链表是一种常见的数据结构,由一系列节点组成。每个节点包含一个数据元素和一个指向下一个节点的指针。节点通过指针连接在一起,形成一个链式结构。
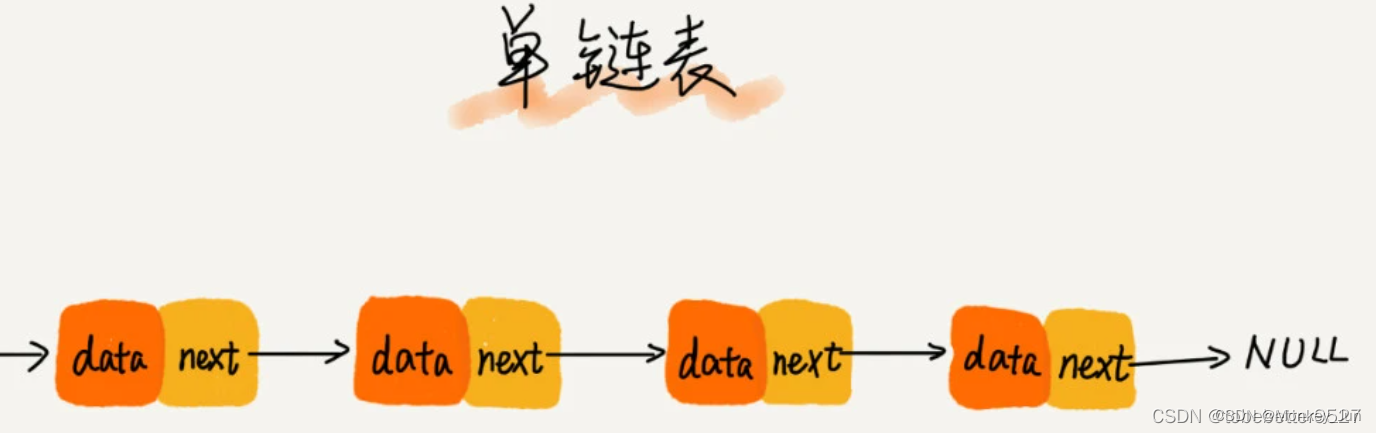
链表适合在需要频繁插入和删除节点的场景中使用,因为链表的插入和删除操作只需要修改相邻节点的指针,而不需要移动其他节点。相比之下,数组在插入和删除操作时需要移动其他元素,效率较低。
在Java中要实现链表,可以定义一个节点类,包含一个数据域和一个指针域。然后定义一个链表类,包含一个头节点指针和一些基本操作。
我们首先要定义出一个节点类
/**
* @Description: 单链表节点类
*/
public class Node<E> {
// 数据
E data;
// 指针
Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(E data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
然后定义一个单链表类
【为了方便操作我们设置了首尾节点,当然也可以不用尾节点,遍历一遍链表就找到尾节点了】
/**
* @Description: 单链表类
*/
public class LinkList<E> {
// 头结点
private Node head;
// 尾节点
private Node last;
// 链表的实际长度
private int size;
public LinkList() {
head = new Node();
last = head;
}
public Node getHead() {
return head;
}
// 判空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 打印单链表
public void display(Node head) {
Node temp = head.next;
while (temp.next != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + "-->");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println(temp.data);
}
}
接下来我们就可以用单链表来实现一些基本操作了
- 创建单链表(头插法、尾插法)
// 传入一个数组作为链表的内容 当然也可以只传入一个data数据,那直接插入就可以,不用for循环了
public void creatLinkList(E[] arr) {
// 头插法
Node p;
/*for(E i:arr){
p = new Node(i);
p.next = head.next;
head.next = p;
size++;
}*/
// 尾插法
for (E i : arr) {
p = new Node(i);
last.next = p;
last = p;
size++;
}
}
- 在指定位置插入节点
public void insertElement(int index, E data) throws Exception {
if (index > size + 1 || index < 0) {
throw new Exception("请选择合适的位置插入!");
}
Node p = new Node(data);
Node temp = head;
if (this.isEmpty()) {
head.next = p;
size++;
last = p;
return;
} else if (index == size + 1) {
last.next = p;
last = p;
size++;
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i < index && temp.next != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
p.next = temp.next;
temp.next = p;
size++;
}
- 修改指定位置节点
public void changeElement(int index, E data) throws Exception {
if (index > size || index <= 0) {
throw new Exception("请选择合适的位置修改!");
}
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i <= index && temp != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.data = data;
}
- 删除指定位置节点
public void removeElement(int index) throws Exception {
if (index > size || index <= 0) {
throw new Exception("请选择合适的位置删除!");
}
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i < index && temp != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
if (index == size) {
temp.next = null;
last = temp;
} else {
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}
}
- 根据索引找元素
public Object getElementByIndex(int index) throws Exception {
if (index > size || index <= 0) {
throw new Exception("超出范围!");
}
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i <= index && temp != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println(temp.data);
return temp.data;
}
- 根据元素找索引
public int getIndexByElement(E data) {
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 0; i <= size && temp != null; i++) {
if (data.equals(temp.data) || data == temp.data) {
System.out.println(i);
return i;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (!data.equals(temp.data) || data != temp.data) {
System.out.println("该链表不存在该元素");
}
return -1;
}
- 删除重复节点
/**
我们可以利用集合不能存放重复元素的特点,往一个集合中添加元素如果添加成功就留着,如果添加失败说明是重复元素
*/
public void deleteIdenticalElement() {
// 判断是否需要删除
if (size < 2) {
System.out.println("该链表不用进行删除重复元素操作!");
