通过这片文章可以回答以下两个问题
1、为啥EventBus的事件处理方法必须申明为Public?但是我用protected也是OK的
2、粘性事件的原理,为啥发送多次Event,只有最新的event能够得到处理?
EventBus类图
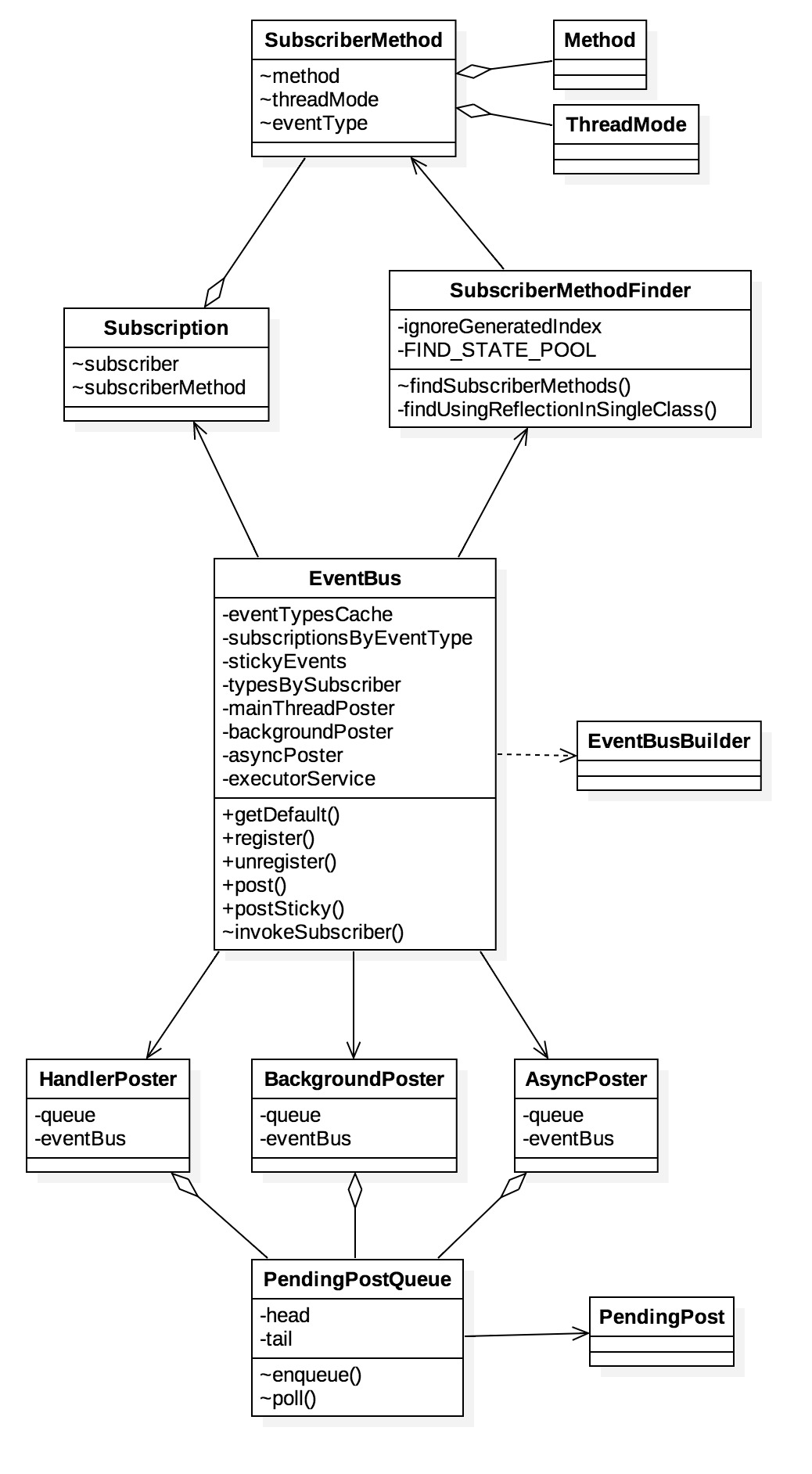
EventBus的类结构相对来说比较简单。其中最核心的类为EventBus和SubscriberMethodFInder,EventBus完成了绝大部分(注册、发布、缓存、发射调用注册者方法等)的逻辑功能,SubscriberMethodFInder则用于查找注册类的事件方法。该类图EventBus上方的类主要用于完成EventBus的注册工作,而下方的结果Poster则用于EventBus的事件发布。
EventBus流程图
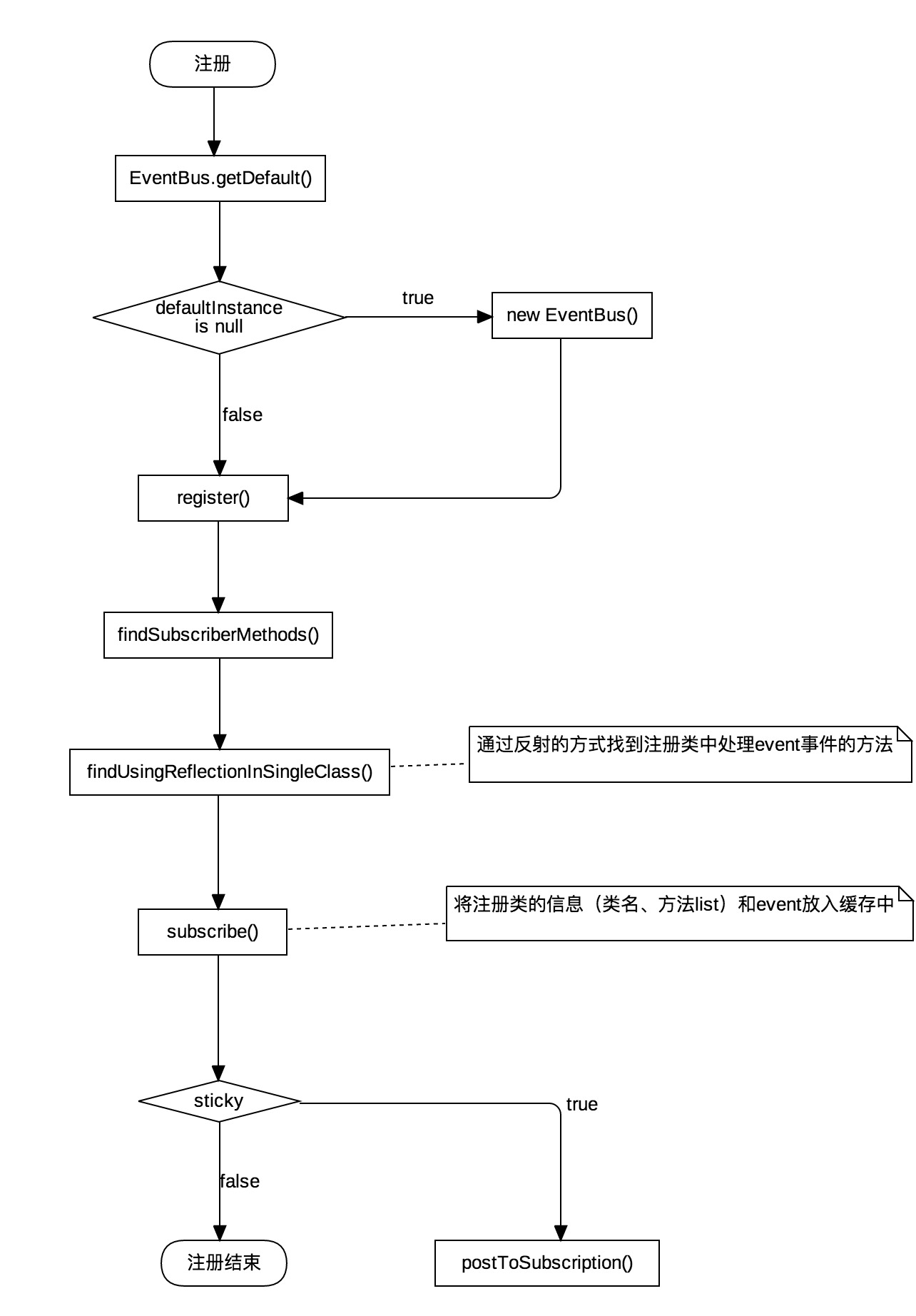
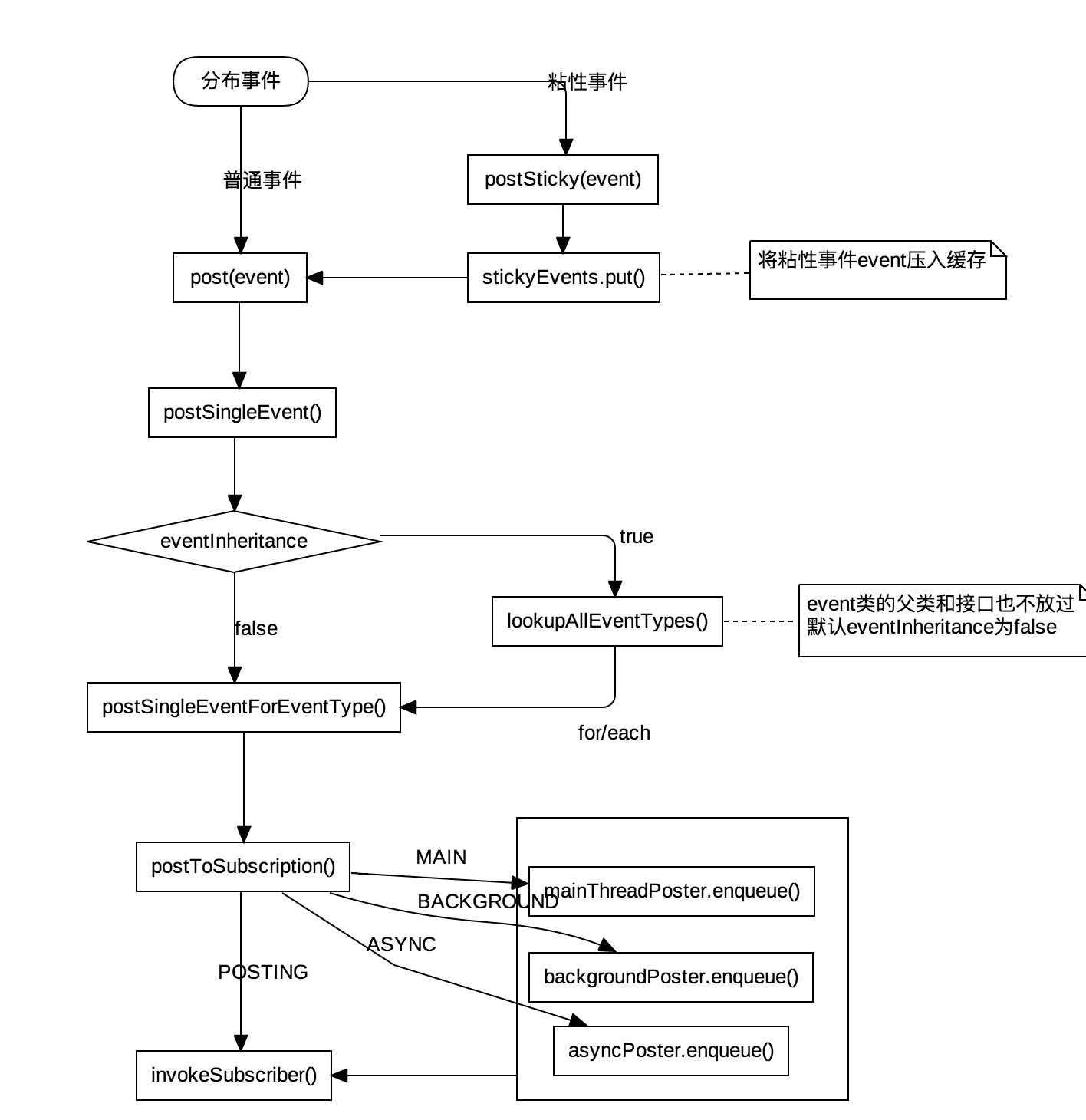
1)EventBus的注册过程中, 通过反射的方式找到注册类中所有的事件处理方法(@Subscriber标注的public方法),再将注册类的信息保存在HashMap中。如果发现注册类中的某个方法是sticky的,那么将会直接进入事件发布的流程
2)EventBus的事件发布过程中,不管采用哪一种线程模型,最重都会调用EventBus类中的invokeSubscriber()方法。如果客户端发送的是一个Sticky事件,EventBus将event事件存入到粘性事件缓存stickyEvents中,然后回到普通事件的处理流程上
源码分析
getDefault()方法,获得默认的EventBus实例
//默认情况下,采用单例模式,线程安全。
//也可以不用单例模式,EventBus的构造方法是public的,因此初始化自己的EventBus对象
public static EventBus getDefault() {
if (defaultInstance == null) {
synchronized (EventBus.class) {
if (defaultInstance == null) {
defaultInstance = new EventBus();
}
}
}
return defaultInstance;
}register()方法,订阅者注册
//subscriber就是订阅发布 模式中的订阅着,如我们的Activity
public void register(Object subscriber) {
Class<?> subscriberClass = subscriber.getClass();//获取订阅者的Class类对象
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriberClass);//获取该类中的事件方法(@subscribe标签),SubscriberMethod类包含了注册者的类、方法、sticky、线程模式等信息
