Python While循环语句
执行语句可以是单个语句或语句块。判断条件可以是任何表达式,任何非零、或非空(null)的值均为true。
当判断条件假false时,循环结束。
实例:
#!/usr/bin/python
count = 0
while (count < 9):
print 'The count is:', count
count = count + 1
print "Good bye!"以上代码执行输出结果:
The count is: 0
The count is: 1
The count is: 2
The count is: 3
The count is: 4
The count is: 5
The count is: 6
The count is: 7
The count is: 8
Good bye!while 语句时还有另外两个重要的命令 continue,break 来跳过循环,continue 用于跳过该次循环,break 则是用于退出循环,此外”判断条件”还可以是个常值,表示循环必定成立,具体用法如下:
# continue 和 break 用法
i = 1
while i < 10:
i += 1
if i%2 > 0: # 非双数时跳过输出
continue
print i # 输出双数2、4、6、8、10
i = 1
while 1: # 循环条件为1必定成立
print i # 输出1~10
i += 1
if i > 10: # 当i大于10时跳出循环
break
无限循环
如果条件判断语句永远为 true,循环将会无限的执行下去,如下实例:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
var = 1
while var == 1 : # 该条件永远为true,循环将无限执行下去
num = raw_input("Enter a number :")
print "You entered: ", num
print "Good bye!"以上实例输出结果:
Enter a number :20
You entered: 20
Enter a number :29
You entered: 29
Enter a number :3
You entered: 3
Enter a number between :Traceback (most recent call last):
File "test.py", line 5, in <module>
num = raw_input("Enter a number :")
KeyboardInterrupt注意:以上的无限循环你可以使用 CTRL+C 来中断循环。
循环使用 else 语句
在 python 中,for … else 表示这样的意思,for 中的语句和普通的没有区别,else 中的语句会在循环正常执行完(即 for 不是通过 break 跳出而中断的)的情况下执行,while … else 也是一样。
#!/usr/bin/python
count = 0
while count < 5:
print count, " is less than 5"
count = count + 1
else:
print count, " is not less than 5"以上实例输出结果为:
0 is less than 5
1 is less than 5
2 is less than 5
3 is less than 5
4 is less than 5
5 is not less than 5简单语句组
类似if语句的语法,如果你的while循环体中只有一条语句,你可以将该语句与while写在同一行中, 如下所示:
#!/usr/bin/python
flag = 1
while (flag): print 'Given flag is really true!'
print "Good bye!"注意:以上的无限循环你可以使用 CTRL+C 来中断循环。
Python for 循环语句
Python for循环可以遍历任何序列的项目,如一个列表或者一个字符串。
语法:
for循环的语法格式如下:
for iterating_var in sequence:
statements(s)实例:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
for letter in 'Python': # 第一个实例
print '当前字母 :', letter
fruits = ['banana', 'apple', 'mango']
for fruit in fruits: # 第二个实例
print '当前字母 :', fruit
print "Good bye!"以上实例输出结果:
当前字母 : P
当前字母 : y
当前字母 : t
当前字母 : h
当前字母 : o
当前字母 : n
当前字母 : banana
当前字母 : apple
当前字母 : mango
Good bye!通过序列索引迭代
另外一种执行循环的遍历方式是通过索引,如下实例:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
fruits = ['banana', 'apple', 'mango']
for index in range(len(fruits)):
print '当前水果 :', fruits[index]
print "Good bye!"以上实例输出结果:
当前水果 : banana
当前水果 : apple
当前水果 : mango
Good bye!以上实例我们使用了内置函数 len() 和 range(),函数 len() 返回列表的长度,即元素的个数。 range返回一个序列的数。
循环使用 else 语句
