在 Java 中使用单向链表及其算法进行搜索和排序的指南
与本系列教程的第 3 部分中介绍的数组一样,链表是一个基本的数据结构类别,更复杂的数据结构可以基于它。然而,与元素序列不同,链表是节点序列,其中每个节点都链接到序列中的前一个和下一个节点。回想一下,节点是从自引用类创建的对象,自引用类至少有一个字段,其引用类型是类名。链表中的节点通过节点引用链接。下面是一个例子:
class Employee
{
private int empno;
private String name;
private double salary;
public Employee next;
// Other members.
}
在这个例子中,Employee是一个自引用类,因为它的next字段类型为Employee。这个字段是链接字段的一个例子,因为它可以存储对其类的另一个对象的引用——在这种情况下是另一个Employee对象。
本教程介绍了 Java 编程中单链表的来龙去脉。您将学习创建单向链表、将节点插入单向链表、从单向链表中删除节点、将单向链表连接到另一个单向链表以及反转单向链表的操作。我们还将探索最常用于对单链表进行排序的算法,并以一个演示插入排序算法的示例结束。
什么是单链表?
甲单链表是节点的链接列表,其中每个节点具有单个链路字段。在这个数据结构中,引用变量包含对第一个(或顶部)节点的引用;每个节点(除了最后一个或底部节点)链接到下一个;并且最后一个节点的链接字段包含空引用以表示列表的结尾。尽管引用变量通常被命名为top,但您可以选择任何您想要的名称。
图 1 显示了一个具有三个节点的单向链表。
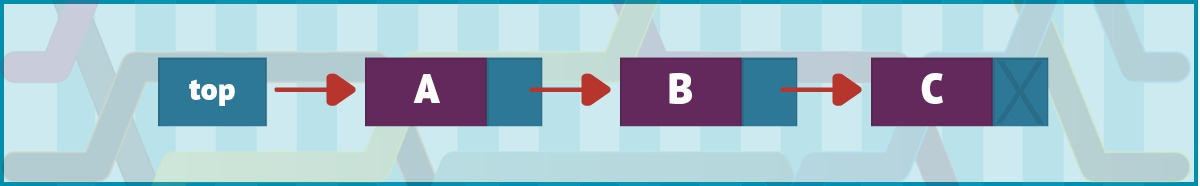
图 1. 一个单向链表,其中
top引用 A 节点,A 连接到 B,B 连接到 C,C 是最后一个节点
下面是单链表的伪代码。
DECLARE CLASS Node
DECLARE STRING name
DECLARE Node next
END DECLARE
DECLARE Node top = NULL
Node是一个具有name数据字段和next链接字段的自引用类。top是一个类型的引用变量,Node它保存对Node单链表中第一个对象的引用。由于列表尚不存在,top的初始值为NULL。
在 Java 中创建单向链表
您可以通过附加单个Node对象来创建单向链表。以下伪代码创建一个Node对象,将其引用分配给top,初始化其数据字段,并分配NULL给其链接字段:
top = NEW Node
top.name = "A"
top.next = NULL
图 2 显示了从这个伪代码中出现的初始单链表。
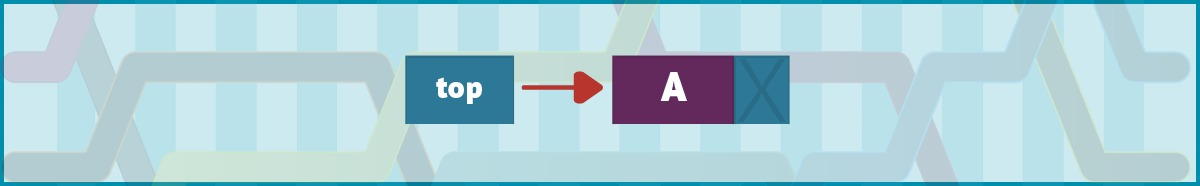
图 2. 初始单向链表由单个节点 (A) 组成
此操作的时间复杂度为 O(1)——常数。回想一下,O(1) 的发音是“Big Oh of 1”。(有关如何使用时间和空间复杂度测量来评估数据结构的提示,请参阅第 1 部分。)
将节点插入单向链表
将节点插入单向链表比创建单向链表要复杂一些,因为需要考虑三种情况:
- 在第一个节点之前插入。
- 在最后一个节点之后插入。
- 在两个节点之间插入。
在第一个节点之前插入
通过将顶部节点的引用分配给新节点的链接字段并将新节点的引用分配给top变量,在第一个节点之前插入一个新节点。此操作由以下伪代码演示:
DECLARE Node temp
temp = NEW Node
temp.name = "B"
temp.next = top
top = temp
