SharedPreferences 就是共享参数,是android专属的轻量级存储数据的方式。
适用场景:
- 简单且孤立的数据。复杂且相关的数据要存储到数据库中。
- 文本形式的数据。二进制数据要保存到文件中。
- 需要持久化存储的数据,在APP退出之后,之前保存的数据依然有效。
实际开发中,共享参数经常存储的数据有APP的个性化配置信息、用户使用APP的行为信息、临时需要保存的片段信息等。
案例: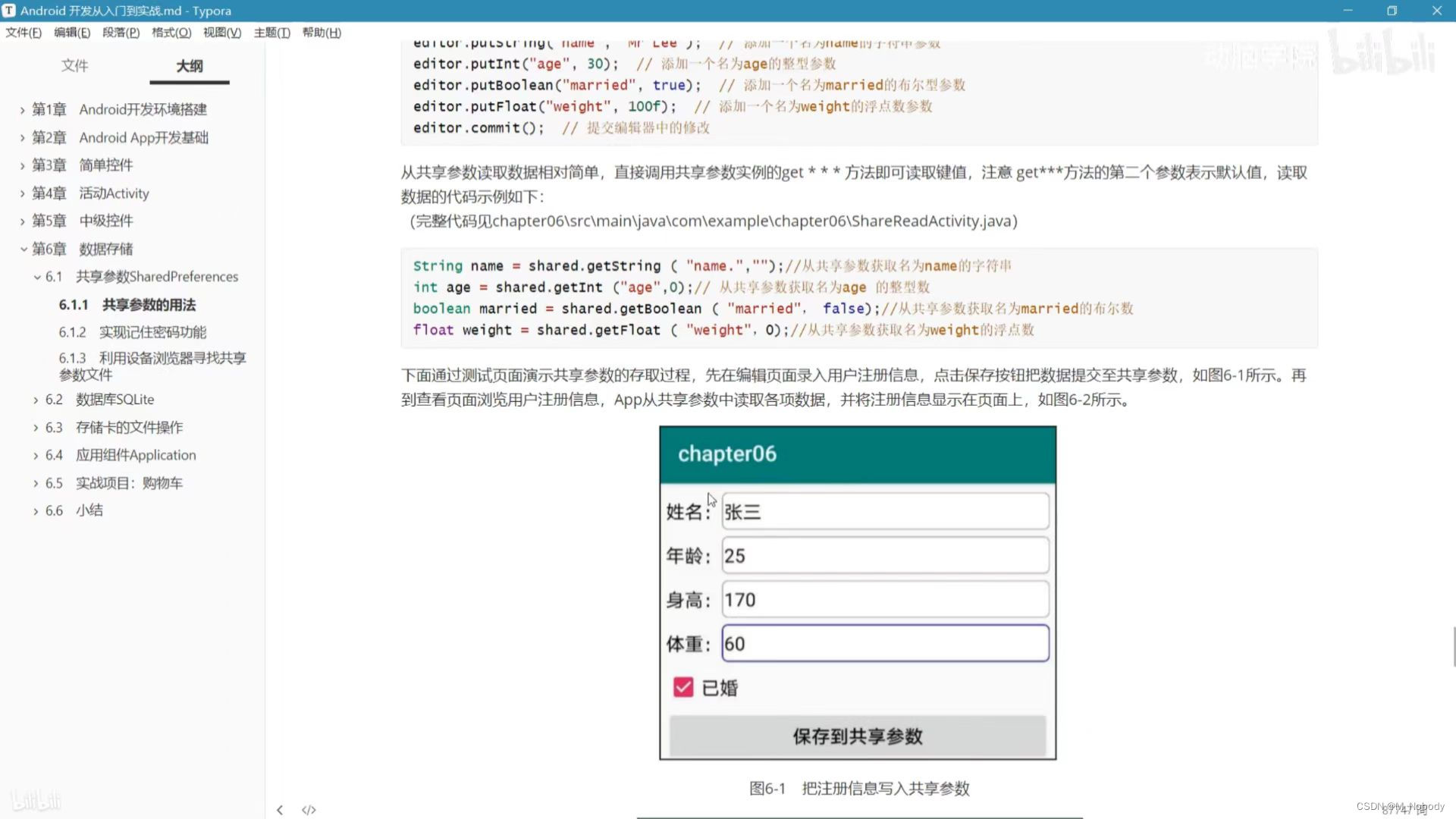
视图:
没啥特殊的,四个线性布局,一个checkbox,一个按钮
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="@dimen/item_layout_height"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="@string/name"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="@dimen/common_font_size"
android:textColor="@color/black" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_name"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="5dp"
android:background="@drawable/editext_selector"
android:hint="@string/input_name"
android:inputType="text"
android:maxLength="6"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textColorHint="@color/grey"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="@dimen/item_layout_height"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="@string/age"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="@dimen/common_font_size"
android:textColor="@color/black" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_age"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="5dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/editext_selector"
android:hint="@string/input_age"
android:inputType="number"
android:maxLength="6"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textColorHint="@color/grey"
android:textSize="@dimen/common_font_size" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="@dimen/item_layout_height"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="@string/height"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="@dimen/common_font_size"
android:textColor="@color/black" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_height"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="5dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/editext_selector"
android:hint="@string/input_height"
android:inputType="number"
android:maxLength="6"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textColorHint="@color/grey"
android:textSize="@dimen/common_font_size" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="@dimen/item_layout_height"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="@string/weight"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="@dimen/common_font_size"
android:textColor="@color/black" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_weight"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="5dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/editext_selector"
android:hint="@string/input_weight"
android:inputType="number"
android:maxLength="6"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textColorHint="@color/grey"
