官网地址详解分析:
http://developer.android.com/guide/components/aidl.html
一)什么是AIDL –》 应用场景 –》 为什么用它–》什么情况下试用
个人理解: aidl应用接口编程语言 因为android系统中的不同程序都有自己的jvm,不同程序之间是不能直接访问对方memory的,为了安全,彼此解耦,一个程序崩溃不至于对其它程序的影响。 那么在android系统中的机制设置成ipc机制,不同应用程序之间通过操作系统可以识别的语言aidl来进行通信。 在多Application 和多Thread情况下使用。
官网上说的和详细:
AIDL (Android Interface Definition Language) is similar to other IDLs you might have worked with. It allows you to define the programming interface that both the client and service agree upon in order to communicate with each other using interprocess communication (IPC). On Android, one process cannot normally access the memory of another process. So to talk, they need to decompose their objects into primitives that the operating system can understand, and marshall the objects across that boundary for you. The code to do that marshalling is tedious to write, so Android handles it for you with AIDL.
Note: Using AIDL is necessary only if you allow clients from different applications to access your service for IPC and want to handle multithreading in your service. If you do not need to perform concurrent IPC across different applications, you should create your interface by implementing a Binder or, if you want to perform IPC, but do not need to handle multithreading, implement your interface using a Messenger. Regardless, be sure that you understand Bound Services before implementing an AIDL.
Before you begin designing your AIDL interface, be aware that calls to an AIDL interface are direct function calls. You should not make assumptions about the thread in which the call occurs. What happens is different depending on whether the call is from a thread in the local process or a remote process. Specifically:
Calls made from the local process are executed in the same thread that is making the call. If this is your main UI thread, that thread continues to execute in the AIDL interface. If it is another thread, that is the one that executes your code in the service. Thus, if only local threads are accessing the service, you can completely control which threads are executing in it (but if that is the case, then you shouldn’t be using AIDL at all, but should instead create the interface by implementing a Binder).
The oneway keyword modifies the behavior of remote calls. When used, a remote call does not block; it simply sends the transaction data and immediately returns. The implementation of the interface eventually receives this as a regular call from the Binder thread pool as a normal remote call. If oneway is used with a local call, there is no impact and the call is still synchronous.
二)aidl的使用
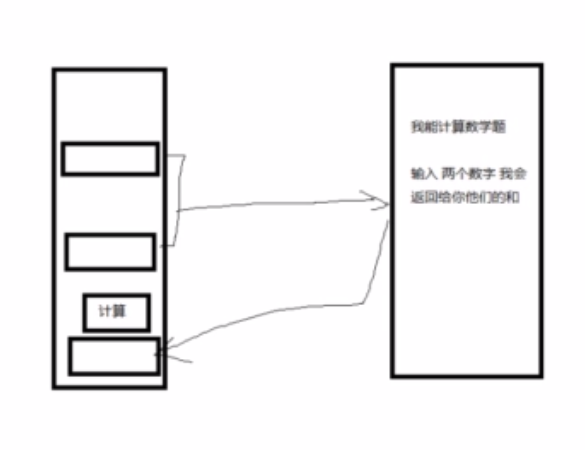
假设我们有这样的需求【其它部门有现有的库,我们拿来直接用】
service端根据client端输入的两个数,相加计算和然后返回
1)在eclipse和AndroidStudio中自动创建方式不一样,可自行度娘。
定义的aidl文件如下:

2)创建了aidl后。实现:基于服务,实现aidl的接口,返回的是binder信使,当activity绑定服务之后,即可得到实现aidl的信使,然后调用服务端的方法。
3)服务端完成以上任务后,接下来就是client需要做的事情了。aidl语言实现ipc通信,那么client和server需要使用同一套aidl规则。那么直接将服务端的aidl接口文件拿到client端就行了。
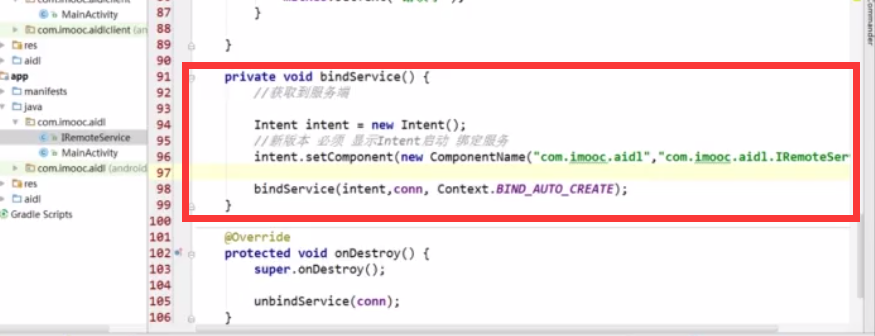
绑定服务
绑定的时候需要拿到连接的回掉:

在回掉中我们已经通过服务端的信使Binder对象,拿到了aidl的service对象,直接调用方法即可。。。
记住:在onDestory()方法中需要解绑。
支持数据类型:

不支持short类型:在自定义类型时候,实现Parcelable时候,没有writeshort方法的,在d操作系统内部也没有这个方法。
一定要区别于Binder和Messager的使用,基于操作系统的操作,耗资源耗时间,只在ipc多线程情况下使用。
























 173
173

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