生成的两个Node列表显示在图 3 中。
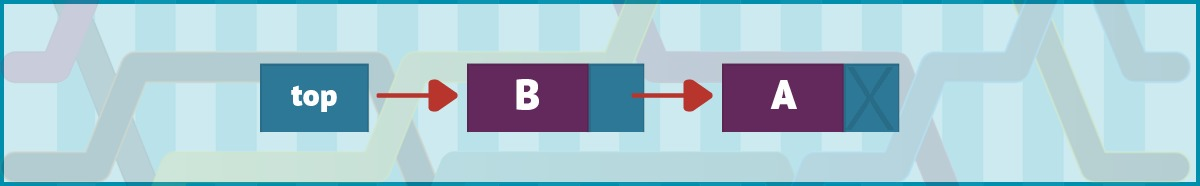
图 3. 扩展的双节点单向链表将节点 B 置于节点 A 之前
此操作的时间复杂度为 O(1)。
在最后一个节点之后插入
通过为新节点的链接字段分配空值,遍历单向链表找到最后一个节点,并将新节点的引用分配给最后一个节点的链接字段,在最后一个节点之后插入一个新节点,如以下伪代码所示:
temp = NEW Node
temp.name = "C"
temp.next = NULL
DECLARE Node temp2
temp2 = top
// We assume top (and temp2) are not NULL
// because of the previous pseudocode.
WHILE temp2.next NE NULL
temp2 = temp2.next
END WHILE
// temp2 now references the last node.
temp2.next = temp
图 4 显示了Node在NodeA之后插入C 之后的列表。
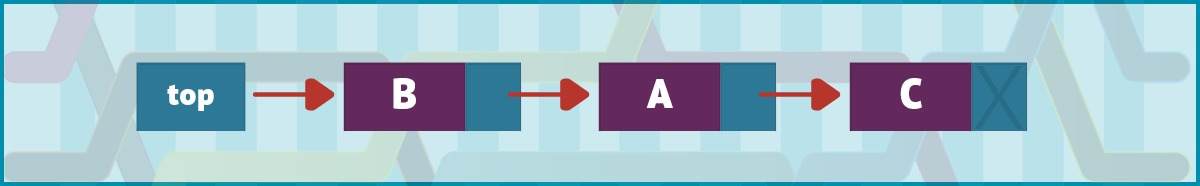
图 4. 节点 C 在扩展的三节点单向链表中排在最后
此操作的时间复杂度为 O( n )–线性。通过维护对最后一个节点的引用,它的时间复杂度可以提高到 O(1)。在这种情况下,没有必要搜索最后一个节点。
在两个节点之间插入
在两个节点之间插入一个节点是最复杂的情况。通过遍历列表找到新节点之前的节点,将找到的节点的链接字段中的引用分配给新节点的链接字段,并将新节点的引用分配给找到的节点的链接,从而在两个节点之间插入一个新节点场地。以下伪代码演示了这些任务:
temp = NEW Node
temp.name = "D"
temp2 = top
// We assume that the newly created Node inserts after Node
// A and that Node A exists. In the real world, there is no
// guarantee that any Node exists, so we would need to check
// for temp2 containing NULL in both the WHILE loop's header
// and after the WHILE loop completes.
WHILE temp2.name NE "A"
temp2 = temp2.next
END WHILE
// temp2 now references Node A.
temp.next = temp2.next
temp2.next = temp
图 5 显示了Node在Nodes A 和 C之间插入D之后的列表。

图 5. 不断增长的单向链表将节点 D 置于节点 A 和 C 之间
此操作的时间复杂度为 O( n )。
从单向链表中删除节点
从单向链表中删除节点也比创建单向链表要复杂一些。但是,只有两种情况需要考虑:
- 删除第一个节点。
- 删除除第一个节点之外的任何节点。
删除第一个节点
删除第一个节点涉及将第一个节点的链接字段中的链接分配给引用第一个节点的变量,但仅当存在第一个节点时:
IF top NE NULL THEN
top = top.next; // Reference the second Node (or NULL when there's only one Node).
