转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/huangxincheng/p/4970231.html
转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/stephen-liu74/archive/2012/02/14/2351859.html
转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/liuling/p/2014-4-19-04.html
转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/binyue/p/4763352.html
一、 Redis list
在Redis中,List类型是按照插入顺序排序的字符串链表。和数据结构中的普通链表一样,我们可以在其头部(left)和尾部(right)添加新的元素。在插入时,如果该键并不存在,Redis将为该键创建一个新的链表。与此相反,如果链表中所有的元素均被移除,那么该键也将会被从数据库中删除。List中可以包含的最大元素数量是4294967295。
从元素插入和删除的效率视角来看,如果我们是在链表的两头插入或删除元素,这将会是非常高效的操作,即使链表中已经存储了百万条记录,该操作也可以在常量时间内完成。然而需要说明的是,如果元素插入或删除操作是作用于链表中间,那将会是非常低效的。相信对于有良好数据结构基础的开发者而言,这一点并不难理解。
Redis List的主要操作为lpush/lpop/rpush/rpop四种,分别代表从头部和尾部的push/pop,除此之外List还提供了两种pop操作的阻塞版本blpop/brpop,用于阻塞获取一个对象。
Redis通常都被用做一个处理各种后台工作或消息任务的消息服务器。 一个简单的队列模式就是:生产者把消息放入一个列表中,等待消息的消费者用 RPOP 命令(用轮询方式), 或者用 BRPOP 命令(如果客户端使用阻塞操作会更好)来得到这个消息。
二、 Redis 生产者/消费者模式实现消息队列的简单例子
采用生产者/消费者的设计模式和阻塞操作,可以很容易得实现一个消息队列。
RedisProducer作为生产者,产生数据。
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
public class RedisProducer {
/**
* jedis操作List
*/
public static void main(String[] args){
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.10.209", 6379);
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++) {
jedis.lpush("informList","value_" + i);
}
jedis.close();
}
}RedisConsumer作为消费者消费数据。
import java.util.List;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
public class RedisConsumer {
/**
* jedis操作List
*/
public static void main(String[] args){
ScheduleMQ mq = new ScheduleMQ();
mq.start();
}
}消费者使用ScheduleMQ接收数据
class ScheduleMQ extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.10.209", 6379);
//阻塞式brpop,List中无数据时阻塞
//参数0表示一直阻塞下去,直到List出现数据
List<String> list = jedis.brpop(0, "informList");
for(String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
jedis.close();
}
}
}如上的例子只是显示了list的基本操作,在实际中往往需要更多操作才能完成正常的业务逻辑。
三、Redis消息队列的入列和出列
Redis提供了RPOPLPUSH命令,用于移除列表的最后一个元素,并将该元素添加到另一个列表并返回。
RPOPLPUSH source destination最后,还可以添加一个客户端专门用于监视备份表,它自动地将超过一定处理时限的消息重新放入队列中去(负责处理该消息的客户端可能已经崩溃),这样就不会丢失任何消息了。
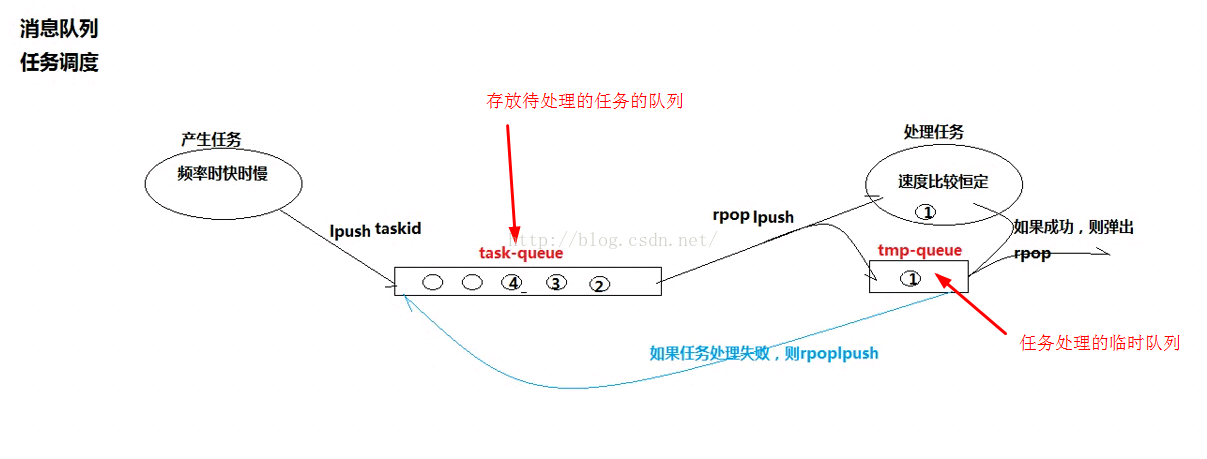
/**
*
*/
package scheduleTest;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.UUID;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
/**
* 模拟一个生产者
* <p>Title: TaskProducer</p>
* <p>Description: </p>
* <p>Company: </p>
* @author 夏 杰
* @date 2015年12月11日 下午4:26:48
* @vesion 1.0
*/
public class TaskProducer implements Runnable{
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("120.55.195.177",6379);
public void run() {
Random random = new Random();
while(true){
try{
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(600) + 600);
// 模拟生成一个任务
UUID taskid = UUID.randomUUID();
//将任务插入任务队列:task-queue
jedis.lpush("task-queue", taskid.toString());
System.out.println("插入了一个新的任务: " + taskid);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
package scheduleTest;
import java.util.Random;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
/**
* 模拟消费者
* <p>Title: TaskConsumer</p>
* <p>Description: </p>
* <p>Company: </p>
* @author 夏 杰
* @date 2015年12月11日 下午4:44:23
* @vesion 1.0
*/
public class TaskConsumer implements Runnable {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("120.55.195.177",6379);
public void run() {
Random random = new Random();
while(true){
//从任务队列"task-queue"中获取一个任务,并将该任务放入暂存队列"tmp-queue"
String taskid = jedis.rpoplpush("task-queue", "tmp-queue");
// 处理任务----纯属业务逻辑,模拟一下:睡觉
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//模拟成功和失败的偶然现象
if(random.nextInt(13) % 7 == 0){// 模拟失败的情况,概率为2/13
//将本次处理失败的任务从暂存队列"tmp-queue"中,弹回任务队列"task-queue"
jedis.rpoplpush("tmp-queue", "task-queue");
System.out.println(taskid + "处理失败,被弹回任务队列");
} else {// 模拟成功的情况
// 将本次任务从暂存队列"tmp-queue"中清除
jedis.rpop("tmp-queue");
System.out.println(taskid+"处理成功,被清除");
}
}
}
}
/**
*
*/
package scheduleTest;
/**
* <p>Title: TaskShedulerSystem</p>
* <p>Description: </p>
* <p>Company: </p>
* @author 夏 杰
* @date 2015年12月11日 下午4:19:09
* @vesion 1.0
*/
public class TaskShedulerSystem {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 启动一个生产者线程,模拟任务的产生
new Thread(new TaskProducer()).start();
Thread.sleep(15000);
//启动一个线程者线程,模拟任务的处理
new Thread(new TaskConsumer()).start();
//主线程休眠
Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
}
四、Java Serializable+Redis List实现消息队列
Redis可以对所有的内容进行二进制的存储,而java是可以对所有对象进行序列化的,因此Redis支持对序列化之后的自定义对象的存储。
自定义消息类的消息队列实现如下:
1. 封装一个消息对象
public class Message implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String titile;
private String info;
public Message(String titile,String info){
this.titile=titile;
this.info=info;
}
public String getTitile() {
return titile;
}
public void setTitile(String titile) {
this.titile = titile;
}
public String getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(String info) {
this.info = info;
}
}2. 实现序列化和反序列化方法
public class MessageUtil {
//convert To String
public static String convertToString(Object obj,String charset) throws IOException{
ByteArrayOutputStream bo = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oo = new ObjectOutputStream(bo);
oo.writeObject(obj);
String str = bo.toString(charset);
bo.close();
oo.close();
return str;
}
//convert To Message
public static Object convertToMessage(byte[] bytes) throws Exception{
ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ObjectInputStream sIn = new ObjectInputStream(in);
return sIn.readObject();
}
}
public class RedisUtil {
public static JedisPool getJedisPool(){
ResourceBundle bundle=ResourceBundle.getBundle("redis");
String host=bundle.getString("host");
int port=Integer.valueOf(bundle.getString("port"));
int timeout=Integer.valueOf(bundle.getString("timeout"));
JedisPoolConfig config=new JedisPoolConfig();
config.setMaxActive(Integer.valueOf(bundle.getString("maxActive")));
config.setMaxWait(Integer.valueOf(bundle.getString("maxWait")));
config.setTestOnBorrow(Boolean.valueOf(bundle.getString("testOnBorrow")));
config.setTestOnReturn(Boolean.valueOf(bundle.getString("testOnReturn")));
JedisPool pool=new JedisPool(config, host, port, timeout);
return pool;
}
}4. 创建Provider类
与第三章中的Provider相同,使用如下语句序列化message:
Message message = new Message(i, "这是第" + i + "个内容");
jedis.lpush(redisKey, ObjectUtil.object2Bytes(message));5. 创建Consumer类
与第三章中的Consumer相同,使用如下语句反序列化message:
byte[] bytes = JedisUtil.rpop(redisKey);
Message msg = (Message) ObjectUtil.bytes2Object(bytes);6. 测试方法
与第三章中的相同。
五、FastJson+Redis List实现消息队列
JSON是一种适宜于网络传输的字节类型数据,采用JSON作为格式存储Redis的value也是十分方便的。FastJson是由阿里提供的JSON Parser,使用其可以很方便的把对象转换成JSON。
1. 引入依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>2. 新建pojo类。
public class Student {
int age;
String name;
String address;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(int age, String name, String address) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [age=" + age + ", name=" + name + ", address="
+ address + "]";
}
}3. 使用Fastjson处理pojo类。
Student student = new Student(20, "hha", "320");
String s = JSON.toJSONString(student);
edis.set("student", s);
String get = edis.get("student");
Object object = JSON.parseObject(get, Student.class);
System.out.println("ss=" + object);如上即完成了类到JSON和JSON到类的转换,结合Redis即可达到保存自定义类的目的。
附一、 Jedis的操作示例
package com.test;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
public class TestRedis {
private Jedis jedis;
@Before
public void setup() {
//连接redis服务器,192.168.0.100:6379
jedis = new Jedis("192.168.0.100", 6379);
//权限认证
jedis.auth("admin");
}
/**
* redis存储字符串
*/
@Test
public void testString() {
//-----添加数据----------
jedis.set("name","xinxin");//向key-->name中放入了value-->xinxin
System.out.println(jedis.get("name"));//执行结果:xinxin
jedis.append("name", " is my lover"); //拼接
System.out.println(jedis.get("name"));
jedis.del("name"); //删除某个键
System.out.println(jedis.get("name"));
//设置多个键值对
jedis.mset("name","liuling","age","23","qq","476777XXX");
jedis.incr("age"); //进行加1操作
System.out.println(jedis.get("name") + "-" + jedis.get("age") + "-" + jedis.get("qq"));
}
/**
* redis操作Map
*/
@Test
public void testMap() {
//-----添加数据----------
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("name", "xinxin");
map.put("age", "22");
map.put("qq", "123456");
jedis.hmset("user",map);
//取出user中的name,执行结果:[minxr]-->注意结果是一个泛型的List
//第一个参数是存入redis中map对象的key,后面跟的是放入map中的对象的key,后面的key可以跟多个,是可变参数
List<String> rsmap = jedis.hmget("user", "name", "age", "qq");
System.out.println(rsmap);
//删除map中的某个键值
jedis.hdel("user","age");
System.out.println(jedis.hmget("user", "age")); //因为删除了,所以返回的是null