synchronized (this) {
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : subscriberMethods) {
subscribe(subscriber, subscriberMethod);//缓存注册者信息
}
}
}findSubscriberMethods()方法,获得订阅者中@Subscribe标识的方法
List<SubscriberMethod> findSubscriberMethods(Class<?> subscriberClass) {
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = METHOD_CACHE.get(subscriberClass);//从缓存中找
if (subscriberMethods != null) {
return subscriberMethods;//缓存命中,直接返回
}
//ignoreGeneratedIndex默认情况为false,但都会走到findUsingReflectionInSingleClass方法中,通过反射来找到@Subscribe标识的方法
if (ignoreGeneratedIndex) {
subscriberMethods = findUsingReflection(subscriberClass);
} else {
subscriberMethods = findUsingInfo(subscriberClass);
}
if (subscriberMethods.isEmpty()) {
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriberClass
+ " and its super classes have no public methods with the @Subscribe annotation");
} else {
METHOD_CACHE.put(subscriberClass, subscriberMethods);//存到缓存中
return subscriberMethods;
}
}
//通过反射来处理,找到订阅者中@Subscribe标识的方法
private void findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(FindState findState) {
Method[] methods;
try {
// 获取注册类的所有申明方法(非继承方法),该方法的效率比getMehtods()高
methods = findState.clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
