前言
下周即将展开一个http接口测试的需求,刚刚完成的java类接口测试工作中,由于之前犯懒,没有提前搭建好自动化回归测试框架,以至于后期rd每修改一个bug,经常导致之前没有问题的case又产生了bug,所以需要一遍遍回归case,过程一直手工去执行,苦不堪言。所以,对于即将开始的http接口测试需求,立马花了两天时间搭建了一个http接口自动化测试框架用于测试后期回归测试,实在是被大量的重复手工执行搞怕了。
基础框架选择
最方便的方法就是用python直接写代码,代码和测试数据分离,测试数据放在excel中保存。这种实现最快捷方便,但也有些缺点:
(1)用例管理不太方便,不直观;
(2)HTMLTestRunner输出报告做的比较烂。
相较而言,robot framework具有用例管理清晰,输出报告美观的特点。但robot的缺点就是编码起来不如python直接写代码方便。所以,为了快速搭建http接口自动化框架用于回归测试,我直接用python写了一个框架。为了后续长远考虑,便于用例管理,测试报告美观,且集成到测试平台工具化以及推广给rd和其他qa同学使用,又用robot搭建了一套框架。本文就详细说明该搭建过程。
搭建思路
框架采用robot和python实现,因为robot中的复杂逻辑实现起来比较繁琐,故选择用python实现,然后以外部库的形式导入robot中使用。测试用例数据保存在excel中。
使用过robot的人了解,robot中测试维度划分为测试套件(Test Suite)和测试用例(Test Case),一个Suite为一组Case的集合,每个Case对应为我们手工执行测试时的Case。
假设测试一个路径为/areaplug/showCityName的http接口,常规方法是在robot中新建一个showCityName的Suite,其下包含测试该http接口的用例集,如下图所示:

showCityName Test Suite
倘若测试该接口有20个异常用例,则建立20条相应的test case。但是,对于测试http接口来讲,以上用例无非就是请求参数和响应不一样而已,发送请求的逻辑是一模一样的。所以,这20条test case其实用一条test case就能实现了,在这1条case中分别遍历读取20个异常用例的测试数据执行测试就ok了。所以最后构造的suite和case如下:
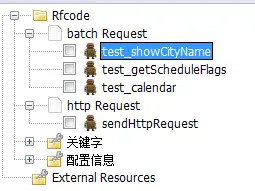
接口case
图中,batch_Request为测试套件,其下的每个robot的test case对应一个http接口测试场景,比如测试路径为/areaplug/showCityName的http接口,该接口的所有正向和异常用例均在test_showCityName中实现,在test_showCityName中读取测试数据文件,获取该接口的测试用例数目,遍历每一条测试用例数据,调用http_Request下的sendHttpRequest发送http请求。其实,这里的test_showCityName就相当于test suite了,而遍历测试数据文件中的每一行测试数据去调用sendHttpRequest时,就相当于生成了一条test case,这样就可以将一个接口的所有测试用例用robot的一条test case实现(实质是robot的一条test case相当于一个test suite,在这个robot的test case中动态生成n条test case)。整个流程如下图所示:
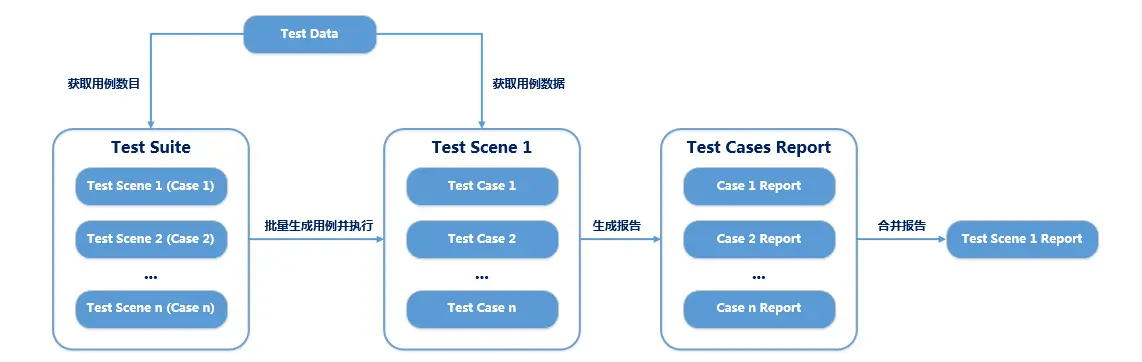
框架流程图
搭建
测试数据