END IF
图 6 显示Node了删除第一个列表之前和之后的视图。节点B消失,NodeA 成为第一个Node。

图 6. 删除第一个节点的单向链表的前后视图。红色 X 和虚线表示顶部从节点 B 到节点 A 的参考变化
此操作的时间复杂度为 O(1)。
删除除第一个节点之外的任何节点
删除除第一个节点之外的任何节点涉及定位在要删除的节点之前的节点并将要删除的节点的链接字段中的引用分配给在前节点的链接字段。考虑以下伪代码:
IF top NE NULL THEN
temp = top
WHILE temp.name NE "A"
temp = temp.next
END WHILE
// We assume that temp references Node A.
temp.next = temp.next.next
// Node D no longer exists.
END IF
图 7 显示了Node删除中间体的列表的前后视图。NodeD 消失。

图 7. 中间节点被删除的单向链表的前后视图。红色 X 和虚线表示节点 A 从节点 D 到节点 C 的链接更改
;.
此操作的时间复杂度为 O( n )。
示例 #1:在单向链表中创建、插入和删除
我创建了一个名为的 Java 应用程序SLLDemo,它演示了如何在单向链表中创建、插入和删除节点。清单 1 展示了这个应用程序的源代码。
清单 1. 单向链表的 Java 应用程序演示(SSLDemo.java,版本 1)
public final class SLLDemo
{
private static class Node
{
String name;
Node next;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node top = null;
// 1. The singly linked list does not exist.
top = new Node();
top.name = "A";
top.next = null;
dump("Case 1", top);
// 2. The singly linked list exists and the node must be inserted
// before the first node.
Node temp;
temp = new Node();
temp.name = "B";
temp.next = top;
top = temp;
dump("Case 2", top);
// 3. The singly linked list exists and the node must be inserted
// after the last node.
temp = new Node();
temp.name = "C";
temp.next = null;
Node temp2;
temp2 = top;
while (temp2.next != null)
temp2 = temp2.next;
temp2.next = temp;
dump("Case 3", top);
// 4. The singly linked list exists and the node must be inserted
// between two nodes.
temp = new Node();
temp.name = "D";
temp2 = top;
while (temp2.name.equals("A") == false)
temp2 = temp2.next;
temp.next = temp2.next;
temp2.next = temp;
dump("Case 4", top);
// 5. Delete the first node.
top = top.next;
dump("After first node deletion", top);
// 5.1 Restore node B.
temp = new Node();
temp.name = "B";
temp.next = top;
top = temp;
// 6. Delete any node but the first node.
temp = top;
while (temp.name.equals("A") == false)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = temp.next.next;
dump("After D node deletion", top);
}
private static void dump(String msg, Node topNode)
{
System.out.print(msg + " ");
while (topNode != null)
{
System.out.print(topNode.name + " ");
topNode = topNode.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
编译清单 1 如下:
javac SLLDemo.java
运行生成的应用程序,如下所示:
java SLLDemo
您应该观察到以下输出:
Case 1 A
Case 2 B A
Case 3 B A C
Case 4 B A D C
After first node deletion A D C
After D node deletion B A C
连接单向链表
您可能偶尔需要将一个单向链表连接到另一个单向链表。例如,假设您有一个以字母 A 到 M 开头的单词列表和另一个以字母 N 到 Z 开头的单词列表,并且您希望将这些列表合并为一个列表。以下伪代码描述了将一个单向链表连接到另一个单向链表的算法:
DECLARE Node top1 = NULL
DECLARE Node top2 = NULL
// Assume code that creates top1-referenced singly linked list.
// Assume code that creates top2-referenced singly linked list.
// Concatenate top2-referenced list to top1-referenced list.
IF top1 EQ NULL
top1 = top2
END
END IF
// Locate final Node in top1-referenced list.