System.out.println(jedis.hlen("user")); //返回key为user的键中存放的值的个数2
System.out.println(jedis.exists("user"));//是否存在key为user的记录 返回true
System.out.println(jedis.hkeys("user"));//返回map对象中的所有key
System.out.println(jedis.hvals("user"));//返回map对象中的所有value
Iterator<String> iter=jedis.hkeys("user").iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()){
String key = iter.next();
System.out.println(key+":"+jedis.hmget("user",key));
}
}
/**
* jedis操作List
*/
@Test
public void testList(){
//开始前,先移除所有的内容
jedis.del("java framework");
System.out.println(jedis.lrange("java framework",0,-1));
//先向key java framework中存放三条数据
jedis.lpush("java framework","spring");
jedis.lpush("java framework","struts");
jedis.lpush("java framework","hibernate");
//再取出所有数据jedis.lrange是按范围取出,
// 第一个是key,第二个是起始位置,第三个是结束位置,jedis.llen获取长度 -1表示取得所有
System.out.println(jedis.lrange("java framework",0,-1));
jedis.del("java framework");
jedis.rpush("java framework","spring");
jedis.rpush("java framework","struts");
jedis.rpush("java framework","hibernate");
System.out.println(jedis.lrange("java framework",0,-1));
}
/**
* jedis操作Set
*/
@Test
public void testSet(){
//添加
jedis.sadd("user","liuling");
jedis.sadd("user","xinxin");
jedis.sadd("user","ling");
jedis.sadd("user","zhangxinxin");
jedis.sadd("user","who");
//移除noname
jedis.srem("user","who");
System.out.println(jedis.smembers("user"));//获取所有加入的value
System.out.println(jedis.sismember("user", "who"));//判断 who 是否是user集合的元素
System.out.println(jedis.srandmember("user"));
System.out.println(jedis.scard("user"));//返回集合的元素个数
}
@Test
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
//jedis 排序
//注意,此处的rpush和lpush是List的操作。是一个双向链表(但从表现来看的)
jedis.del("a");//先清除数据,再加入数据进行测试
jedis.rpush("a", "1");
jedis.lpush("a","6");
jedis.lpush("a","3");
jedis.lpush("a","9");
System.out.println(jedis.lrange("a",0,-1));// [9, 3, 6, 1]
System.out.println(jedis.sort("a")); //[1, 3, 6, 9] //输入排序后结果
System.out.println(jedis.lrange("a",0,-1));
}
@Test
public void testRedisPool() {
RedisUtil.getJedis().set("newname", "中文测试");
System.out.println(RedisUtil.getJedis().get("newname"));
}
}
附二、一个封装良好的Jedis操作类
package com.redis.util;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
public class JedisUtil {
private static String JEDIS_IP;
private static int JEDIS_PORT;
private static String JEDIS_PASSWORD;
//private static String JEDIS_SLAVE;
private static JedisPool jedisPool;
static {
Configuration conf = Configuration.getInstance();
JEDIS_IP = conf.getString("jedis.ip", "127.0.0.1");
JEDIS_PORT = conf.getInt("jedis.port", 6379);
JEDIS_PASSWORD = conf.getString("jedis.password", null);
JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig();
config.setMaxActive(5000);
config.setMaxIdle(256);//20
config.setMaxWait(5000L);
config.setTestOnBorrow(true);
config.setTestOnReturn(true);
config.setTestWhileIdle(true);
config.setMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(60000l);
config.setTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis(3000l);
config.setNumTestsPerEvictionRun(-1);
jedisPool = new JedisPool(config, JEDIS_IP, JEDIS_PORT, 60000);
}
/**
* 获取数据
* @param key
* @return
*/
public static String get(String key) {
String value = null;
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
value = jedis.get(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
return value;
}
public static void close(Jedis jedis) {
try {
jedisPool.returnResource(jedis);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (jedis.isConnected()) {
jedis.quit();
jedis.disconnect();
}
}
}
/**
* 获取数据
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public static byte[] get(byte[] key) {
byte[] value = null;
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
value = jedis.get(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
return value;
}
public static void set(byte[] key, byte[] value) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.set(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
}
public static void set(byte[] key, byte[] value, int time) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.set(key, value);
jedis.expire(key, time);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
}
public static void hset(byte[] key, byte[] field, byte[] value) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.hset(key, field, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
