虽然我们说, 应用层协议是我们程序猿自己定的. 但实际上, 已经有大佬们定义了一些现成的, 又非常好用的应用层协议, 供我们直接参考使用. HTTP(超文本传输协议) 就是其中之一.
认识URL
统一资源定位符(Uniform Resource Locator,缩写:URL),是对资源的引用和访问该资源的方法。俗称网址。


- 主机名:表示IP地址的注册名称(域名)或IP地址,用于识别连接到网络设备的数字标识符
- 端口:跟在域名后面,不是一个URL必须的部分,如果省略端口会使用默认端口。
80是http协议的默认端口,是在输入网站的时候其实浏览器(非IE)已经帮你输入协议了,所以你输入 http://baidu.com,其实是访问 http://baidu.com:80。而8080,一般用与webcahe,完全不一样的两个,比如linux服务器里 apache默认跑80端口,而apache-tomcat默认跑 8080端口,其实端口没有实际意义只是一个接口,主要是看服务的 监听端口。
- 路径:表示服务器上资源的路径,过去这样的路径标记的是服务器上文件的物理路径,但是现在,路径表示的只是一个抽象地址,并不指代任何物理地址.
- 参数:请求里提供的额外参数.这些参数是以键值对的形式,通过
&符号分隔开来,服务器可以通过这些参数进行相应的个性化处理 - 锚:用于为页面上的标题提供快速链接,如锚点链接
urlencode和urldecode
像 / ? : 等这样的字符, 已经被url当做特殊意义理解了. 因此这些字符不能随意出现. 比如, 某个参数中需要带有这些特殊字符, 就必须先对特殊字符进行转义.
转义的规则如下: 将需要转码的字符转为16进制,然后从右到左,取4位(不足4位直接处理),每2位做一位,前面加上%,编码成%XY 格式
HTTP协议
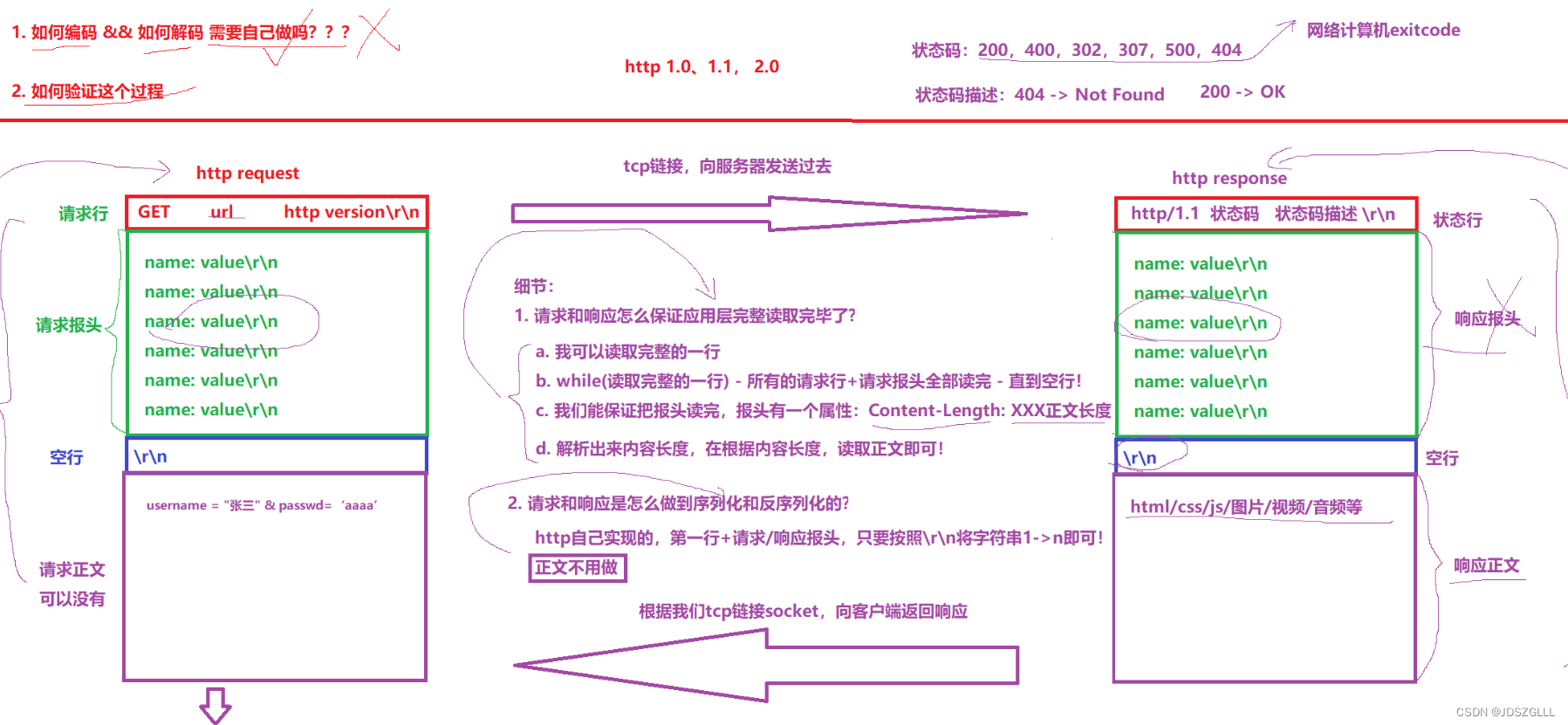
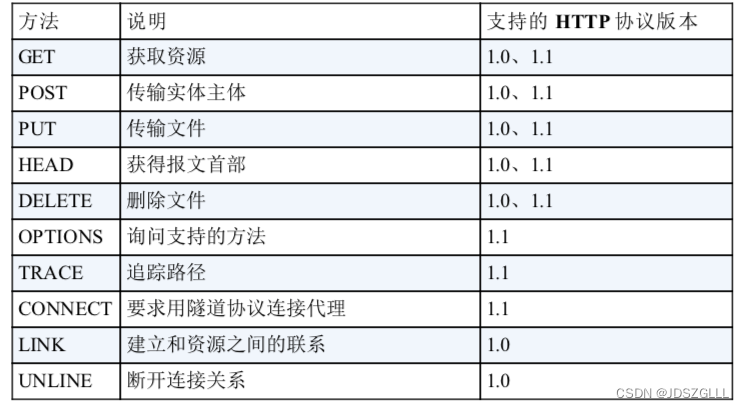
HTTP的方法

创建html文件,输入!并按tab键,可以得到一个简单的模板。
传输正文时中英文会乱码:
在html文件的头标签中加入<meta charset="UTF-8">
添加一个报头 Content-type: text/html
要获取文件信息可以使用stat接口:
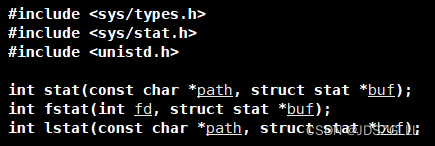
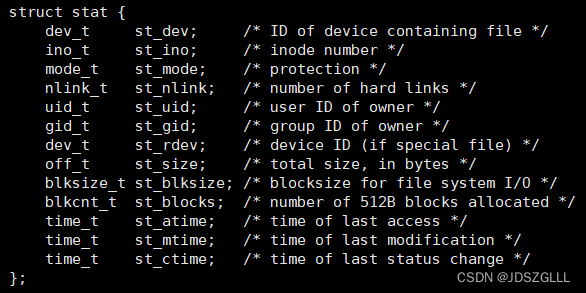
//以文件尺寸为例
struct stat st;
int n = stat(path.c_str(), &st);
if(n == 0) size = st.st_size;
else size = -1; 网页教程详情见:w3cschool官网 - 编程狮,随时随地学编程
在Linux中可以使用
wget [域名]
获取网页数据。
一个简单的网站服务器
Util.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
class Util
{
public:
// XXXX XXX XXX\r\nYYYYY
static std::string getOneLine(std::string &buffer, const std::string &sep)
{
auto pos = buffer.find(sep);
if(pos == std::string::npos) return "";
std::string sub = buffer.substr(0, pos);
buffer.erase(0, sub.size()+sep.size());
return sub;
}
static bool ReadFile(const string& name, string& body)
