Spring通过配置文件描述了Bean和Bean之间的依赖关系,通过java反射实例化bean并建立彼此的依赖关系。除此之外还提供了Bean实例的缓存,生命周期的管理,bean实例代理,时间发布,资源装载等
1 BeanFactory
1.1 简介
属于Spring的核心接口,提供了高级IOC的配置机制,BeanFactory是框架的基本设施,面向spring本身,BeanFactory在启动容器时,并不会初始化配置文件中定义的Bean,初始化发生在第一次调用,对于单例的Bean,BeanFactory会缓存在Bean实例,所以在第二次使用时,直接从缓存中获取Bean实例
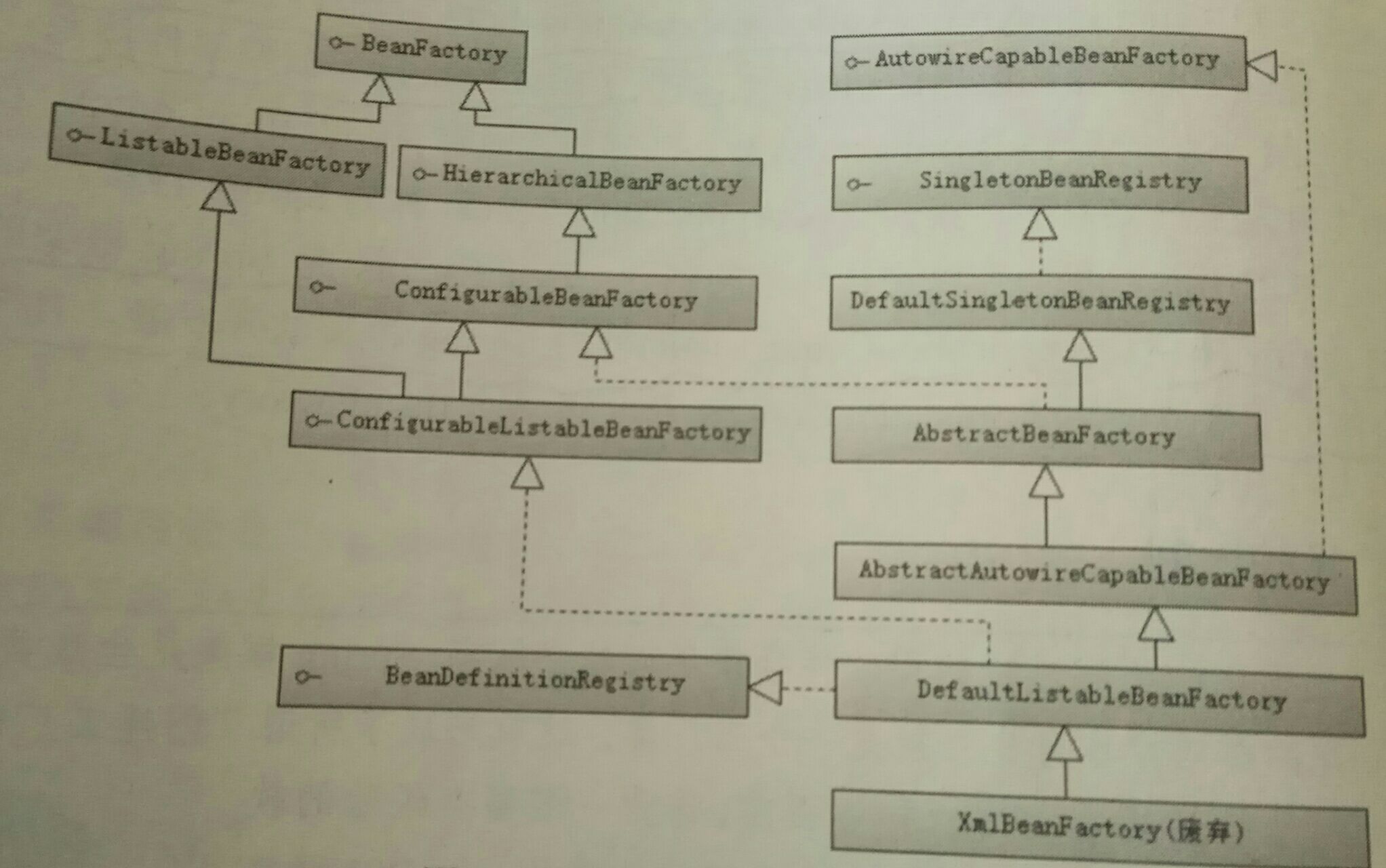
1.2 BeanFactory继承体系
1.3 类简介
1.3.1 BeanFactory
需要管理Bean的生命周期,初始化时需要实现如下接口
* <ol>
* <li>BeanNameAware's {@code setBeanName}
* <li>BeanClassLoaderAware's {@code setBeanClassLoader}
* <li>BeanFactoryAware's {@code setBeanFactory}
* <li>EnvironmentAware's {@code setEnvironment}
* <li>EmbeddedValueResolverAware's {@code setEmbeddedValueResolver}
* <li>ResourceLoaderAware's {@code setResourceLoader}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
* <li>ApplicationEventPublisherAware's {@code setApplicationEventPublisher}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
* <li>MessageSourceAware's {@code setMessageSource}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
* <li>ApplicationContextAware's {@code setApplicationContext}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
* <li>ServletContextAware's {@code setServletContext}
* (only applicable when running in a web application context)
* <li>{@code postProcessBeforeInitialization} methods of BeanPostProcessors
* <li>InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* <li>a custom init-method definition
* <li>{@code postProcessAfterInitialization} methods of BeanPostProcessors
* </ol>
*
* <p>On shutdown of a bean factory, the following lifecycle methods apply:
* <ol>
* <li>{@code postProcessBeforeDestruction} methods of DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors
* <li>DisposableBean's {@code destroy}
* <li>a custom destroy-method definition
* </ol>public interface BeanFactory {
///对FactoryBean转义,因为如果使用bean的名字检索FactoryBean得到的对象是工厂生成的对象
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
//通过名称获取bena实例
