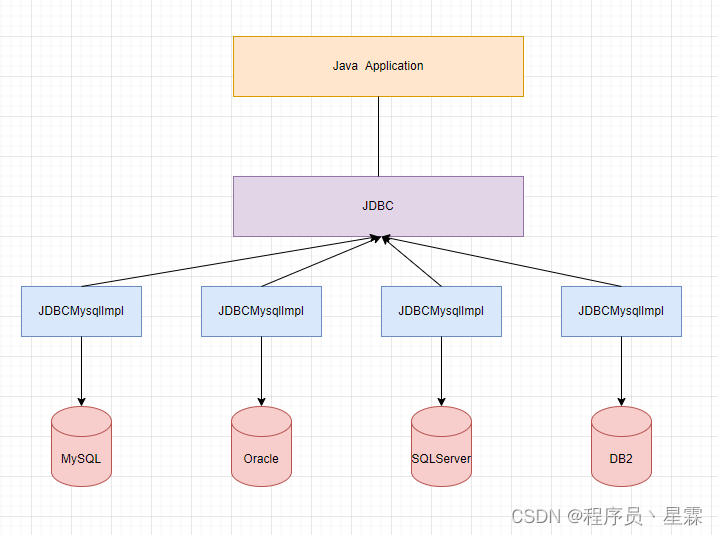
即JDBC技术包含两个部分:
(1)java.sql包和javax.sql包中的API
因为为了项目代码的可移植性,可维护性,SUN公司从最初的就制定了Java程序连接各种数据库的统一接口规范。这样的话,不管连接哪一种DBMS软件,Java代码可以保持一致性。
(2)各个数据库厂商提供的jar
因为各个数据库厂商的DBMS软件各有不同,那么内部如何通过SQL实现增、删、改、查等管理数据,只有这个数据库厂商自己清楚,因此把接口规范的实现交给各个数据库厂商自己实现。
1.2 JDBC使用步骤
1.2.1 注册驱动
// 1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
1.2.2 获取Connection连接对象
// 2. 获得连接
// jdbc:mysql://服务器的主机地址:端口号/day04?characterEncoding=utf8
// 如果数据库主机地址是localhost,并且端口号是3306,那么可以省略localhost:3306
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day04?characterEncoding=utf8";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
1.2.3 执行SQL并处理结果
// 3. 创建statement对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// 4. 使用statement对象执行SQL语句
// 增删改:调用executeUpda方法
// 查询:调用executeQuery方法
String sql = "SELECT * FROM USER";
// 执行查询数据的SQL语句,获得查询到的结果集
ResultSet rst = statement.executeQuery(sql);
// 处理结果
// 增删改:返回的是整数值,表示受到影响的数据条数
// 查询:返回ResultSet结果
// 5. 遍历啊rst,从中获取到查询
while(rst.next()){
// 每次调用next()就是将游标移动到结果集的下一行
// 获取当前行的每列数据,根据列名获取
int id = (int)rst.getObject("id");
String username = (String) rst.getObject("username");
String pwd = (String) rst.getObject("password");
String nickname = (String) rst.getObject("nickname");
System.out.println(id + ":" + username + ":" + pwd + ":" + nickname);
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------------");
}
1.2.4 释放资源
原则是后创建的资源先关闭。
// 6. 关闭资源
rst.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
二、JDBC的练习
2.1 执行添加的SQL语句
public static void testInsert()throws Exception {
// 目标:增加新用户
// 1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 获得连接
// jdbc:mysql://服务器的主机地址:端口号/day04?characterEncoding=utf8
// 如果数据库主机地址是localhost,并且端口号是3306,那么可以省略localhost:3306
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day04?characterEncoding=utf8";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// 3. 创建statement对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// 4. 使用statement对象执行SQL语句
String sql = "insert into user (username,password,nickname) values ('tq',77777,'田七')";
// 执行查询数据的SQL语句,获得收到影响的数据行数
int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(i);
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
2.2 执行删除的SQL语句
public static void testDelete() throws Exception{
// 目标:删除id为2的用户
// 1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 获得连接
// jdbc:mysql://服务器的主机地址:端口号/day04?characterEncoding=utf8
// 如果数据库主机地址是localhost,并且端口号是3306,那么可以省略localhost:3306
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day04?characterEncoding=utf8";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// 3. 创建statement对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// 4. 使用statement对象执行SQL语句
String sql = "delete from user where id = 2 ";
// 执行查询数据的SQL语句,获得收到影响的数据行数
int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(i);
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
2.3 执行修改的SQL语句
public static void testUpdate() throws Exception{
// 目标:更新id为6的用户的密码为88888888
// 1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 获得连接
// jdbc:mysql://服务器的主机地址:端口号/day04?characterEncoding=utf8
// 如果数据库主机地址是localhost,并且端口号是3306,那么可以省略localhost:3306
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day04?characterEncoding=utf8";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// 3. 创建statement对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// 4. 使用statement对象执行SQL语句
String sql = "update user set password = '88888888' where id = 6 ";
// 执行查询数据的SQL语句,获得收到影响的数据行数
int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(i);
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
2.4 执行查询单行数据的SQL语句
public static void testFindById() throws Exception{
// 目标:查询id为1的用户的信息
// 1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 获得连接
// jdbc:mysql://服务器的主机地址:端口号/day04?characterEncoding=utf8
// 如果数据库主机地址是localhost,并且端口号是3306,那么可以省略localhost:3306