{
auto pos = name.find(".");
string typeofFile = name.substr(pos);
ifstream fs(name, fstream::in | fstream::binary);
char c;
while(fs.get(c))
{
body += c;
}
fs.close();
return true;
}
};Protocal.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include "Util.hpp"
const std::string sep = "\r\n";
const std::string default_root = "./wwwroot";
const std::string home_page = "index.html";
class HttpRequest
{
public:
HttpRequest(){}
~HttpRequest(){}
void parse()
{
// 1. 从inbuffer中拿到第一行,分隔符\r\n
std::string line = Util::getOneLine(inbuffer, sep);
if(line.empty()) return;
// 2. 从请求行中提取三个字段
// std::cout << "line: " << line << std::endl;
std::stringstream ss(line);
ss >> method >> url >> httpversion;
// 3. 添加web默认路径
path = default_root; // ./wwwroot,
path += url; //./wwwroot/a/b/c.html, ./wwwroot/
if(path[path.size()-1] == '/') path += home_page;
// 4. 获取path对应的资源后缀
// ./wwwroot/index.html
// ./wwwroot/test/a.html
// ./wwwroot/image/1.jpg
auto pos = path.rfind(".");
if (pos == std::string::npos)
suffix = ".html";
else
suffix = path.substr(pos);
}
public:
std::string inbuffer;
// std::string reqline;
// std::vector<std::string> reqheader;
// std::string body;
std::string method;
std::string url;
std::string httpversion;
std::string path;
std::string suffix;
};
class HttpResponse
{
public:
std::string outbuffer;
};httpServer.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <functional>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include "Protocol.hpp"
namespace server
{
enum
{
USAGE_ERR = 1,
SOCKET_ERR,
BIND_ERR,
LISTEN_ERR
};
static const uint16_t gport = 8080;
static const int gbacklog = 5;
