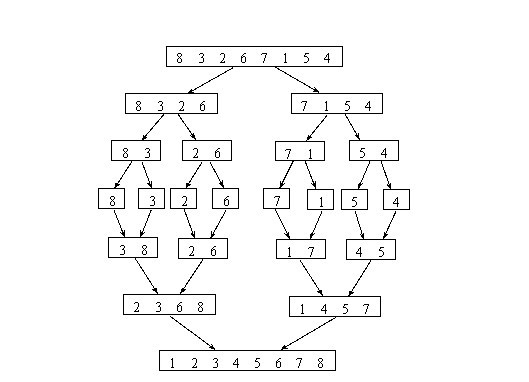
Merge sort is a recursive algorithm that continually splits a list in half. If the list is empty or has one item, it is sorted by definition (the base case). If the list has more than one item, we split the list and recursively invoke a merge sort on both halves. Once the two halves are sorted, the fundamental operation, called a merge, is performed. Merging is the process of taking two smaller sorted lists and combining them together into a single, sorted, new list.
split each element into partitions of size 1
recursively merge adjancent partitions
for i = leftPartStartIndex to rightPartLastIndex inclusive
if leftPartHeadValue <= rightPartHeadValue
copy leftPartHeadValue
else: copy rightPartHeadValue
copy elements back to original arraydef mergeSort(alist):
print("Splitting ",alist)
if len(alist)>1:
mid = len(alist)//2
lefthalf = alist[:mid]
righthalf = alist[mid:]
mergeSort(lefthalf)
mergeSort(righthalf)
#递归对半把LIST分成一个一个,直到不能分割的时候
i=0
j=0
k=0
#初始值为0
#The rest of the function (lines 11–31) is responsible for merging the two smaller sorted lists into a larger sorted list.
# Notice that the merge operation places the items back into the original list (alist) one at a time
# by repeatedly taking the smallest item from the sorted lists.
#俩个元素的比较
while i < len(lefthalf) and j < len(righthalf):
#两边的0-》长度的循环
if lefthalf[i] < righthalf[j]:# 54,26
#左右二个元素比较大小
alist[k]=lefthalf[i]#把值放入ALIST
i=i+1#向后移动
else:
alist[k]=righthalf[j]
j=j+1
k=k+1
while i < len(lefthalf):
alist[k]=lefthalf[i]
i=i+1
k=k+1
while j < len(righthalf):
alist[k]=righthalf[j]
j=j+1
k=k+1
alist = [54,26,93,17,77,31,44,55,20]
mergeSort(alist)
print(alist)
A merge sort is an O(nlogn) algorithm.
It is important to notice that the mergeSort function requires extra space to hold the two halves as they are extracted with the slicing operations. This additional space can be a critical factor if the list is large and can make this sort problematic when working on large data sets.
Q-44: Given the following list of numbers:
[21, 1, 26, 45, 29, 28, 2, 9, 16, 49, 39, 27, 43, 34, 46, 40]
which answer illustrates the list to be sorted after 3 recursive calls to mergesort?
[21,1]
Q-45: Given the following list of numbers:
[21, 1, 26, 45, 29, 28, 2, 9, 16, 49, 39, 27, 43, 34, 46, 40]
which answer illustrates the first two lists to be merged?
[21] and [1]
























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