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
//按照类象获得Bean,requiredType可以是父类
<T> T getBean(String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
//按照给定的参数创建bean实例(仅在创建新实例时才应用,而不是在检索现有实例时应用)
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
//根据类型获得Bean
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
//按照给定的参数创建对应的Bean(仅在创建新实例时才应用,而不是在检索现有实例时应用)
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
//根据name判断,是否含有某个Bean
boolean containsBean(String name);
//是否单例Bean
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//是否为原型Bean
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//检查bean是否和给定的类型匹配
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, @Nullable Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//获取Bean的Calss类型
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//获取Bean别名
String[] getAliases(String name);
}1.3.2 AutowireCapableBeanFactory
提供自动装配bean能力的功能支持,在BeanFactory基础上实现对已存在实例的管理,默认实现AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory,可以使用这个接口集成其它框架,捆绑并填充并不由Spring管理的已存在的实例,通过ApplicationContext的getAutowireCapableBeanFactory接口获取.定义5种自动装配策略:不注入AUTOWIRE_NO,使用bean name策略装配AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME,使用类型装配策略AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE,使用构造器装配策略AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR,自动装配策略AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT
1.3.3 HierarchicalBenFactory
父子级联IOC容器接口,子容器可以访问父容器中的Bean,但是父容器不能访问子容器中的Bean,在同一个容器中Bean的id时唯一的,但在父子容器中子容器可以拥有一个和父容器id相同的Bean
public interface HierarchicalBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
/**
* Return the parent bean factory, or {@code null} if there is none.
*/
@Nullable
BeanFactory getParentBeanFactory();
/**
* Return whether the local bean factory contains a bean of the given name,
* ignoring beans defined in ancestor contexts.
* <p>This is an alternative to {@code containsBean}, ignoring a bean
* of the given name from an ancestor bean factory.