} catch (Throwable th) {
methods = findState.clazz.getMethods();
findState.skipSuperClasses = true;
}
for (Method method : methods) {
int modifiers = method.getModifiers();//方法的修饰符:public
//找到public修饰的方法,这里奇怪的是,protected的方法通过反射得到的方法修饰符也是public,这就是为什么protected修饰的方法也能使用的原因!!
if ((modifiers & Modifier.PUBLIC) != 0 && (modifiers & MODIFIERS_IGNORE) == 0) {
//找到参数个数为1的方法
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (parameterTypes.length == 1) {
//找到注解@Subscribe标识的方法
Subscribe subscribeAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(Subscribe.class);
if (subscribeAnnotation != null) {
Class<?> eventType = parameterTypes[0];//获取参数
if (findState.checkAdd(method, eventType)) {
ThreadMode threadMode = subscribeAnnotation.threadMode();//从注解获取线程模型
findState.subscriberMethods.add(new SubscriberMethod(method, eventType, threadMode,
subscribeAnnotation.priority(), subscribeAnnotation.sticky()));
}
}
} else if (strictMethodVerification && method.isAnnotationPresent(Subscribe.class)) {
String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName();
throw new EventBusException("@Subscribe method " + methodName +
"must have exactly 1 parameter but has " + parameterTypes.length);
}
} else if (strictMethodVerification && method.isAnnotationPresent(Subscribe.class)) {
String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName();
throw new EventBusException(methodName +
" is a illegal @Subscribe method: must be public, non-static, and non-abstract");
}
}
}subscribe()方法,在找到注册类的方法后,就需要对这些方法也注册,存入缓存中
private void subscribe(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) {
Class<?> eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType;//消息事件的类型
Subscription newSubscription = new Subscription(subscriber, subscriberMethod);//Subscription类封装了注册者和它的一个方法
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);//从缓存,是否已经注册过
if (subscriptions == null) {
subscriptions = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
subscriptionsByEventType.put(eventType, subscriptions);
} else {
//缓存命中,无序重新注册,抛出异常。
if (subscriptions.contains(newSubscription)) {
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriber.getClass() + " already registered to event "
+ eventType);
}
}
int size = subscriptions.size();
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
//优先级排序
if (i == size || subscriberMethod.priority > subscriptions.get(i).subscriberMethod.priority) {
subscriptions.add(i, newSubscription);
break;
}
}
//向缓存中添加subscriber所对应的Event。感觉typesBySubscriber没啥用?
