使用Spring事务管理
现在我们来学习一下Spring提供的事务管理(Spring事务管理分为编程式事务和声明式事务,但是编程式事务过于复杂并且具有高度耦合性,违背了Spring框架的设计初衷,因此这里只讲解声明式事务)声明式事务是基于AOP实现的。
使用声明式事务非常简单,我们只需要在配置类添加@EnableTransactionManagement注解即可,这样就可以开启Spring的事务支持了。接着,我们只需要把一个事务要做的所有事情封装到Service层的一个方法中即可,首先需要在配置文件中注册一个新的Bean,事务需要执行必须有一个事务管理器:
@Bean
public TransactionManager transactionManager(@Autowired DataSource dataSource){
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}接着编写Mapper操作:
@Mapper
public interface TestMapper {
@Insert("insert into student(name, sex) values('测试', '男')")
void insertStudent();
}这样会向数据库中插入一条新的学生信息,接着,假设我们这里有一个业务需要连续插入两条学生信息,首先编写业务层的接口:
public interface TestService {
void test();
}接着,我们再来编写业务层的实现,我们可以直接将其注册为Bean,交给Spring来进行管理,这样就可以自动将Mapper注入到类中了,并且可以支持事务:
@Component
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService{
@Resource
TestMapper mapper;
@Transactional
@Override
public void test() {
mapper.insertStudent();
if(true) throw new RuntimeException("我是测试异常!");
mapper.insertStudent();
}
}我们只需在方法上添加@Transactional注解,即可表示此方法执行的是一个事务操作,在调用此方法时,Spring会通过AOP机制为其进行增强,一旦发现异常,事务会自动回滚。最后我们来调用一下此方法:
@Slf4j
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("项目正在启动...");
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class);
TestService service = context.getBean(TestService.class);
service.test();
}
}得到的结果是出现错误:
十二月 08, 2021 3:09:29 下午 com.test.Main main
信息: 项目正在启动...
十二月 08, 2021 3:09:29 下午 com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource getConnection
信息: HikariPool-1 - Starting...
十二月 08, 2021 3:09:29 下午 com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource getConnection
信息: HikariPool-1 - Start completed.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: 我是测试异常!
at com.test.service.TestServiceImpl.test(TestServiceImpl.java:22)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(AopUtils.java:344)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.invokeJoinpoint(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:198)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:163)
at org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor$1.proceedWithInvocation(TransactionInterceptor.java:123)
at org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(TransactionAspectSupport.java:388)
at org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor.invoke(TransactionInterceptor.java:119)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:186)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke(JdkDynamicAopProxy.java:215)
at com.sun.proxy.$Proxy30.test(Unknown Source)
at com.test.Main.main(Main.java:17)我们发现,整个栈追踪信息中包含了大量aop包下的相关内容,也就印证了,它确实是通过AOP实现的,那么我们接着来看一下,数据库中的数据是否没有发生变化(出现异常回滚了)
结果显而易见,确实被回滚了,数据库中没有任何的内容。
我们接着来研究一下@Transactional注解的一些参数:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Transactional {
@AliasFor("transactionManager")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String transactionManager() default "";
String[] label() default {};
Propagation propagation() default Propagation.REQUIRED;
Isolation isolation() default Isolation.DEFAULT;
int timeout() default -1;
String timeoutString() default "";
boolean readOnly() default false;
Class<? extends Throwable>[] rollbackFor() default {};
String[] rollbackForClassName() default {};
Class<? extends Throwable>[] noRollbackFor() default {};
String[] noRollbackForClassName() default {};
}我们来讲解几个比较关键的信息:
- transactionManager:指定事务管理器
- propagation:事务传播规则,一个事务可以包括N个子事务
- isolation:事务隔离级别,不多说了
- timeout:事务超时时间
- readOnly:是否为只读事务,不同的数据库会根据只读属性进行优化,比如MySQL一旦声明事务为只读,那么久不允许增删改操作了。
- rollbackFor和noRollbackFor:发生指定异常时回滚或是不回滚,默认发生任何异常都回滚
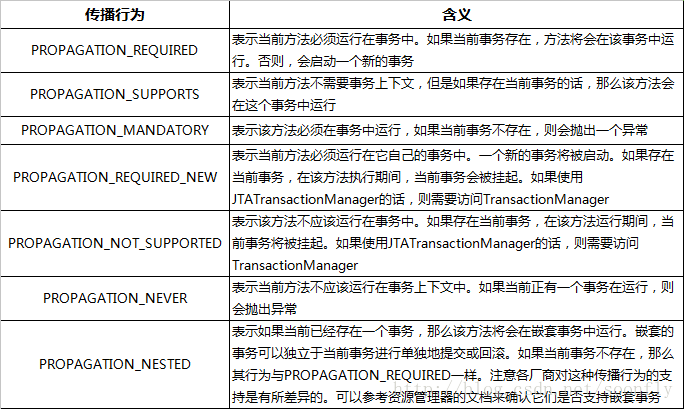
除了事务的传播规则,其他的内容其实已经给大家讲解过了,那么我们就来看看事务的传播。事务传播一共有七种级别:
Spring默认的传播级别是PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,那么我们来看看,它是如何传播的,现在我们的Service类中一共存在两个事务,而一个事务方法包含了另一个事务方法:
@Transactional
public void test() {
test2();
if(true) throw new RuntimeException("我是测试异常!"); //发生异常时,会回滚另一个事务吗?
}
@Transactional
public void test2() {
mapper.insertStudent();
}最后我们得到结果,另一个事务被回滚了,也就是说,相当于另一个事务直接加入到此事务中了,也就是表中所描述的那样。
如果单独执行test2()则会开启一个新的事务,而执行test()则会直接让内部的test2()加入到当前事务中。
@Transactional
public void test() {
test2();
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS)
public void test2() {
mapper.insertStudent();
if(true) throw new RuntimeException("我是测试异常!");
}现在我们将test2()的传播级别设定为SUPPORTS,那么这时如果单独调用test2()方法,并不会以事务的方式执行,当发生异常时,虽然依然存在AOP增强,但是不会进行回滚操作,而现在再调用test()方法,才会以事务的方式执行。
我们接着来看MANDATORY,它非常严格,如果当前方法并没有在任何事务中进行,会直接出现异常:
@Transactional
public void test() {
test2();
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.MANDATORY)
public void test2() {
mapper.insertStudent();
if(true) throw new RuntimeException("我是测试异常!");
}直接运行test2()方法,报错如下:
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.transaction.IllegalTransactionStateException: No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'
at org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.getTransaction(AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.java:362)
at org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport.createTransactionIfNecessary(TransactionAspectSupport.java:595)
at org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(TransactionAspectSupport.java:382)
at org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor.invoke(TransactionInterceptor.java:119)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:186)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke(JdkDynamicAopProxy.java:215)
at com.sun.proxy.$Proxy29.test2(Unknown Source)
at com.test.Main.main(Main.java:17)NESTED级别表示如果存在外层事务,则此方法单独创建一个子事务,回滚只会影响到此子事务,实际上就是利用创建Savepoint,然后回滚到此保存点实现的。NEVER级别表示此方法不应该加入到任何事务中,其余类型适用于同时操作多数据源情况下的分布式事务管理,这里暂时不做介绍。
至此,有关Spring的核心内容就讲解完毕了。





















 548
548











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