* @param name the name of the bean to query
* @return whether a bean with the given name is defined in the local factory
* @see BeanFactory#containsBean
*/
boolean containsLocalBean(String name);
}1.3.4 ConfigurableBeanFactory
增强IOC容器的可定制性,定义了设置类装载器,属性编辑器,容器初始化后置处理器,定义的边界很多,具体的需要查看API
1.3.5 SingletonBeanRegistry
允许在运行期间向容器注册单实例Bean
void registerSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject);1.3.6 BeanDefinitionRegistry
配置文件中每一个<bean>节点都可以通过一个BeanDefinition表示,该接口提供以编码的形式向容器中注册Bean,提供了删除Bean的方法以及获得BeanDefintion的方法
void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
/**
* Remove the BeanDefinition for the given name.
* @param beanName the name of the bean instance to register
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no such bean definition
*/
void removeBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Return the BeanDefinition for the given bean name.
* @param beanName name of the bean to find a definition for
* @return the BeanDefinition for the given name (never {@code null})
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no such bean definition
*/
BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;1.3.7 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
提供bean definition的解析,注册功能,对单例Bean预加载(解决循环依赖问题).
1.3.7.1 设置忽略的依赖关系,注册找到的特殊依赖
void ignoreDependencyType(Class<?> type); // 忽略类型
void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> ifc); // 忽略接口
void registerResolvableDependency(Class<?> dependencyType, Object autowiredValue);
boolean isAutowireCandidate(String beanName, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
1.3.7.2 获取bean定义 (可以访问属性值跟构造方法的参数值)
BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
1.3.7.3 锁定配置信息.在调用refresh时会使用到.
void freezeConfiguration();
boolean isConfigurationFrozen();
1.3.7.4 预加载不是懒加载的单例.用于解决循环依赖问题
void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException;
2 ApplicationContext
2.1 简介