List<Class<?>> subscribedEvents = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);
if (subscribedEvents == null) {
subscribedEvents = new ArrayList<>();
typesBySubscriber.put(subscriber, subscribedEvents);
}
subscribedEvents.add(eventType);
//注册粘性事件
if (subscriberMethod.sticky) {
if (eventInheritance) {
// Existing sticky events of all subclasses of eventType have to be considered.
// Note: Iterating over all events may be inefficient with lots of sticky events,
// thus data structure should be changed to allow a more efficient lookup
// (e.g. an additional map storing sub classes of super classes: Class -> List<Class>).
Set<Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object>> entries = stickyEvents.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : entries) {
Class<?> candidateEventType = entry.getKey();
if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(candidateEventType)) {
Object stickyEvent = entry.getValue();
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
} else {
Object stickyEvent = stickyEvents.get(eventType);
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);//该方法将会直接跳转到事件发布历程中执行
}
}
}post()方法,发布者发布消息事件
//currentPostingThreadState是一个ThredLocal变量,线程内部共享数据,线程间安全
private final ThreadLocal<PostingThreadState> currentPostingThreadState = new ThreadLocal<PostingThreadState>() {
@Override
protected PostingThreadState initialValue() {
return new PostingThreadState();
}
};
//发布event粘性事件
public void postSticky(Object event) {
synchronized (stickyEvents) {
//stickyEvents是ConcurrentHashMap,每次往map中put键值对,会覆盖具有相同event.getClass()的值,因此导致即使发布多次粘性事件,也只会处理最新的那一个
//换句话即:同一个event类,在缓存中只会保存一个粘性事件!
stickyEvents.put(event.getClass(), event);
}
post(event);
}
//发布event事件
public void post(Object event) {
PostingThreadState postingState = currentPostingThreadState.get();
List<Object> eventQueue = postingState.eventQueue;
eventQueue.add(event);//向队列中添加event事件
if (!postingState.isPosting) {
postingState.isMainThread = Looper.getMainLooper() == Looper.myLooper();//发布时间的线程是否是主线程
postingState.isPosting = true;
if (postingState.canceled) {
throw new EventBusException("Internal error. Abort state was not reset");
}
try {
//每次发送一个event事件,直到对列为空为止。
while (!eventQueue.isEmpty()) {
postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0), postingState);
}
} finally {
postingState.isPosting = false;
postingState.isMainThread = false;
}
}
}
private void postSingleEvent(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState) throws Error {
Class<?> eventClass = event.getClass();
boolean subscriptionFound = false;
if (eventInheritance) {
List<Class<?>> eventTypes = lookupAllEventTypes(eventClass);//event的父类和接口都不放过
int countTypes = eventTypes.size();
for (int h = 0; h < countTypes; h++) {
Class<?> clazz = eventTypes.get(h);
subscriptionFound |= postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, clazz);
}
} else {
subscriptionFound = postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, eventClass);
}
if (!subscriptionFound) {
if (logNoSubscriberMessages) {
Log.d(TAG, "No subscribers registered for event " + eventClass);
}
if (sendNoSubscriberEvent && eventClass != NoSubscriberEvent.class &&
eventClass != SubscriberExceptionEvent.class) {
post(new NoSubscriberEvent(this, event));
}
}
}
private boolean postSingleEventForEventType(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState, Class<?> eventClass) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions;
synchronized (this) {
subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventClass);//更具event的类名,从缓存中找到能够接收该event事件的订阅者
}
//遍历所有的订阅者
if (subscriptions != null && !subscriptions.isEmpty()) {
for (Subscription subscription : subscriptions) {
postingState.event = event;
postingState.subscription = subscription;
boolean aborted = false;
try {
postToSubscription(subscription, event, postingState.isMainThread);//到这里才正儿八经开始处理event
aborted = postingState.canceled;
} finally {
postingState.event = null;
postingState.subscription = null;
postingState.canceled = false;
}
if (aborted) {
break;
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
//处理事件,将event分发给各个对应线程
private void postToSubscription(Subscription subscription, Object event, boolean isMainThread) {
switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode) {
case POSTING:
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);//当前线程处理
break;
case MAIN:
