1、TreeSet类图
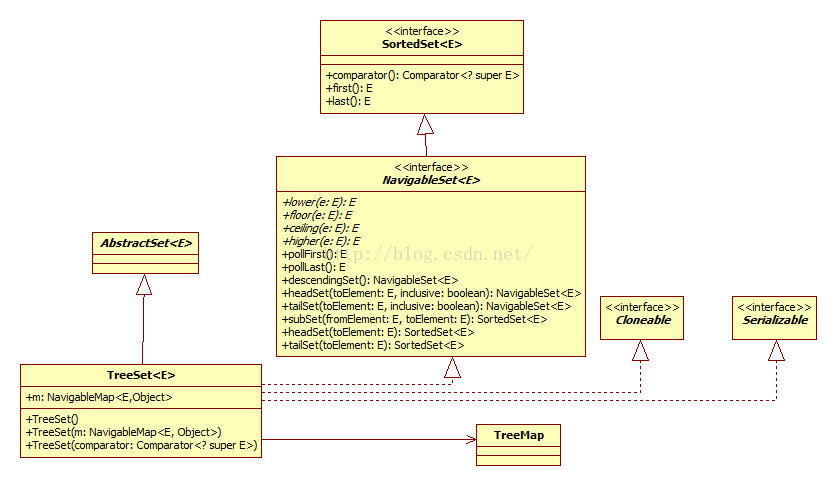
TreeSet
会调用集合元素的
compareTo
(Object
obj
)
方法来比较元素之间的大小关系,然后将集合元素按升序排列
如果试图把一个对象添加到
TreeSet
时,则该对象的类必须实现
Comparable
接口。
实现
Comparable
的类必须实现
compareTo
(Object
obj
)
方法,两个对象即通过
compareTo
(Object
obj
)
方法的返回值来比较大小。
因为只有相同类的两个实例才会比较大小,所以
向
TreeSet
中添加的应该是同一个类的对象,
当需要把一个对象放入
TreeSet
中,重写该对象对应的
equals()
方法时,应保证该方法与
compareTo
(Object
obj
)
方法有一致的结果
:如果两个对象通过
equals()
方法比较返回
true
,则通过
compareTo
(Object
obj
)
方法比较应返回
0 。
如果需要实现定制排序,则需要在创建
TreeSet
集合对象时,提供一个
Comparator
接口的实现类对象。由该
Comparator
对象负责集合元素的排序逻辑。
注意,此实现不是同步(线程安全)的。
2、TreeSet构造实现以及重要方法
对TreeSet而言,其实现是依靠内部关联一个TreeMap对象,对TreeSet的操作都转为对这个TreeMap对象响应对象的操作。添加到Set中的元素作为Map对象的key,,对应的value为一个公用的静态对象PRESENT ,代码中为:
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
1)构造器
TreeSet提供了5个不同的构造器。
//构造器 构造参数是一个NavigableMap
TreeSet(NavigableMap<E,Object> m) {
this.m = m;
}
//默认的无参数构造器,构造时创建一个TreeMap,然后调用之前的构造器
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
}
//构造一个
指定定制排序
Comparator 实现类的新Set
public TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
this(new TreeMap<>(comparator));
}
// 构造一个包含指定collection中的元素的新set。
public TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
// 构造一个已有的SortedSet集合的新Set。
public TreeSet(SortedSet<E> s) {
this(s.comparator());
addAll(s);
}
2)
iterator(): Iterator<E>
遍历Set的迭代器
// 返回对此set中元素进行迭代的迭代器。返回元素的顺序是增序。
//底层实际调用底层TreeMap的keySet来返回所有的key,由此 可见TreeSet中的元素,只是存放在了底层Map的key上。
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return m.navigableKeySet().iterator();
}
3) contains(o: Object): boolean 判断Set中是否包含对应的元素
// 如果此set包含指定元素,则返回true。 更确切地讲,当且仅当此set包含一个满足(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e)) 的e元素时,返回true。
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return m.containsKey(o);
}
4) add(e: E): boolean 向Set中添加元素方法
// 如果此set中尚未包含指定元素,则添加指定元素。 更确切地讲,如果此 set 没有包含满足(e==null ? e2==null : e.equals(e2)) 的元素e2,则向此set 添加指定的元素e。 如果此set已包含该元素,则该调用不更改set并返回false。
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
5) remove(o: Object): boolean 将元素从Set中移除的方法
// 如果指定元素存在于此set中,则将其移除。 更确切地讲,如果此set包含一个满足(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))的元素e, 则将其移除。如果此set已包含该元素,则返回true (或者:如果此set因调用而发生更改,则返回true)。(一旦调用返回,则此set不再包含该元素)。
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return m.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
6)subSet(fromElement: E,boolean fromInclusive, toElement: E,
boolean toInclusive): SortedSet<E> 获取从fromElement到toElement之间的子Set方法
//fromInclusive和toInclusive 布尔值若为true,则相应fromElement或toElement元素包含在子集中。
public NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive,
E toElement, boolean toInclusive) {
return new TreeSet<>(m.subMap(fromElement, fromInclusive,
toElement, toInclusive));
}
7) headSet(toElement: E, inclusive: boolean): NavigableSet<E> 获取所有小于
toElement元素的子集视图方法
//若
inclusive为true,则toElement包含在内
public NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) {
return new TreeSet<>(m.headMap(toElement, inclusive));
}
8) tailSet(fromElement: E, inclusive: boolean): NavigableSet<E>
获取所有大于等于
toElement元素的子集视图方法
//
若
inclusive为true,则fromElement包含在内
public NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) {
return new TreeSet<>(m.tailMap(fromElement, inclusive));
}
9) first(): E 获取第一个(最低)的元素方法
public E first() {
return m.firstKey();
}
10) last(): E 获取最后一个(最高)的元素方法
public E last() {
return m.lastKey();
}
11) pollFirst(): E 获取并移除第一个(最低)的元素方法
public E pollFirst() {
Map.Entry<E,?> e = m.pollFirstEntry();
return (e == null) ? null : e.getKey();
}
12) pollLast(): E 获取并移除最后一个(最高)的元素方法
public E pollLast() {
Map.Entry<E,?> e = m.pollLastEntry();
return (e == null) ? null : e.getKey();
}






















 77
77

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