using func_t = std::function<bool (const HttpRequest &, HttpResponse &)>;
class HttpServer
{
public:
HttpServer(func_t func, const uint16_t &port = gport) : _func(func), _listensock(-1), _port(port)
{
}
void initServer()
{
// 1. 创建socket文件套接字对象
_listensock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (_listensock < 0)
{
exit(SOCKET_ERR);
}
// 2. bind绑定自己的网络信息
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_port = htons(_port);
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
if (bind(_listensock, (struct sockaddr *)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0)
{
exit(BIND_ERR);
}
// 3. 设置socket 为监听状态
if (listen(_listensock, gbacklog) < 0) // 第二个参数backlog后面在填这个坑
{
exit(LISTEN_ERR);
}
}
void HandlerHttp(int sock)
{
// 1. 读到完整的http请求
// 2. 反序列化
// 3. httprequst, httpresponse, _func(req, resp)
// 4. resp序列化
// 5. send
char buffer[4096];
HttpRequest req;
HttpResponse resp;
size_t n = recv(sock, buffer, sizeof(buffer)-1, 0); // 大概率我们直接就能读取到完整的http请求
if(n > 0)
{
buffer[n] = 0;
req.inbuffer = buffer;
req.parse();
_func(req, resp); // req -> resp
send(sock, resp.outbuffer.c_str(), resp.outbuffer.size(), 0);
}
}
void start()
{
for (;;)
{
// 4. server 获取新链接
// sock, 和client进行通信的fd
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
int sock = accept(_listensock, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, &len);
if (sock < 0)
{
continue;
}
// version 2 多进程版(2)
pid_t id = fork();
if (id == 0) // child
{
close(_listensock);
if(fork()>0) exit(0);
HandlerHttp(sock);
close(sock);
exit(0);
}
close(sock);
// father
waitpid(id, nullptr, 0);
}
}
~HttpServer() {}
private:
int _listensock; // 不是用来进行数据通信的,它是用来监听链接到来,获取新链接的!
