530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差

可以遍历一遍得到一个有序数组,看数组中相邻两个元素最小绝对差即可:
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode* root,vector<int> & res)
{
if(root==NULL)return;
traversal(root->left,res);
res.push_back(root->val);
traversal(root->right,res);
}
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
traversal(root,res);
int mindif=INT32_MAX;
for(int i=0;i<res.size();i++)
{
if(i>0)
{
if(mindif>abs(res[i-1]-res[i]))
mindif=abs(res[i-1]-res[i]);
}
}
return mindif;
}
};之后还有一种方法就是双指针的方法,我这里迭代和递归都写了一遍:
class Solution {
public:
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* preroot=NULL;
int mindf=INT32_MAX;
auto cur=root;
while(cur!=NULL||!st.empty())
{
if(cur!=NULL)
{
st.push(cur);
cur=cur->left;
}
else
{
auto node=st.top();
st.pop();
if(preroot!=NULL)
{ mindf=min(mindf,abs(node->val-preroot->val));
preroot=node;
}
else
{
preroot=node;
}
cur=node->right;
}
}
return mindf;
}
};class Solution {
public:
int mindif=INT32_MAX;
TreeNode* pre=NULL;
void getmin(TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL)return ;
getmin(root->left);
if(pre!=NULL)
mindif=min(mindif,abs(pre->val-root->val));
pre=root;
getmin(root->right);
}
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
getmin(root);
return mindif;
}
};501.二叉搜索树中的众数
给定一个有相同值的二叉搜索树(BST),找出 BST 中的所有众数(出现频率最高的元素)。
假定 BST 有如下定义:
- 结点左子树中所含结点的值小于等于当前结点的值
- 结点右子树中所含结点的值大于等于当前结点的值
- 左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
例如:
给定 BST [1,null,2,2],

返回[2].
提示:如果众数超过1个,不需考虑输出顺序
进阶:你可以不使用额外的空间吗?(假设由递归产生的隐式调用栈的开销不被计算在内)
笨蛋解法就是遍历得到数组,然后用map统计频率:
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode* root,vector<int> &res)
{
if(root==NULL)return;
traversal(root->left,res);
res.push_back(root->val);
traversal(root->right,res);
}
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
vector<int> result;
unordered_map<int,int> mapp;
int flag=INT32_MIN;
traversal(root,res);
for(int i=0;i<res.size();i++)
{
mapp[res[i]]++;
}
for(auto it=mapp.begin();it!=mapp.end();it++)
{
cout << it->first;
flag=max(flag,it->second);
}
for(auto iter=mapp.begin();iter!=mapp.end();iter++)
{
if(iter->second==flag)
result.push_back(iter->first);
}
//cout <<flag;
return result;
}
};递归的话用到一个技巧,就是vector数组的clear()
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> res;int count=0;int maxcount=0;TreeNode* prenode=NULL;
void traversal(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)return;
traversal(root->left);
if(prenode==NULL)count=1;
else if(prenode->val==root->val)
count++;
else
count=1;
prenode=root;
if(count==maxcount)
res.push_back(root->val);
if(count>maxcount)
{ maxcount=count;
res.clear();
res.push_back(root->val);
}
traversal(root->right);
}
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
traversal(root);
return res;
}
};用这个思路同样可以写出迭代法:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> res;
int count=0;
int maxcount=0;
auto cur=root;
TreeNode* prenode=NULL;
while(cur!=NULL||!st.empty())
{
if(cur!=NULL)
{
st.push(cur);
cur=cur->left;
}
else
{
auto node=st.top();
st.pop();
if(prenode==NULL)count=1;
else if(prenode->val==node->val)count++;
else
count=1;
prenode=node;
if(count==maxcount)res.push_back(node->val);
else if(count>maxcount)
{
maxcount=count;
res.clear();
res.push_back(node->val);
}
cur=node->right;
}
}
return res;
}
};236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
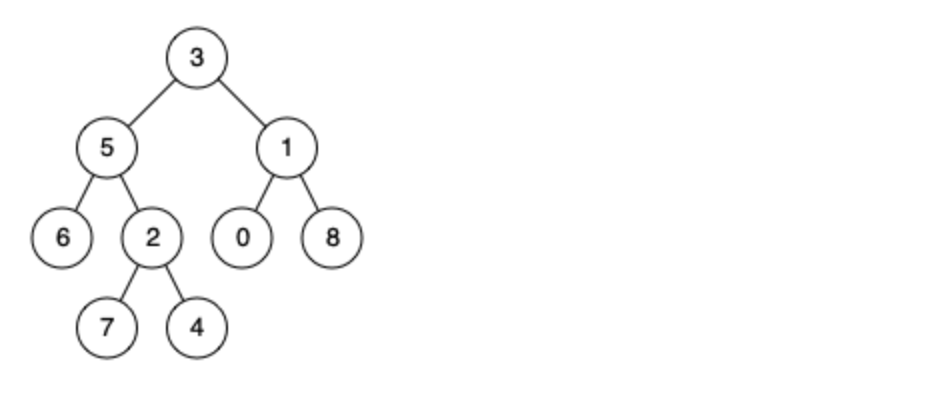
后序遍历,然后left和right都不为NULL的话,说明这个结点就是公共祖先,这种解法已经包括了所有情况
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowest(TreeNode* root,TreeNode* p,TreeNode* q){
if(root==NULL)return root;
else if(root==p||root==q)return root;
auto left=lowest(root->left,p,q);
auto right=lowest(root->right,p,q);
if(left!=NULL&&right!=NULL)return root;
else if(left==NULL&&right!=NULL)return right;
else if(left!=NULL&&right==NULL)return left;
else
return NULL;
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
return lowest(root,p,q);
}
};






 文章介绍了在二叉搜索树中求解最小绝对差、查找众数以及寻找最近公共祖先的两种方法,包括递归和迭代的解决方案。
文章介绍了在二叉搜索树中求解最小绝对差、查找众数以及寻找最近公共祖先的两种方法,包括递归和迭代的解决方案。














 178
178











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