在 python 中,for … else 表示这样的意思,for 中的语句和普通的没有区别,else 中的语句会在循环正常执行完(即 for 不是通过 break 跳出而中断的)的情况下执行,while … else 也是一样。
如下实例:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
for num in range(10,20): # 迭代 10 到 20 之间的数字
for i in range(2,num): # 根据因子迭代
if num%i == 0: # 确定第一个因子
j=num/i # 计算第二个因子
print '%d 等于 %d * %d' % (num,i,j)
break # 跳出当前循环
else: # 循环的 else 部分
print num, '是一个质数'以上实例输出结果:
10 等于 2 * 5
11 是一个质数
12 等于 2 * 6
13 是一个质数
14 等于 2 * 7
15 等于 3 * 5
16 等于 2 * 8
17 是一个质数
18 等于 2 * 9
19 是一个质数Python 循环嵌套
Python 语言允许在一个循环体里面嵌入另一个循环。
Python for 循环嵌套语法:
for iterating_var in sequence:
for iterating_var in sequence:
statements(s)
statements(s)Python while 循环嵌套语法:
while expression:
while expression:
statement(s)
statement(s)你可以在循环体内嵌入其他的循环体,如在while循环中可以嵌入for循环, 反之,你可以在for循环中嵌入while循环。
实例:
以下实例使用了嵌套循环输出2~100之间的素数:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
i = 2
while(i < 100):
j = 2
while(j <= (i/j)):
if not(i%j): break
j = j + 1
if (j > i/j) : print i, " 是素数"
i = i + 1
print "Good bye!"以上实例输出结果:
2 是素数
3 是素数
5 是素数
7 是素数
11 是素数
13 是素数
17 是素数
19 是素数
23 是素数
29 是素数
31 是素数
37 是素数
41 是素数
43 是素数
47 是素数
53 是素数
59 是素数
61 是素数
67 是素数
71 是素数
73 是素数
79 是素数
83 是素数
89 是素数
97 是素数
Good bye!Python Number(数字)
Python Number 数据类型用于存储数值。
数据类型是不允许改变的,这就意味着如果改变 Number 数据类型的值,将重新分配内存空间。
以下实例在变量赋值时 Number 对象将被创建:
var1 = 1
var2 = 10您也可以使用del语句删除一些 Number 对象引用。
del语句的语法是:
del var1[,var2[,var3[....,varN]]]]您可以通过使用del语句删除单个或多个对象,例如:
del var
del var_a, var_bPython 支持四种不同的数值类型:
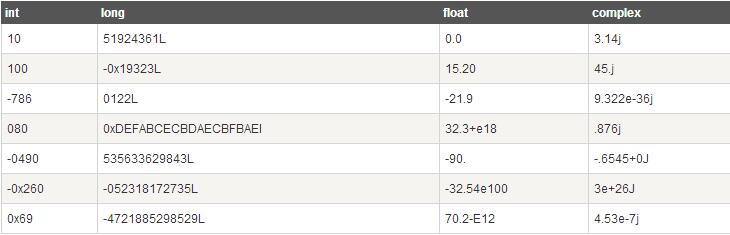
- 整型(Int) - 通常被称为是整型或整数,是正或负整数,不带小数点。
- 长整型(long integers) - 无限大小的整数,整数最后是一个大写或小写的L。
- 浮点型(floating point real values) - 浮点型由整数部分与小数部分组成,浮点型也可以使用科学计数法表示(2.5e2 = 2.5 x 102 = 250)
- 复数( (complex numbers)) - 复数由实数部分和虚数部分构成,可以用a + bj,或者complex(a,b)表示, 复数的实部a和虚部b都是浮点型。
-
- 长整型也可以使用小写”L”,但是还是建议您使用大写”L”,避免与数字”1”混淆。Python使用”L”来显示长整型。
- Python还支持复数,复数由实数部分和虚数部分构成,可以用a + bj,或者complex(a,b)表示, 复数的实部a和虚部b都是浮点型
-
Python Number 类型转换
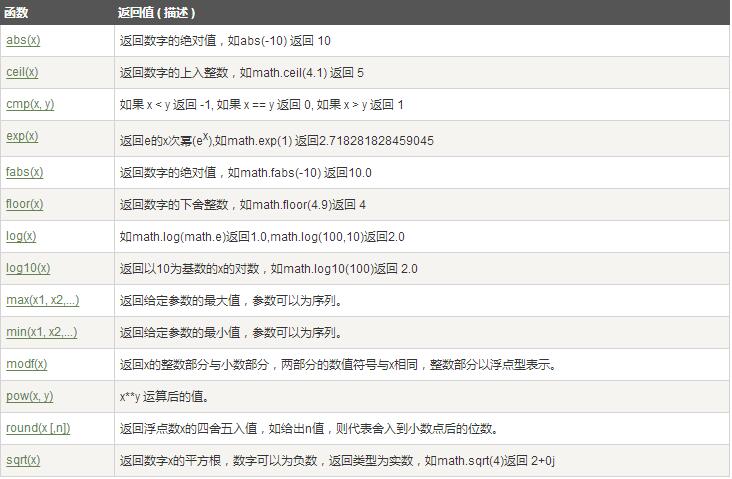
int(x [,base ]) 将x转换为一个整数 long(x [,base ]) 将x转换为一个长整数 float(x ) 将x转换到一个浮点数 complex(real [,imag ]) 创建一个复数 str(x ) 将对象 x 转换为字符串 repr(x ) 将对象 x 转换为表达式字符串 eval(str ) 用来计算在字符串中的有效Python表达式,并返回一个对象 tuple(s ) 将序列 s 转换为一个元组 list(s ) 将序列 s 转换为一个列表 chr(x ) 将一个整数转换为一个字符 unichr(x ) 将一个整数转换为Unicode字符 ord(x ) 将一个字符转换为它的整数值 hex(x ) 将一个整数转换为一个十六进制字符串 oct(x ) 将一个整数转换为一个八进制字符串Python数学函数
Python随机数函数
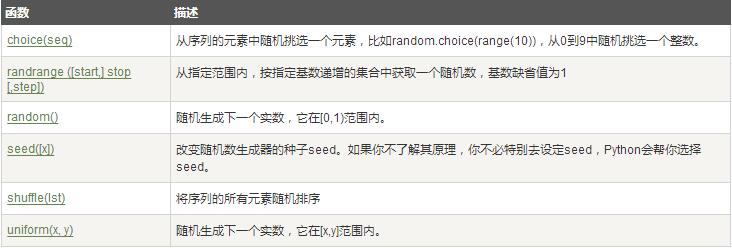
随机数可以用于数学,游戏,安全等领域中,还经常被嵌入到算法中,用以提高算法效率,并提高程序的安全性。
Python包含以下常用随机数函数:Python三角函数
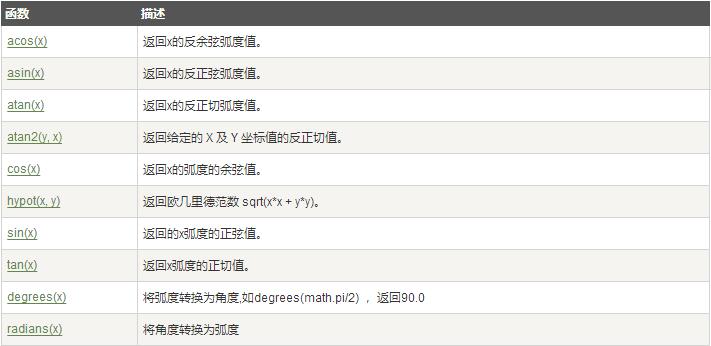
Python包括以下三角函数:























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








