在网络编程中,常用的操作莫过于读写了,最重要的,也是最经常让程序员犯迷糊的地方。想要具体理解,当然还是看源码,看下面代码:
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(4887);
Socket client= serverSocket.accept();
InputStream is= client.getInputStream();
OutputStream out= client.getOutputStream();
byte[] buffer= new byte[4];
int len=is.read(buffer);
System.out.println(new String (buffer,0,len));
len=is.read(buffer);
System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,len));
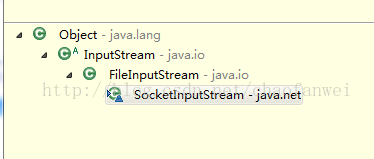
在调用client.getInputStream()方法返回的实际是SocketInputStream,
最主要的是socketRead0方法,是一个native方法,然后重要的就是int read(byte b[], int off, int length)方法了,值得注意的是 int read(),其内部调用的竟是 read(temp, 0, 1);这个是和inputstream刚好相反的。
看SocketInputStream源码如下:
/*
* %W% %E%
*
* Copyright (c) 2006, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*/
package java.net;
import java.io.FileDescriptor;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import sun.net.ConnectionResetException;
/**
* This stream extends FileInputStream to implement a
* SocketInputStream. Note that this class should <b>NOT</b> be
* public.
*
* @version %I%, %G%
* @author Jonathan Payne
* @author Arthur van Hoff
*/
class SocketInputStream extends FileInputStream
{
static {
init();
}
private boolean eof;
private PlainSocketImpl impl = null;
private byte temp[];
private Socket socket = null;
/**
* Creates a new SocketInputStream. Can only be called
* by a Socket. This method needs to hang on to the owner Socket so
* that the fd will not be closed.
* @param impl the implemented socket input stream
*/
SocketInputStream(PlainSocketImpl impl) throws IOException {
super(impl.getFileDescriptor());
this.impl = impl;
socket = impl.getSocket();
}
/**
* Returns the unique {@link java.nio.channels.FileChannel FileChannel}
* object associated with this file input stream.</p>
*
* The <code>getChannel</code> method of <code>SocketInputStream</code>
* returns <code>null</code> since it is a socket based stream.</p>
*
* @return the file channel associated with this file input stream
*
* @since 1.4
* @spec JSR-51
*/
public final FileChannel getChannel() {
return null;
}
/**
* Reads into an array of bytes at the specified offset using
* the received socket primitive.
* @param fd the FileDescriptor
* @param b the buffer into which the data is read
* @param off the start offset of the data
* @param len the maximum number of bytes read
* @param timeout the read timeout in ms
* @return the actual number of bytes read, -1 is
* returned when the end of the stream is reached.
* @exception IOException If an I/O error has occurred.
*/
private native int socketRead0(FileDescriptor fd,
byte b[], int off, int len,
int timeout)
throws IOException;
/**
* Reads into a byte array data from the socket.
* @param b the buffer into which the data is read
* @return the actual number of bytes read, -1 is
* returned when the end of the stream is reached.
* @exception IOException If an I/O error has occurred.
*/
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return read(b, 0, b.length);
}
/**
* Reads into a byte array <i>b</i> at offset <i>off</i>,
* <i>length</i> bytes of data.
* @param b the buffer into which the data is read
* @param off the start offset of the data
* @param len the maximum number of bytes read
* @return the actual number of bytes read, -1 is
* returned when the end of the stream is reached.
* @exception IOException If an I/O error has occurred.
*/
public int read(byte b[], int off, int length) throws IOException {
int n;
// EOF already encountered
if (eof) {
return -1;
}
// connection reset
if (impl.isConnectionReset()) {
throw new SocketException("Connection reset");
}
// bounds check
if (length <= 0 || off < 0 || off + length > b.length) {
if (length == 0) {
return 0;
}
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
boolean gotReset = false;
// acquire file descriptor and do the read
FileDescriptor fd = impl.acquireFD();
try {
n = socketRead0(fd, b, off, length, impl.getTimeout());
if (n > 0) {
return n;
}
} catch (ConnectionResetException rstExc) {
gotReset = true;
} finally {
impl.releaseFD();
}
/*
* We receive a "connection reset" but there may be bytes still
* buffered on the socket
*/
if (gotReset) {
impl.setConnectionResetPending();
impl.acquireFD();
try {
n = socketRead0(fd, b, off, length, impl.getTimeout());
if (n > 0) {
return n;
}
} catch (ConnectionResetException rstExc) {
} finally {
impl.releaseFD();
}
}
/*
* If we get here we are at EOF, the socket has been closed,
* or the connection has been reset.
*/
if (impl.isClosedOrPending()) {
throw new SocketException("Socket closed");
}
if (impl.isConnectionResetPending()) {
impl.setConnectionReset();
}
if (impl.isConnectionReset()) {
throw new SocketException("Connection reset");
}
eof = true;
return -1;
}
/**
* Reads a single byte from the socket.
*/
public int read() throws IOException {
if (eof) {
return -1;
}
temp = new byte[1];
int n = read(temp, 0, 1);
if (n <= 0) {
return -1;
}
return temp[0] & 0xff;
}
/**
* Skips n bytes of input.
* @param n the number of bytes to skip
* @return the actual number of bytes skipped.
* @exception IOException If an I/O error has occurred.
*/
public long skip(long numbytes) throws IOException {
if (numbytes <= 0) {
return 0;
}
long n = numbytes;
int buflen = (int) Math.min(1024, n);
byte data[] = new byte[buflen];
while (n > 0) {
int r = read(data, 0, (int) Math.min((long) buflen, n));
if (r < 0) {
break;
}
n -= r;
}
return numbytes - n;
}
/**
* Returns the number of bytes that can be read without blocking.
* @return the number of immediately available bytes
*/
public int available() throws IOException {
return impl.available();
}
/**
* Closes the stream.
*/
private boolean closing = false;
public void close() throws IOException {
// Prevent recursion. See BugId 4484411
if (closing)
return;
closing = true;
if (socket != null) {
if (!socket.isClosed())
socket.close();
} else
impl.close();
closing = false;
}
void setEOF(boolean eof) {
this.eof = eof;
}
/**
* Overrides finalize, the fd is closed by the Socket.
*/
protected void finalize() {}
/**
* Perform class load-time initializations.
*/
private native static void init();
}





















 5388
5388











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