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day04?characterEncoding=utf8";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// 3. 创建statement对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// 4. 使用statement对象执行SQL语句
String sql = "select * from user where id = 1";
// 执行查询数据的SQL语句,获得收到影响的数据行数
ResultSet rst = statement.executeQuery(sql);
// 遍历结果集
while(rst.next()){
// 获取当前行的每列数据
int id = rst.getInt("id");
String username = rst.getString("username");
String pwd = rst.getString("password");
String nickname = rst.getString("nickname");
System.out.println(id + ":" + username + ":" + pwd + ":" + nickname);
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------------");
// 从数据库查询数据的目的是:为了在Java代码的内存中操作查询出来的数据
// 将查询出来的一行数据作为一个整体:就将查询出来的这行数据中的各列数据存储到一个Map中或者User对象中
// Map<String,Object> userMap = new HashMap<>();
// userMap.put("id",id);
// userMap.put("username",username);
// userMap.put("password",password);
// userMap.put("nickname",nickname);
User user1 = new User(id, username, password, nickname);
System.out.println(user1);
}
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
三、使用PreparedStatement处理增删改查
3.1 Statement存在的问题
- 每次执行一个SQL语句都需要先编译
- SQL语句拼接
- SQL注入
public static void testError() throws Exception{
// 1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 获得连接
// jdbc:mysql://服务器的主机地址:端口号/day04?characterEncoding=utf8
// 如果数据库主机地址是localhost,并且端口号是3306,那么可以省略localhost:3306
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day04?characterEncoding=utf8";
String user = "root";
String pwd = "root";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd);
// 3. 创建statement对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// SQL注入:由于SQL语句中的字符串拼接,导致SQL语句的格式发生了变化而引发的问题
// 演示SQL注入的问题
String username = "hahah' or '1'='1";
String password = "";
// 根据username和password查询用户,其实就是模拟登录
String sql = "select * from user where username = '"+username+"' and password = '"+password+"'";
ResultSet rst = statement.executeQuery(sql);
// 只需要判断rst里有没有数据
if(rst.next()){
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
}
3.2 PreparedStatement解决问题
3.2.1 预编译
PreparedStatement会先对参数化的SQL语句进行预编译,执行SQL语句的时候不会再进行编译。
// 3.1 编写参数化的SQL语句,需要传入参数的地方使用?占位
String sql = "select * from user where username=? and password=?";
// 3.2 预编译SQL语句:可以确定SQL语句的结构,那么预编译之后就无法再通过SQL注入改变SQL语句的结构
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
3.2.2 避免SQL拼接
// 3. 预编译参数化的SQL语句
String username = "zs";
String password = "123456";
// 3.1 编写参数化的SQL语句,需要传入参数的地方使用?占位
String sql = "select * from user where username=? and password=?";
// 3.2 预编译SQL语句:可以确定SQL语句的结构,那么预编译之后就无法再通过SQL注入改变SQL语句的结构
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 4. 给?占位符传入对应的参数
preparedStatement.setObject(1,username);
preparedStatement.setObject(2,password);
// 5. 执行SQL语句,此时不要再传入SQL语句了,因为再预编译的时候已经传过了
ResultSet rst = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if (rst.next()){
System.out.println("登陆成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登陆失败");
}
3.2.3防止SQL注入
PreparedStatement在进行预编译的时候,就已经确定好了SQL语句的格式,不会再因为SQL语句的拼接改变SQL语句的格式。
public static void testLogin() throws Exception{
// 1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day04?characterEncoding=utf8";
String user = "root";
String pwd = "root";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd);
// 3. 预编译参数化的SQL语句
String username = "zs";
String password = "123456";
// 3.1 编写参数化的SQL语句,需要传入参数的地方使用?占位
String sql = "select * from user where username=? and password=?";
// 3.2 预编译SQL语句:可以确定SQL语句的结构,那么预编译之后就无法再通过SQL注入改变SQL语句的结构
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 4. 给?占位符传入对应的参数
preparedStatement.setObject(1,username);
preparedStatement.setObject(2,password);
// 5. 执行SQL语句,此时不要再传入SQL语句了,因为再预编译的时候已经传过了
ResultSet rst = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if (rst.next()){