ApplicationContext是由BeanFactory派生而来的,主要的实现是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ,FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,XmlWebApplicationContext。面向的是框架开发者,几乎所有的应用都可以使用ApplicationContext而不是BeanFactory。ClassPathXmlApplicationContext默认从类路径下加载配置文件,FileSystemXmlApplicationContext默认从系统文件中加载配置文件。XmlWebApplicationContext默认从相对于Web根目录下加载配置文件ApplocationContext在初始化应用上下文容器时,会初始化所有单例Bean。
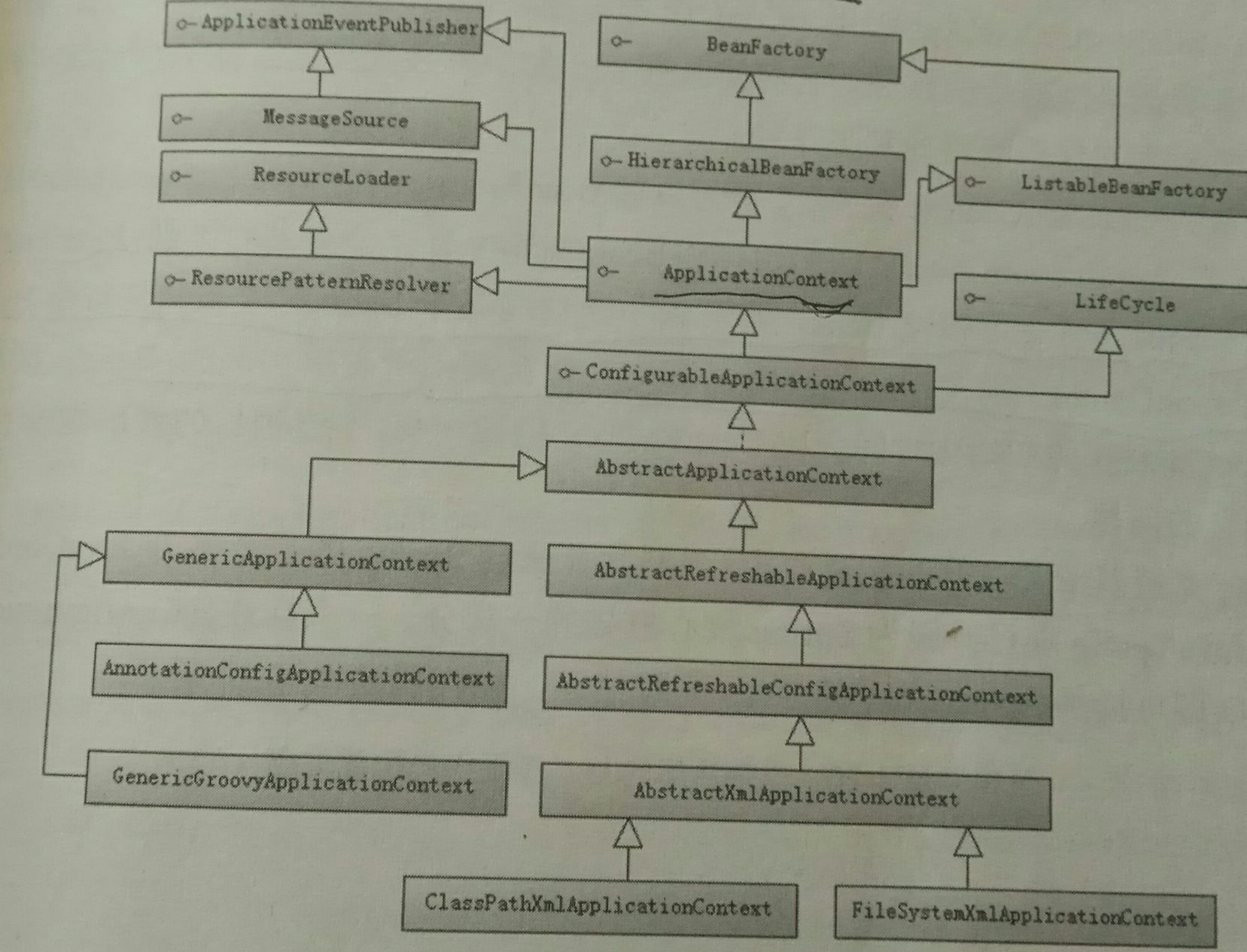
2.2 继承体系
2.3 类简介
2.3.1 ApplicationContext
访问应用程序组件的Bean工厂方法。继承自ListableBeanFactory,提供如下功能:1. 以通用的方式加载文件资源的能力。2. 将事件发布到注册监听器的功能。3. 解析消息的能力,支持国际化。4. 从父上下文继承
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
省略部分代码
//获得父应用上下文容器
ApplicationContext getParent();
//获得自动装配Bean能力
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}2.3.2 ApplicationEventPublisher
使容器具有发布应用上下文事件的功能,包括容器的启动,关闭事件等,凡是实现了ApplicationListener事件监听接口的Bean都能够接收到容器事件并对该事件进行处理。在ApplicationContext抽象实现类AbstractApplicationContext中存在ApplicationEventMulticaster负责存储所有的监听器并在事件发生时通知监听器
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher {
//通知该应用中注册的匹配的事件监听器,事件有可能是框架事件也有可能是特定的应用程序事件
default void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
publishEvent((Object) event);
}
//向监听器通知事件
void publishEvent(Object event);
}2.3.3 MessageSource
为应用提供i18n国际化消息访问的功能
2.3.4 LifeCycle
主要提供了start() & stop()两个方法,主要用于控制异步处理过程,在具体使用时该接口需要同时被ApplicationContext和具体的Bean实现,ApplicationContext会将start/stop信息传递给该容器中所有实现了该接口的Bean,达到控制和任务调度等目的
2.3.5 ConfigurableApplicationContext
扩展了ApplicationContext,主要新增了两个方法refresh和close,让容器具有刷新,关闭应用上下文的能力。在应用上下文关闭的情况下,调用refresh可以启动应用上下文,在已经启动的情况下,调用refresh可以清除应用上下文的缓存并重新加载配置信息。close关闭应用上下文
/**
* Load or refresh the persistent representation of the configuration,
* which might an XML file, properties file, or relational database schema.
* <p>As this is a startup method, it should destroy already created singletons
* if it fails, to avoid dangling resources. In other words, after invocation
* of that method, either all or no singletons at all should be instantiated.