uint16_t _port;
func_t _func;
};
} // namespace serverhttpServer.cc
#include "httpServer.hpp"
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
using namespace server;
void Usage(std::string proc)
{
cerr << "Usage:\n\t" << proc << " port\r\n\r\n";
}
// 1. 服务器和网页分离,html
// 2. url -> / : web根目录
bool Get(const HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse &resp)
{
// for test
cout << "----------------------http start---------------------------" << endl;
std::cout << "method: " << req.method << std::endl;
std::cout << "url: " << req.url << std::endl;
std::cout << "httpversion: " << req.httpversion << std::endl;
std::cout << "path: " << req.path << std::endl;
cout << req.inbuffer << std::endl;
cout << "----------------------http end---------------------------" << endl;
std::string respline = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n";
std::string respheader = "Content-Type: ";
if (req.suffix == ".html")
respheader += "text/html";
else if (req.suffix == ".jpg")
respheader += "application/x-jpg;image/jpeg";
respheader += "\r\n";
std::string respblank = "\r\n";
std::string body;
if(!Util::ReadFile(req.path, body))
{
Util::ReadFile("./wwwroot/404.html", body);
}
resp.outbuffer += respline;
resp.outbuffer += respheader;
resp.outbuffer += respblank;
resp.outbuffer += body;
return true;
}
// ./httpServer 8080
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc != 2)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
uint16_t port = atoi(argv[1]);
unique_ptr<HttpServer> httpsvr(new HttpServer(Get, port));
httpsvr->initServer();
httpsvr->start();
return 0;
}index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>main tittle</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>每天都刷leetcode</h1>
<img src="https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fsafe-img.xhscdn.com%2Fbw1%2F83b66036-a374-424f-ab45-4a02aaf45a4f%3FimageView2%2F2%2Fw%2F1080%2Fformat%2Fjpg&refer=http%3A%2F%2Fsafe-img.xhscdn.com&app=2002&size=f9999,10000&q=a80&n=0&g=0n&fmt=auto?sec=1688195268&t=19cab953a51d9bd85e9b057dc82d7345" alt="测试图片">