DECLARE Node temp = top1
WHILE temp.next NE NULL
temp = temp.next
END WHILE
// Concatenate top2 to top1.
temp.next = top2
END
在一般情况下,没有top1-referenced 列表,因此top1分配了top2的值,NULL如果没有top2-referenced 列表,则会是这样。
此操作在平凡情况下的时间复杂度为 O( 1 ),否则时间复杂度为 O( n )。但是,如果您维护对最后一个节点的引用,则无需搜索此节点的列表;时间复杂度变为 O(1)。
反转单链表
单向链表上另一个有用的操作是inversion,它反转链表的链接,让您可以在相反的方向遍历其节点。以下伪代码反转top1-referenced 列表的链接:
DECLARE Node p = top1 // Top of original singly linked list.
DECLARE Node q = NULL // Top of reversed singly linked list.
DECLARE Node r // Temporary Node reference variable.
WHILE p NE NULL // For each Node in original singly linked list ...
r = q // Save future successor Node's reference.
q = p // Reference future predecessor Node.
p = p.next // Reference next Node in original singly linked list.
q.next = r // Link future predecessor Node to future successor Node.
END WHILE
top1 = q // Make top1 reference first Node in reversed singly linked list.
END
此操作的时间复杂度为 O( n )。
示例 2:连接和反转单向链表
我创建了SLLDemoJava 应用程序的第二个版本,用于演示串联和反转。清单 2 展示了这个应用程序的源代码。
清单 2. 用于在单向链表中进行串联和反转的 Java 应用程序演示(SSLDemo.java,版本 2)
public final class SLLDemo
{
private static class DictEntry
{
String word;
String meaning;
DictEntry next;
}
// ListInfo is necessary because buildList() must return two pieces
// of information.
private static class ListInfo
{
DictEntry top;
DictEntry last;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String[] wordsMaster = { "aardvark", "anxious", "asterism" };
ListInfo liMaster = new ListInfo();
buildList(liMaster, wordsMaster);
dump("Master list =", liMaster.top);
String[] wordsWorking = { "carbuncle", "catfish", "color" };
ListInfo liWorking = new ListInfo();
buildList(liWorking, wordsWorking);
dump("Working list =", liWorking.top);
// Perform the concatenation
liMaster.last.next = liWorking.top;
dump("New master list =", liMaster.top);
invert(liMaster);
dump("Inverted new master list =", liMaster.top);
}
private static void buildList(ListInfo li, String[] words)
{
if (words.length == 0)
return;
// Create a node for first word/meaning.
li.top = new DictEntry();
li.top.word = words[0];
li.top.meaning = null;
// Initialize last reference variable to
// simplify append and make concatenation possible.
li.last = li.top;
for (int i = 1; i < words.length; i++)
{
// Create (and append) a new node for next word/meaning.
li.last.next = new DictEntry();
li.last.next.word = words[i];
li.last.next.meaning = null;
// Advance last reference variable to simplify append and
// make concatenation possible.
li.last = li.last.next;
}
li.last.next = null;
}
private static void dump(String msg, DictEntry topEntry)
{
System.out.print(msg + " ");
while (topEntry != null)
{
System.out.print(topEntry.word + " ");
topEntry = topEntry.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
private static void invert(ListInfo li)
{
DictEntry p = li.top, q = null, r;
while (p != null)
{
r = q;
q = p;
p = p.next;
q.next = r;
}
li.top = q;
}
}
编译清单 2 如下:
javac SLLDemo.java
运行生成的应用程序,如下所示:
java SLLDemo
您应该观察到以下输出:
Master list = aardvark anxious asterism
Working list = carbuncle catfish color
New master list = aardvark anxious asterism carbuncle catfish color
Inverted new master list = color catfish carbuncle asterism anxious aardvark
搜索和排序算法
搜索特定数据项的单向链表是一项非常常见的编程任务。虽然线性搜索算法(在第 2 部分中介绍)最常用于此类任务,但也可以使用各种其他算法。您可能会为了追求更好的性能而调整二分搜索算法,但在这种情况下,您会感到失望。必须重复搜索列表以查找所需节点,并且性能将下降到 O( n )。更好的选择是Merge Sort,这是一种分而治之的算法,将未排序的列表划分为n子列表(每个子列表包含一个元素,一个元素的列表被视为已排序)。合并排序反复合并子列表以产生新的排序子列表,直到只剩下一个子列表:排序列表。
另一种可能性是插入排序,我们在第 2 部分中用于对数组进行排序。现在我们将使用此算法对单向链表进行排序。
示例 #3:单向链表的插入排序
插入排序将n 个数据项的单链表按升序或降序排序。它从一个最初为空的(因此简单排序)列表开始。节点一次一个地从列表中删除,然后插入到排序列表中的适当位置。如果正在排序的列表为空,则排序列表具有所需的结果。
以下伪代码在字符串的单向链表/升序排序上下文中表示插入排序:
// Exit if list is empty or contains one node.