* @throws BeansException if the bean factory could not be initialized
* @throws IllegalStateException if already initialized and multiple refresh
* attempts are not supported
*/
void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
/**
* Close this application context, releasing all resources and locks that the
* implementation might hold. This includes destroying all cached singleton beans.
* <p>Note: Does <i>not</i> invoke {@code close} on a parent context;
* parent contexts have their own, independent lifecycle.
* <p>This method can be called multiple times without side effects: Subsequent
* {@code close} calls on an already closed context will be ignored.
*/
@Override
void close();3 BeanFactory & ApplicationContext
BeanFactory:面向的是Spring,属于Spring的基础设施,是Bean集合的工厂类,其中包含了各种Bean的定义,客户端请求时将对应的Bean实例化,缓存所有单实例的Bean。生成协作类之间的关键即解决类之间的依赖关系,还包含了Bean生命周期的控制,默认实现是DefalutListableBeanFactory。在首次使用Bean的时候会初始化Bean
ApplicationContext:面向的是Spring应用的,ApplicationContext扩展于BeanFactory,所以它具有BeanFactory所有的功能,除此之外ApplicationContext提供:1. 以通用的方式加载文件资源的能力。2. 将事件发布到注册监听器的功能。3. 解析消息的能力,支持国际化。4. 从父上下文继承的特性。在容器启动时,会创建所有单实例的Bean。默认实现有ClassPathXmlAC,FileSystemXmlAC,WebXmlAC
4 WebApplicationContext
适用于Web应用,默认从相对于Web根目录的路径中加载配置文件并完成初始化。WebApplicationContext中可以获得ServletContext的引用。这个Web应用上下文作为属性放在ServletContext中,一般web应用能够访问Spring应用上下文。可以通过WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc )从ServletContext中获取Spring应用上下文(WebApplicationContext)
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext {
/**
* Context attribute to bind root WebApplicationContext to on successful startup.
* <p>Note: If the startup of the root context fails, this attribute can contain
* an exception or error as value. Use WebApplicationContextUtils for convenient
* lookup of the root WebApplicationContext.
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils#getWebApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils#getRequiredWebApplicationContext
*/
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
/**
* Scope identifier for request scope: "request".
* Supported in addition to the standard scopes "singleton" and "prototype".
*/
String SCOPE_REQUEST = "request";
/**
* Scope identifier for session scope: "session".
* Supported in addition to the standard scopes "singleton" and "prototype".
*/
String SCOPE_SESSION = "session";
/**
* Scope identifier for the global web application scope: "application".
* Supported in addition to the standard scopes "singleton" and "prototype".
*/
String SCOPE_APPLICATION = "application";
/**
* Name of the ServletContext environment bean in the factory.
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext
*/
String SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME = "servletContext";
/**
* Name of the ServletContext/PortletContext init-params environment bean in the factory.
* <p>Note: Possibly merged with ServletConfig/PortletConfig parameters.
* ServletConfig parameters override ServletContext parameters of the same name.
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#getInitParameterNames()
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#getInitParameter(String)
* @see javax.servlet.ServletConfig#getInitParameterNames()
* @see javax.servlet.ServletConfig#getInitParameter(String)
*/
String CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME = "contextParameters";
/**
* Name of the ServletContext/PortletContext attributes environment bean in the factory.
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#getAttributeNames()
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#getAttribute(String)
*/
String CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME = "contextAttributes";
/**
* Return the standard Servlet API ServletContext for this application.