return;
}
HashSet<E> set = new HashSet<>();
Node temp = head.next;
Node h1 = head;
while (temp != null) {
if (set.contains(temp.data)) {
h1.next = temp.next;
size--;
} else{
set.add((E) temp.data);
h1 = temp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
- 将单链表置逆
// 将单链表就地置逆
public void ReverseOrder() {
Node temp = head;
Node temp1 = temp.next;
Node n;
while (temp1 != null) {
n = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
if (temp == head) {
// 把第一个节点断开
n.next = null;
} else {
// 用头插法置逆
n.next = temp;
}
temp = n;
}
head.next = temp;
}
// 将单链表置逆算法二
public void ReverseOrder2() {
Node prev = null;
Node current = head.next;
while (current != null) {
Node next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
head.next = prev;
}
- 在一个递增有序列表中,插入一个值使其依旧保持有序
public void insertKeepOrderly(E data) {
Node p = new Node(data);
if (size == 0) {
head.next = p;
size++;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
if ((Integer) temp.next.data < (Integer) data) {
temp = temp.next;
} else {
p.next = temp.next;
temp.next = p;
return;
}
}
temp.next = p;
}
- 合并两个递增有序单链表A,B到有序单链表C
public Node mergeLinkList(LinkList<Integer> list1, LinkList<Integer> list2) {
Node h1 = list1.getHead().next;
Node h2 = list2.getHead().next;
if (h1 == null) {
return h2;
}
if (h2 == null) {
return h1;
}
Node h = new Node();
Node last = h;
while (h1 != null && h2 != null) {
if ((int) h1.data <= (int) h2.data) {
last.next = h1;
last = h1;
h1 = h1.next;
} else {
last.next = h2;
last = h2;
h2 = h2.next;
}
}
if (h1 != null) {
last.next = h1;
}
if (h2 != null) {
last.next = h2;
}
return h;
}
最后附上完整的代码
/**
* @Description: 单链表类
*/
public class LinkList<E> {
// 头结点
private Node head;
// 尾节点
private Node last;
// 链表的实际长度
private int size;
public LinkList() {
head = new Node();
last = head;
}
public Node getHead() {
return head;
}
public Node getLast() {
Node temp = head.next;
while (temp != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp;
}
// 判空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 打印单链表
public void display(Node head) {
Node temp = head.next;
while (temp.next != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + "-->");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println(temp.data);
}
// 头插法,尾插法
public void creatLinkList(E[] arr) {
// 头插法
Node p;
/*for(E i:arr){
p = new Node(i);
p.next = head.next;
head.next = p;
size++;
}*/
// 尾插法
for (E i : arr) {
p = new Node(i);
last.next = p;
last = p;
size++;
}
}
// 指定位置插入元素
public void insertElement(int index, E data) throws Exception {
if (index > size + 1 || index <= 0) {
throw new Exception("超出范围!");
}
Node p = new Node(data);
Node temp = head;
if (this.isEmpty()) {
head.next = p;
size++;
last = p;
return;
} else if (index == size + 1) {
last.next = p;
last = p;
size++;
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i < index && temp.next != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
p.next = temp.next;
temp.next = p;
size++;
}
// 修改指定位置元素
public void changeElement(int index, E data) throws Exception {
if (index > size || index <= 0) {
throw new Exception("超出范围!");
}
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i <= index && temp != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.data = data;
}
// 删除指定位置元素
public void removeElement(int index) throws Exception {
if (index > size || index <= 0) {