IF top EQ NULL OR top.next EQ NULL THEN
END
END IF
// sTop is first node of sorted list.
DECLARE Node sTop = NULL
WHILE top NE NULL
DECLARE Node current = top
top = top.next
IF sTop EQ NULL OR current.name LT sTop.name THEN
// Insert into the head of the sorted list (sTop) or as the first
// element into an empty sorted list.
current.next = sTop
sTop = current
ELSE
// Insert current element into the proper position in the nonempty
// sorted list.
DECLARE Node p = sTop
WHILE p NE NULL
// p.next EQ NULL means last element of the sorted list.
// current.name LT p.next.name means middle of the sorted list.
IF p.next EQ NULL OR current.name LT p.next.name THEN
// Insert into the middle of the sorted list or as the last
// element.
current.next = p.next
p.next = current
BREAK // Finished.
END IF
p = p.next
END WHILE
END IF
END WHILE
在最坏和平均情况下,插入排序的时间复杂度为 O( n 2 )–二次。在最佳情况下,列表已排序或接近排序,其时间复杂度为 O( n )。就空间复杂度而言,插入排序需要 O(1) 额外空间(用于变量存储)。
我创建了一个InsSortJava 应用程序,可以让您试验插入排序。该应用程序的源代码如清单 3 所示。
清单 3. 一个用于试验插入排序的 Java 应用程序 (InsSort.java)
public final class InsSort
{
private static class Node
{
String name;
Node next;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node top = null;
// 1. The singly linked list does not exist.
top = new Node();
top.name = "B";
top.next = null;
// 2. The singly linked list exists and the node must be inserted
// after the last node.
Node temp = new Node();
temp.name = "D";
temp.next = null;
Node temp2 = top;
while (temp2.next != null)
temp2 = temp2.next;
temp2.next = temp;
// 3. The singly linked list exists and the node must be inserted
// after the last node.
temp = new Node();
temp.name = "C";
temp.next = null;
temp2 = top;
while (temp2.next != null)
temp2 = temp2.next;
temp2.next = temp;
// 4. The singly linked list exists and the node must be inserted
// after the last node.
temp = new Node();
temp.name = "A";
temp.next = null;
temp2 = top;
while (temp2.next != null)
temp2 = temp2.next;
temp2.next = temp;
// 5. Dump the unsorted list.
dump("Unsorted list", top);
// 6. Sort the list.
top = sort(top);
// 7. Dump the sorted list.
dump("Sorted list", top);
}
private static void dump(String msg, Node topNode)
{
System.out.print(msg + " ");
while (topNode != null)
{
System.out.print(topNode.name + " ");
topNode = topNode.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
private static Node sort(Node top)
{
if (top == null || top.next == null)
return top;
Node sTop = null;
while (top != null)
{
Node current = top;
top = top.next;
if (sTop == null || current.name.compareTo(sTop.name) < 0)
{
current.next = sTop;
sTop = current;
}
else
{
Node p = sTop;
while (p != null)
{
if (p.next == null || current.name.compareTo(p.next.name) < 0)
{
current.next = p.next;
p.next = current;
break;
}
p = p.next;
}
}
}
return sTop;
}
}
编译清单 3 如下:
javac InsSort.java
运行生成的应用程序,如下所示:
java InsSort
您应该观察到以下输出:
Unsorted list B D C A
Sorted list A B C D
总结
本教程介绍了单向链表以及在 Java 中使用它们的基本操作























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