*/
@Nullable
ServletContext getServletContext();
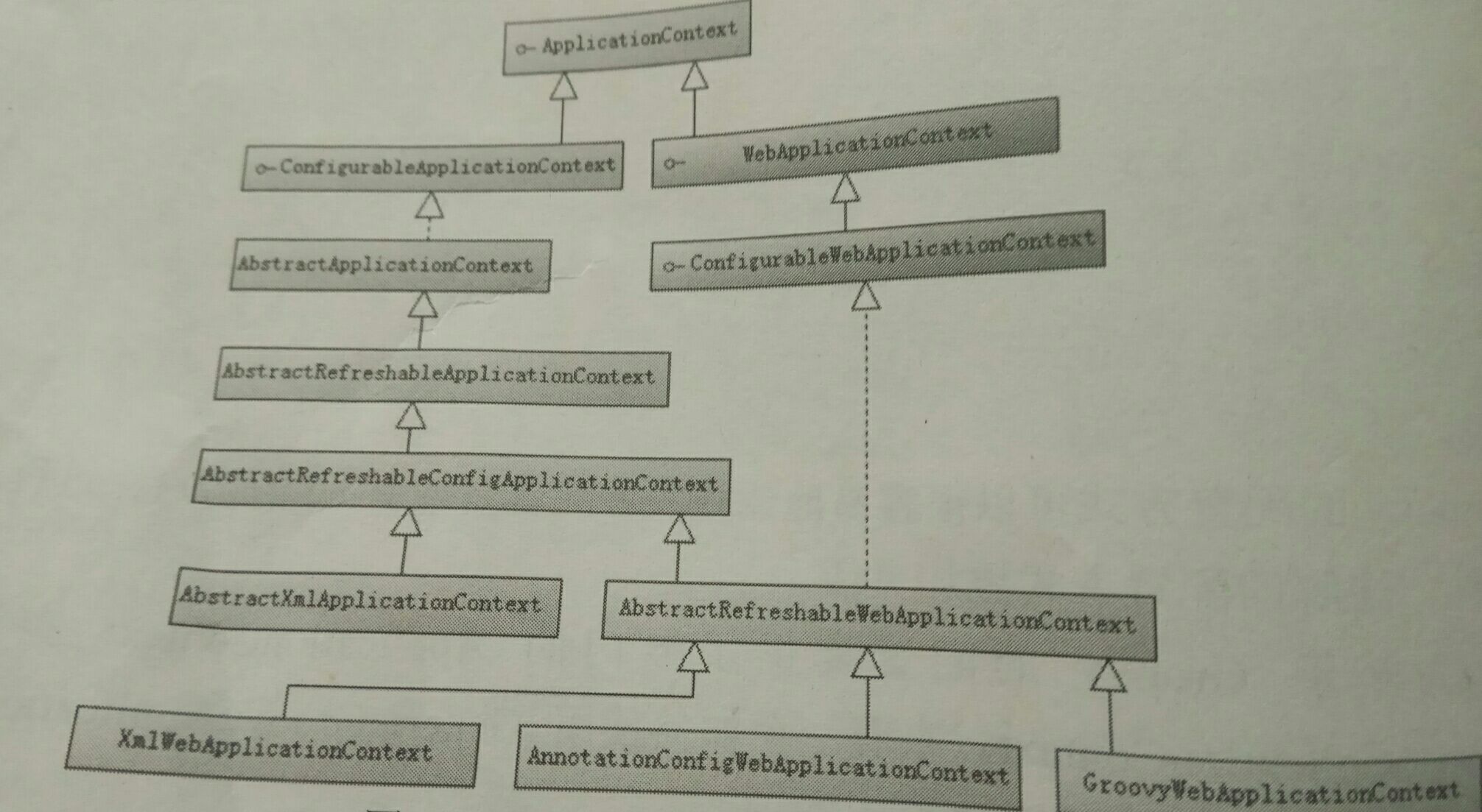
}4.1 继承体系
4.2 类简介
4.1.1 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
允许通过配置的方式实例化WebApplicationContext,提供了为Spring设置Web应用上下文以及设置Spring配置文件地址的功能。配置文件地址是相对于Web根目录的地址
/**
* Set the ServletContext for this web application context.
* <p>Does not cause an initialization of the context: refresh needs to be
* called after the setting of all configuration properties.
* @see #refresh()
*/
void setServletContext(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext);
/**
* Set the config locations for this web application context in init-param style,
* i.e. with distinct locations separated by commas, semicolons or whitespace.
* <p>If not set, the implementation is supposed to use a default for the
* given namespace or the root web application context, as appropriate.
*/
void setConfigLocation(String configLocation);
/**
* Set the config locations for this web application context.
* <p>If not set, the implementation is supposed to use a default for the
* given namespace or the root web application context, as appropriate.