if (isMainThread) {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);//当前线程处理
} else {
mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);//主线程处理
}
break;
case BACKGROUND:
if (isMainThread) {
backgroundPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);//如果当前线程是主线程,在子线程处理
} else {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);//如果当前线程是一个子线程,则当前线程处理
}
break;
case ASYNC:
asyncPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);//每次都新建一个线程进行处理
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode);
}
}AsyncPoster类,实现了Runnable接口
class AsyncPoster implements Runnable {
private final PendingPostQueue queue;
private final EventBus eventBus;
AsyncPoster(EventBus eventBus) {
this.eventBus = eventBus;
queue = new PendingPostQueue();
}
public void enqueue(Subscription subscription, Object event) {
PendingPost pendingPost = PendingPost.obtainPendingPost(subscription, event);
queue.enqueue(pendingPost);//加入队列中
eventBus.getExecutorService().execute(this);//调用线程池执行,并发执行
}
@Override
public void run() {
PendingPost pendingPost = queue.poll();
if(pendingPost == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No pending post available");
}
eventBus.invokeSubscriber(pendingPost);//调用EventBus的反射方法
}
}BackgroundPoster类,虽然也实现了Runnable接口,虽然也在子线程中执行EventBus的反射回调方法。但是与AsyncPoster类不同的是:
1)AsyncPoster类每次任务都会新建一个线程,并发执行队列中的任务
2)而BackgroundPoster类只会新建一个子线程,队列中的任务,只会顺序执行。
final class BackgroundPoster implements Runnable {
private final PendingPostQueue queue;
private final EventBus eventBus;
private volatile boolean executorRunning;
BackgroundPoster(EventBus eventBus) {
this.eventBus = eventBus;
queue = new PendingPostQueue();
}
public void enqueue(Subscription subscription, Object event) {
PendingPost pendingPost = PendingPost.obtainPendingPost(subscription, event);
synchronized (this) {
queue.enqueue(pendingPost);
if (!executorRunning) {
executorRunning = true;
eventBus.getExecutorService().execute(this);
}
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
try {
while (true) {
PendingPost pendingPost = queue.poll(1000);
if (pendingPost == null) {
synchronized (this) {
// Check again, this time in synchronized
pendingPost = queue.poll();
if (pendingPost == null) {
executorRunning = false;
return;
}
}
}
eventBus.invokeSubscriber(pendingPost);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Log.w("Event", Thread.currentThread().getName() + " was interruppted", e);
}
} finally {
executorRunning = false;
}
}
}mainThreadPoster是HandlerPoster变量,他继承Handler,不难猜出,他通过Handler+Looper机制,来实现主线程调用
mainThreadPoster = new HandlerPoster(this, Looper.getMainLooper(), 10);//绑定主线程的Looper
final class HandlerPoster extends Handler {
private final PendingPostQueue queue;
private final int maxMillisInsideHandleMessage;
private final EventBus eventBus;
private boolean handlerActive;
HandlerPoster(EventBus eventBus, Looper looper, int maxMillisInsideHandleMessage) {
super(looper);//绑定主线程的Looper
this.eventBus = eventBus;
this.maxMillisInsideHandleMessage = maxMillisInsideHandleMessage;
queue = new PendingPostQueue();
}
void enqueue(Subscription subscription, Object event) {
PendingPost pendingPost = PendingPost.obtainPendingPost(subscription, event);
synchronized (this) {
queue.enqueue(pendingPost);
if (!handlerActive) {
handlerActive = true;
if (!sendMessage(obtainMessage())) {
throw new EventBusException("Could not send handler message");
}
}
}
}
//处理event事件,调用EventBus的invokeSubscriber反射回调
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
boolean rescheduled = false;
try {
long started = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
while (true) {
PendingPost pendingPost = queue.poll();
if (pendingPost == null) {
synchronized (this) {
// 双重判0,线程安全
pendingPost = queue.poll();
if (pendingPost == null) {
handlerActive = false;
return;
}
}
}
eventBus.invokeSubscriber(pendingPost);//调用EventBus的反射方法
long timeInMethod = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - started;
if (timeInMethod >= maxMillisInsideHandleMessage) {
if (!sendMessage(obtainMessage())) {
throw new EventBusException("Could not send handler message");
}
rescheduled = true;
return;
}
}
} finally {
handlerActive = rescheduled;
}
}
}







 本文深入解析了EventBus的工作原理,包括其核心组件的功能、事件处理流程及粘性事件的机制。详细介绍了EventBus如何通过反射查找事件处理方法,并探讨了不同线程模式下事件的分发策略。
本文深入解析了EventBus的工作原理,包括其核心组件的功能、事件处理流程及粘性事件的机制。详细介绍了EventBus如何通过反射查找事件处理方法,并探讨了不同线程模式下事件的分发策略。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