System.out.println("登陆成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登陆失败");
}
rst.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
3.3 获取自增长键值
主要使用在添加完主表的一条数据之后,要获取到这条数据的主键值,然后将该值添加进从表的外键字段的场景。
3.3.1 获取自增长键值的步骤
- 在预编译的时候,指定要返回自增长的key
- 在执行完添加数据的SQL语句之后,通过PreparedStatement的对象调用getGeneratedKeys()方法来获取自增长键值,遍历结果集。
- 遍历获取自增长的键值。
public static void testObtainPrimaryKeyAfterInsert() throws Exception{
// 1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day04?characterEncoding=utf8";
String user = "root";
String pwd = "root";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd);
// 测试在添加数据之后获取主键值
String sql = "insert into user(username,password,nickname) values (?,?,?)";
// 预编译的时候,要指定,不仅要预编译,还需要获取自增长的主键值
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
// 设置SQL语句的参数
preparedStatement.setObject(1,"aobama");
preparedStatement.setObject(2,"111111");
preparedStatement.setObject(3,"圣枪游侠");
// 执行SQL语句
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(i);
// 单独获取自增长的主键值
ResultSet rst = preparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys();
// 因为主键值只有一个,可以不遍历
if (rst.next()) {
int id = rst.getInt(1);
System.out.println(id);
}
rst.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
3.4 批处理
批处理相比较单独一条条执行SQL语句来说,其效率高很多。批处理一般会使用在批量添加多条数据和批量修改多条数据。
3.4.1 批处理的具体操作步骤
- 在url中要添加一个参数rewriteBatchedStatements=true
- 在完成所有参数设置之后,调用PreparedStatement的addBatch()方法,添加到批处理中
- 最后执行PreparedStatement的executeBatch()方法执行批处理语句
// 测试批量添加
public static void testBatchedInsert() throws Exception{
// 1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day04?characterEncoding=utf8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true";
String user = "root";
String pwd = "root";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd);
// 预编译SQL语句
String sql = "insert into user (username,password,nickname) values (?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置参数
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(1,"Bob-"+i);
preparedStatement.setObject(2,"11111"+i);
preparedStatement.setObject(3,"饱不?-"+i);
// 添加到批量操作中
preparedStatement.addBatch();
}
// 执行批量操作
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
// 关闭资源
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
3.5 事务
3.5.1 事务操作的步骤
- 执行逻辑单元之前先开启事务
- 逻辑单元执行完毕,没有出现异常则提交事务
- 逻辑单元执行过程中出现异常,则回滚事务
3.5.2 事务相关API
| Connection中与事务有关的方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) | 参数是true或false,如果设置为false,表示关闭自动提交,相当于开启事务;类似SQL里面的start transaction |
| void commit() | 提交事务;类似SQL里面的commit |
| void rollback() | 回滚事务;类似SQL里面的rollback |
3.5.3 使用JDBC的事务完成转账案例
/**
* 事务相关的API:
* 1. 开启事务 connection.setAutoCommit(false);
* 2. 提交事务 connection.commit();
* 3. 回滚事务 connection.rollback();
* 4. 事务结束之后,要将此次连接的autoCommit还原成true
*/
public static void testTransaction() throws Exception{
// 测试转账
// 1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day04?characterEncoding=utf8";
String user = "root";
String pwd = "root";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd);
// 3. 预编译SQL语句
String sql = "update account set money=money+? where name=?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 开启事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
try {
// 3.1 zs扣款500
preparedStatement.setObject(1,-500);
preparedStatement.setObject(2,"zs");
// 执行zs扣款的SQL语句
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
// 异常
// int num = 10/0;
// 3.2 ls收款500
preparedStatement.setObject(1,500);
preparedStatement.setObject(2,"ls");
// 执行ls收款的SQL语句
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
// 提交事务
connection.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
connection.rollback();
}finally {
// 还原connection的AutoCommit为TRUE
connection.setAutoCommit(true);
}
// 关闭资源
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}






















 155
155











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