*/
void setConfigLocations(String... configLocations);4.3 Spring应用上下文和Web应用上下文的关系
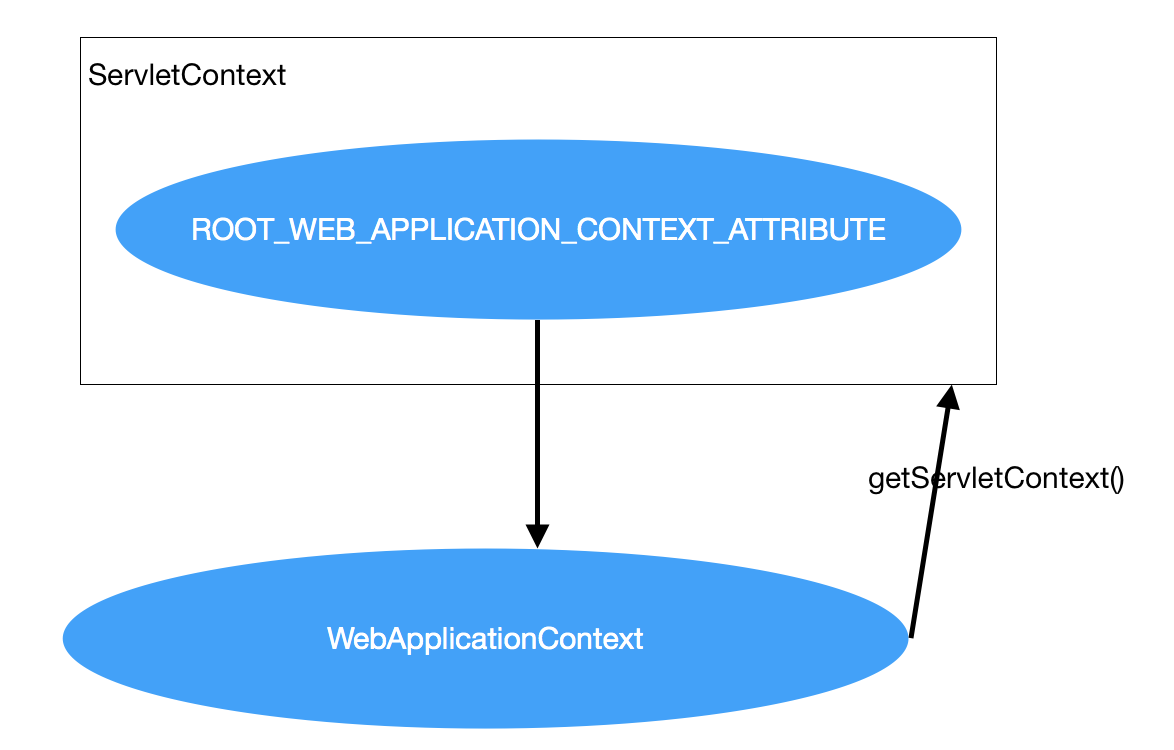
WebApplicationContext 中定义了一个常量ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE,在上下文启动时,WebApplicationContext实例以此键存放在ServletContext的属性列表中,可以通如下语句获得WebApplicationContext。
servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext,ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE).它们的关系如下
4.4 Bean在WebApplicationContext中的范围
之前Bean的范围有两个:singleton & prototype,在WebApplicationContext中新增了3个:request,session,global session
4.5 WebApplicationContext初始化
WebApplicationContext需要ServletContext实例,必须在拥有Web容器的前提下才能够完成启动工作。可以在web.xml中配置自启动的servlet或者web容器监听器,就可以完成spring web应用上下文的启动。不管是哪种配置都需要使用日志功能。
4.5.1 配置自启动servlet
<!—配置自启动servlet—>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderServlet</listener-class>
</listener>
<!—指定配置文件路径—>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml,/WEB-INF/applicationContextd.xml</param-value>
</context-param> 4.5.2 配置web容器监听器
<!—配置web容器监听器—>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!—指定配置文件路径—>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param> 






















 362
362

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