<img src="/image/1.jpg" alt="本地图片">
<img src="/image/2.jpg" alt="石榴花">
<a href="/test/a.html">新闻</a>
<a href="/test/c.html">电商</a>
</body>
</html>3开头的状态——重定向
重定向流程图:
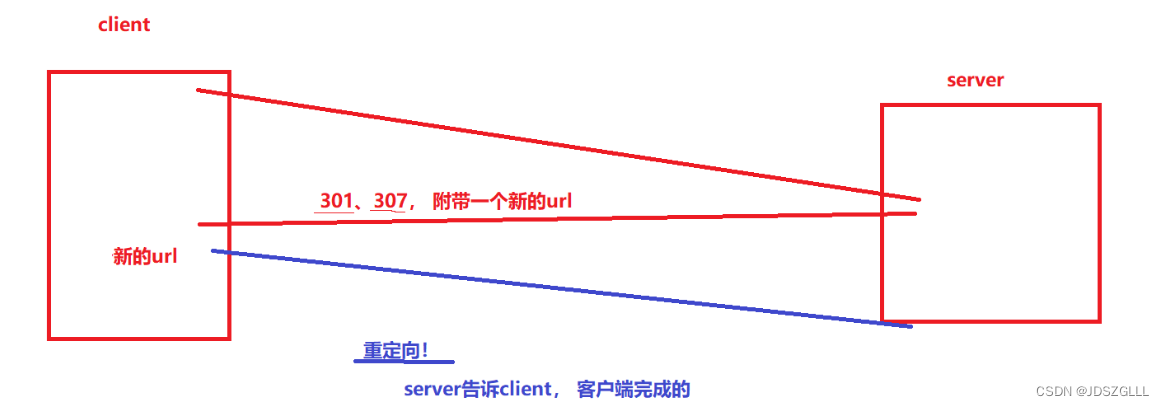
实现一个简单的临时重定向:
1.将服务器返回的状态行改为
std::string respline = "HTTP/1.1 307 Temporary Redirect\r\n";2.在响应报头中加入重定向的域名
respheader += "Location: https://www.qq.com/\r\n";
浏览器在访问我们的服务器时会自动跳转到QQ。
表单
<form action="/a/b/c.py" method="POST">
姓名:<br> <input type="text" name="xname"> <br>
密码:<br> <input type="password" name="ypwd"> <br>
<br> <input type="submit" value="登陆">
</form>

使用GET方法和POST方法的区别:

http长连接
HTTP长连接(HTTP keep-alive)是一种在单个TCP连接上可以发送多个HTTP请求和响应的机制。它的主要目的是减少建立和关闭TCP连接的开销,提高性能和效率。
在传统的HTTP协议中,每个HTTP请求都需要建立一个TCP连接,并在请求完成后关闭连接。这意味着在请求的过程中,需要进行多次TCP的三次握手和四次挥手,这些操作会带来一定的开销。而HTTP长连接通过在同一个TCP连接上发送多个HTTP请求,可以避免这些开销,从而提高网络性能。
HTTP长连接的实现方式如下:
建立连接:客户端通过发送一个HTTP请求到服务器来建立TCP连接。在请求头中包含"Connection: keep-alive"字段,告诉服务器希望使用长连接。
多个请求:在建立连接后,客户端可以通过同一个TCP连接发送多个HTTP请求。每个请求都与传统的HTTP请求相同,包括请求行、请求头和请求体。
响应:服务器接收到每个请求后,会发送对应的HTTP响应给客户端。每个响应包括响应行、响应头和响应体。
连接保持:在响应完成后,TCP连接并不关闭,而是继续保持打开状态。这样客户端可以通过这个连接发送下一个HTTP请求,而无需重新建立连接。
关闭连接:当客户端不再需要与服务器通信时,可以发送一个特殊的HTTP请求来关闭连接。在请求头中设置"Connection: close"字段,服务器收到该请求后会关闭TCP连接。
需要注意的是,尽管HTTP长连接可以在一个TCP连接上发送多个请求和响应,但服务器和客户端都需要注意适当的管理连接,以避免连接过多导致资源浪费。一般来说,服务器会根据一定的策略(如超时时间)来关闭闲置的连接,或者客户端可以在不使用连接时主动关闭连接。
HTTP长连接在减少网络延迟和提高性能方面具有显著的优势,特别是对于频繁请求的场景,例如网页浏览和API调用等。然而,需要注意的是,长时间的连接可能会占用服务器资源,因此在设计和实现时需要权衡和优化。
http会话保持
HTTP协议是无状态的,但是我们在网站上登陆,浏览器会保持登陆状态,这就是会话保持实现的。
那么服务器是如何识别用户的。
浏览器将用户信息保留,访问同一个网站时自动推送(cookie技术)

cookie文件由客户端维护,会被木马盗取。
新方法:服务端chanssession文件(包含用户信息——账号密码)和session id,浏览器保持session id发送请求时推送id。
postman和fiddler
postman和fiddler都是调试工具。
postman(模拟浏览器)查看网络信息。
Fiddler是抓包工具,相当于作为浏览器的代理,隔绝的浏览器和服务器。























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