throw new Exception("超出范围!");
}
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i < index && temp != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
if (index == size) {
temp.next = null;
last = temp;
} else {
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}
}
// 查找第i个元素
public Object getElementByIndex(int index) throws Exception {
if (index > size || index <= 0) {
throw new Exception("超出范围!");
}
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i <= index && temp != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println(temp.data);
return temp.data;
}
// 查找元素i的索引
public int getIndexByElement(E data) {
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 0; i <= size && temp != null; i++) {
if (data.equals(temp.data) || data == temp.data) {
System.out.println(i);
return i;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (!data.equals(temp.data) || data != temp.data) {
System.out.println("该链表不存在该元素");
}
return -1;
}
// 删除重复元素
/*public void deleteIdenticalElement() throws Exception {
// 判断是否需要删除
if (size < 2) {
System.out.println("该链表不用进行删除重复元素操作!");
return;
}
// 第一层遍历用来获取待判断的节点
// 第二层循环用来查找是否有相同元素,有的话直接删除
Node p1 = head.next;
Node p2;
int l = 0; //用来记录删除了几个元素
int t; //用来记录第二层遍历下标
while (p1 != null) {
p2 = p1.next;
t = 2;
while (p2 != null) {
if (p2.data.equals(p1.data)) {
this.removeElement(t - l);
l++;
}
t++;
p2 = p2.next;
}
l = 0;
t++;
p1 = p1.next;
}
}*/
public void deleteIdenticalElement() {
// 判断是否需要删除
if (size < 2) {
System.out.println("该链表不用进行删除重复元素操作!");
return;
}
HashSet<E> set = new HashSet<>();
Node temp = head.next;
Node h1 = head;
while (temp != null) {
if (set.contains(temp.data)) {
h1.next = temp.next;
size--;
} else{
set.add((E) temp.data);
h1 = temp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = head.next;
while (temp.next != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
last = temp;
System.out.println(last.data);
}
// 将单链表就地置逆
public void ReverseOrder() {
Node temp = head;
Node temp1 = temp.next;
Node n;
while (temp1 != null) {
n = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
if (temp == head) {
// 把第一个节点断开
n.next = null;
} else {
// 用头插法置逆
n.next = temp;
}
temp = n;
}
head.next = temp;
}
// 将单链表置逆算法二
public void ReverseOrder2() {
Node prev = null;
Node current = head.next;
while (current != null) {
Node next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
head.next = prev;
}
// 在一个递增有序列表中,插入一个值使其依旧保持有序
public void insertKeepOrderly(E data) {
Node p = new Node(data);
if (size == 0) {
head.next = p;
size++;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
if ((Integer) temp.next.data < (Integer) data) {
temp = temp.next;
} else {
p.next = temp.next;
temp.next = p;
return;
}
}
temp.next = p;
}
// 合并两个递增有序单链表A,B到有序单链表C
public Node mergeLinkList(LinkList<Integer> list1, LinkList<Integer> list2) {
Node h1 = list1.getHead().next;
Node h2 = list2.getHead().next;
if (h1 == null) {
return h2;
}
if (h2 == null) {
return h1;
}
Node h = new Node();
Node last = h;
while (h1 != null && h2 != null) {
if ((int) h1.data <= (int) h2.data) {
last.next = h1;
last = h1;
h1 = h1.next;
} else {
last.next = h2;
last = h2;
h2 = h2.next;
}
}
if (h1 != null) {
last.next = h1;
}
if (h2 != null) {
last.next = h2;
}
return h;
}
}





















 1031
1031











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