}
public static void hset(String key, String field, String value) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.hset(key, field, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
}
/**
* 获取数据
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public static String hget(String key, String field) {
String value = null;
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
value = jedis.hget(key, field);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
return value;
}
/**
* 获取数据
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public static byte[] hget(byte[] key, byte[] field) {
byte[] value = null;
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
value = jedis.hget(key, field);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
return value;
}
public static void hdel(byte[] key, byte[] field) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.hdel(key, field);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
}
/**
* 存储REDIS队列 顺序存储
* @param byte[] key reids键名
* @param byte[] value 键值
*/
public static void lpush(byte[] key, byte[] value) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.lpush(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
}
/**
* 存储REDIS队列 反向存储
* @param byte[] key reids键名
* @param byte[] value 键值
*/
public static void rpush(byte[] key, byte[] value) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.rpush(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
}
/**
* 将列表 source 中的最后一个元素(尾元素)弹出,并返回给客户端
* @param byte[] key reids键名
* @param byte[] value 键值
*/
public static void rpoplpush(byte[] key, byte[] destination) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.rpoplpush(key, destination);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
}
/**
* 获取队列数据
* @param byte[] key 键名
* @return
*/
public static List<byte[]> lpopList(byte[] key) {
List<byte[]> list = null;
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
list = jedis.lrange(key, 0, -1);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 获取队列数据
* @param byte[] key 键名
* @return
*/
public static byte[] rpop(byte[] key) {
byte[] bytes = null;
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
bytes = jedis.rpop(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
return bytes;
}
public static void hmset(Object key, Map<String, String> hash) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.hmset(key.toString(), hash);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
}
public static void hmset(Object key, Map<String, String> hash, int time) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.hmset(key.toString(), hash);
jedis.expire(key.toString(), time);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
}
public static List<String> hmget(Object key, String... fields) {
List<String> result = null;
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
result = jedis.hmget(key.toString(), fields);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
return result;
}
public static Set<String> hkeys(String key) {
Set<String> result = null;
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
result = jedis.hkeys(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
return result;
}
public static List<byte[]> lrange(byte[] key, int from, int to) {
List<byte[]> result = null;
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
result = jedis.lrange(key, from, to);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
return result;
}
public static Map<byte[], byte[]> hgetAll(byte[] key) {
Map<byte[], byte[]> result = null;
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
result = jedis.hgetAll(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
return result;
}
public static void del(byte[] key) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.del(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
}
public static long llen(byte[] key) {
long len = 0;
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.llen(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放redis对象
jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//返还到连接池
close(jedis);
}
return len;
}
}

























 470
470











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








