**二分三分小结**
在ACM程序竞赛中,经常要用到二分的方法来求值,因为二分的复杂度是lgn,比直接for循环枚举所有可能高效得多,但用二分时往往是单调函数的情况,如查找一个数组中的某个值,要先将该数组排序。不同的题目二分往往有不同的形式,但其本质都是相同的,只不过不同的问题里要求不同。
简单定义:在一个单调有序的集合中查找元素,每次将集合分为左右两部分,判断解在哪个部分中并调整集合上下界,重复直到找到目标元素。
时间复杂度:O (logn),优于直接顺序查找O(n)
/***************
对于左闭右闭的区间
***************/
int search1(int array[], int n, int v)
//这个是左闭右闭区间的二分。比较常用
{
int left, right, middle;
left = 0, right = n - 1;
//写成 right = n ; 则初始化的区间是左闭右开区间。
while (left <= right)
{
middle = (left + right) / 2;
if (array[middle] > v)
right = middle - 1;
//循环机判断的区间是左闭右闭 区间。
else if (array[middle] < v)
left = middle + 1;
else
return middle;
}
return -1;
}/***************
对于左闭右开的区间
***************/
int search2(int array[], int n, int v)
{
int left, right, middle;
left = 0, right = n; //左闭右开区间的二分查找。
while (left < right)
//如果left,right是浮点数,往往定义一个精度eps,则应写成while(r-l > eps)
{
middle = (left + right) / 2;
if (array[middle] > v)
right = middle;
else if (array[middle] < v)
left = middle + 1;
else
return middle;
}
return -1;
}
左闭右闭区间
//right=n-1 => while(left <= right) => right=middle-1;
左闭右开区间
//right=n => while(left < right) => right=middle;除了上述直接根据二分的定义来写之外,C++的STL中还提供了非常方便的函数可直接用于二分查找
STL
lower_bound()
Returns an iterator pointing to the first element in the range [first,last) which does not compare less than val.
The elements are compared using operator< for the first version, and comp for the second. The elements in the range shall already be sorted according to this same criterion (operator< or comp), or at least partitioned with respect to val.
The function optimizes the number of comparisons performed by comparing non-consecutive elements of the sorted range, which is specially efficient for random-access iterators.
Unlike upper_bound, the value pointed by the iterator returned by this function may also be equivalent to val, and not only greater.
/**
lower_bound()
在前闭后开的有序区间进行二分查找,返回大于或等于查找值的第一个元素的位置。
**/
/**
函数原型
**/
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
ForwardIterator lower_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& val)
{
ForwardIterator it;
iterator_traits<ForwardIterator>::difference_type count, step;
count = distance(first,last);
while (count>0)
{
it = first; step=count/2; advance (it,step);
if (*it<val) { // or: if (comp(*it,val)), for version (2)
first=++it;
count-=step+1;
}
else count=step;
}
return first;
}/***
示例
***/
// lower_bound/upper_bound example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::lower_bound, std::upper_bound, std::sort
#include <vector> // std::vector
int main () {
int myints[] = {10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20};
std::vector<int> v(myints,myints+8); // 10 20 30 30 20 10 10 20
std::sort (v.begin(), v.end()); // 10 10 10 20 20 20 30 30
std::vector<int>::iterator low,up;
low=std::lower_bound (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^
up= std::upper_bound (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^
std::cout << "lower_bound at position " << (low- v.begin()) << '\n';
std::cout << "upper_bound at position " << (up - v.begin()) << '\n';
return 0;
}
Output:
lower_bound at position 3
upper_bound at position 6
upper_bound()
返回大于查找值的第一个元素的位置,与lower_bound用法一致。
0 1 2 3
1 3 3 5 查找3 查找4
lower_bound() 2 3
upper_bound() 3 3
函数lower_bound()在first和last中的前闭后开区间进行二分查找,返回大于或等于val的第一个元素位置。如果所有元素都小于val,则返回last的位置,且last的位置是越界的!!~
返回查找元素的第一个可安插位置,也就是“元素值>=查找值”的第一个元素的位置
另外,STL还有一个binary_search函数也是用于对前闭后开的[first,last)有序序列二分查找,若包含所查找元素则返回true,否则返回false。函数原型如下:
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
bool binary_search (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& val)
{
first = std::lower_bound(first,last,val);
return (first!=last && !(val<*first));
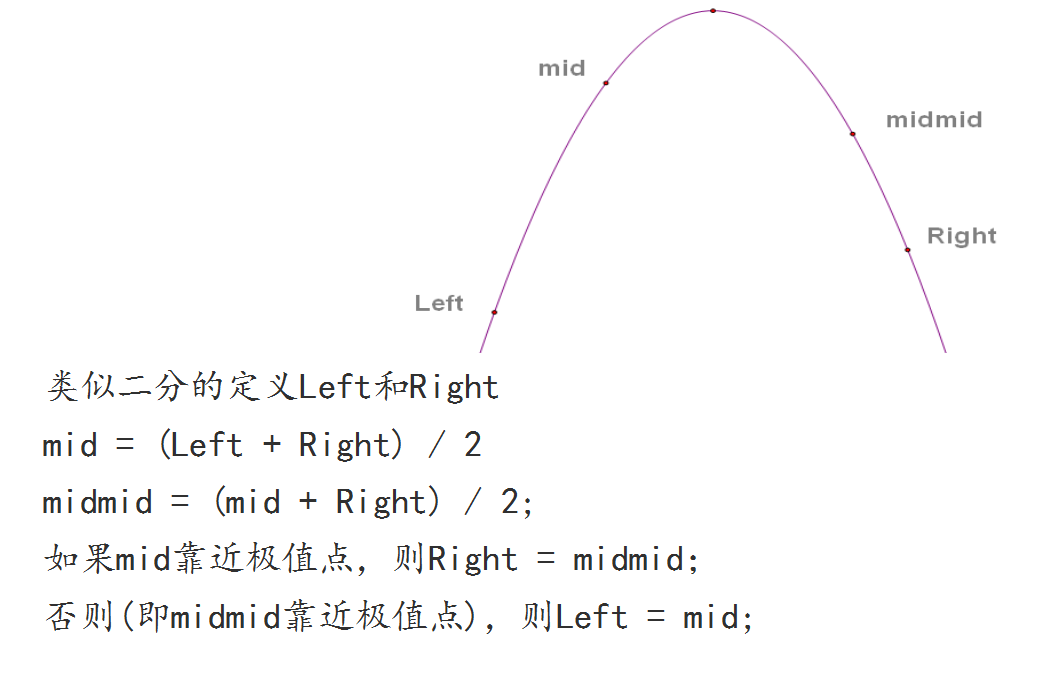
}三分法一般用于凹函数或凸函数的求极值问题。
简单定义:当需要求某凸性或凹形函数的极值,通过函数本身表达式并不容易求解时,就可以用三分法不断逼近求解。
对于求解一些实际问题,当公式难以推导出来时,二分、三分法可以较为精确地求解出一些临界值,且效率也是令人满意的。
灵活应用这些方法对解题会很有帮助。给出部分题解如下:
POJ 1905
POJ 1434
POJ 3273
POJ 3518
HDU 2899
HDU 1969
HDU 2141
ZOJ 3203























 777
777

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