android:textSize="@dimen/common_font_size" />
</LinearLayout>
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/ck_married"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/married"
android:textSize="@dimen/common_font_size"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_save"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/save_share"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="@dimen/common_font_size" />
</LinearLayout>对应java文件:
- 获取组件的id
- 给保存按钮创建一个点击方法,用来获取编辑框里的值,用SharedPreferences.Editor使用共享参数的编辑器,这样可以对每一项进行编辑,最后commit提交一下
-
preferences = getSharedPreferences("config", Context.MODE_PRIVATE); - Context.MODE_PRIVATE:为默认操作模式,代表该文件是私有数据,只能被应用本身访问,在该模式下,写入的内容会覆盖原文件的内容。
- reload()方法重新加载一下保存的数据。
package com.example.chapter06;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.CheckBox;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class ShareWriteActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private EditText et_name;
private EditText et_age;
private EditText et_height;
private EditText et_weight;
private CheckBox ck_married;
private SharedPreferences preferences;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_share_write);
et_name = findViewById(R.id.et_name);
et_age = findViewById(R.id.et_age);
et_height = findViewById(R.id.et_height);
et_weight = findViewById(R.id.et_weight);
ck_married = findViewById(R.id.ck_married);
findViewById(R.id.btn_save).setOnClickListener(this);
preferences = getSharedPreferences("config", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
reload();
}
private void reload() {
String name = preferences.getString("name", null);
if (name != null) {
et_name.setText(name);
}
int age = preferences.getInt("age", 0);
if (age != 0) {
et_age.setText(String.valueOf(age));
}
float height = preferences.getFloat("height", 0f);
if (height != 0f) {
et_height.setText(String.valueOf(height));
}
float weight = preferences.getFloat("weight", 0f);
if (weight != 0f) {
et_weight.setText(String.valueOf(weight));
}
boolean married = preferences.getBoolean("married", false);
ck_married.setChecked(married);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
String name = et_name.getText().toString();
String age = et_age.getText().toString();
String height = et_height.getText().toString();
String weight = et_weight.getText().toString();
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = preferences.edit();
editor.putString("name",name);
editor.putInt("age",Integer.parseInt(age));
editor.putFloat("height",Float.parseFloat(height));
editor.putFloat("weight",Float.parseFloat(weight));
editor.putBoolean("married", ck_married.isChecked());
editor.commit();
}
}只要我们关掉后台之后重新打开程序数据还有的话就成功啦 !





















 466
466











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