测试数据保存在excel中,每一个sheet页对应一个测试场景,即一个http接口。该sheet也保存有测试该接口的所有测试用例数据以及接口路径和请求方法,如下图所示(这里仅仅是一个demo,实际回归测试时,会有大量的用例和数据):
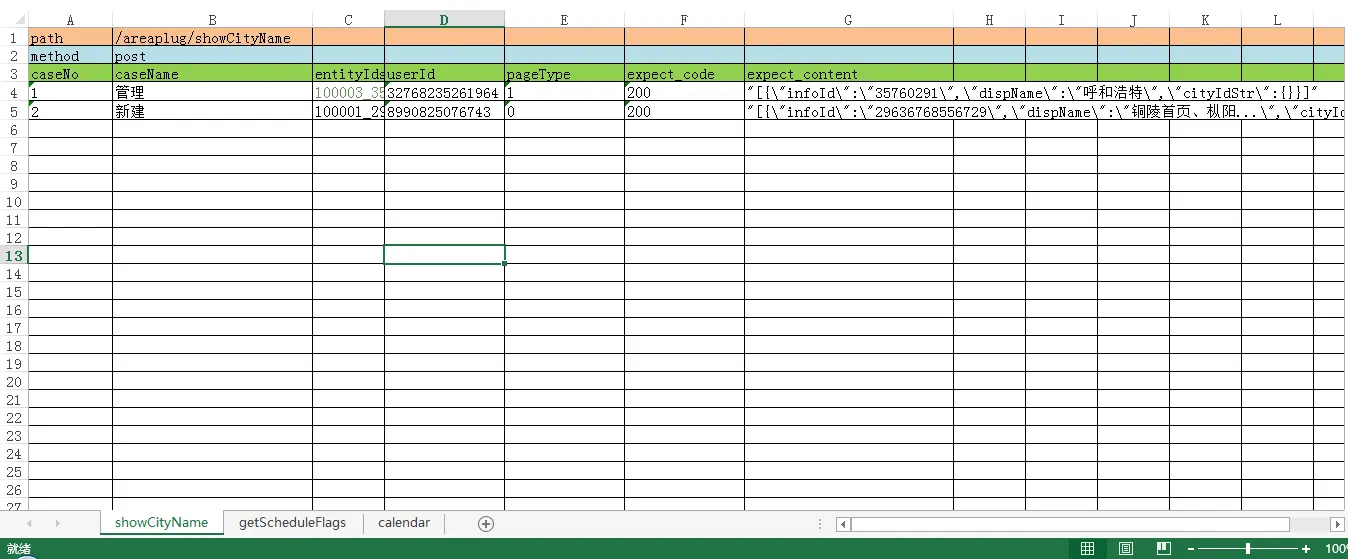
测试数据
测试框架
整个工程目录如下:
E:\LLF_58TESTSUITES\JZ_WEBINTERGRATION\ROBOT_CODE
│ execPybot.bat
│
├─pycode
│ │ Common_Excel.py
│ │ Common_Excel.pyc
│ │ Common_Exec.py
│ │ Common_Exec.pyc
│ │ testHTTP.py
│ │ __init__.py
│ │
│ ├─.idea
│ │ │ misc.xml
│ │ │ modules.xml
│ │ │ pycode.iml
│ │ │ workspace.xml
│ │ │
│ │ └─inspectionProfiles
│ └─__pycache__
│ Common_Excel.cpython-36.pyc
│ Common_Exec.cpython-36.pyc
│ __init__.cpython-36.pyc
│
├─report
│ │ log.html
│ │ output.xml
│ │ report.html
│ │
│ └─TestCaseReport
│ ├─result_calendar
│ │ log_20180130195712.html
│ │ output_20180130195712.xml
│ │ report_20180130195712.html
│ │
│ ├─result_getScheduleFlags
│ │ log_20180130195710.html
│ │ output_20180130195710.xml
│ │ report_20180130195710.html
│ │
│ └─result_showCityName
│ log_20180130195707.html
│ output_20180130195707.xml
│ report_20180130195707.html
│
├─rfcode
│ │ batch_Request.txt
│ │ http_Request.txt
│ │ __init__.robot
│ │
│ ├─关键字
│ │ 关键字index.txt
│ │ 自定义关键字.txt
│ │
│ └─配置信息
│ config.txt
│ configIndex.txt
│ RequestHeaders.txt
│
└─testData
testData.xlsx工程有4部分构成:
- pycode
由于robot中复杂逻辑的实现比较繁琐,所以将一些复杂逻辑直接用python代码实现,然后以外部库的形式导入robot中调用。共有2个文件:
Common_Excel.py
主要负责对测试数据excel文件的读取操作。
# coding: utf-8
import xlrd
def getTestData(testDataFile, testScene, host, caseNo):
'''
从excel中获取测试数据
:param testDataFile: 测试数据文件
:param testScene: 测试场景
:param host: 服务器主机
:param caseNo: 用例No
:param method: 请求方法
:return: url,用例No,用例名称,请求参数,预期返回码,预期响应内容
'''
caseNo = int(caseNo)
data = xlrd.open_workbook(testDataFile)
table = data.sheet_by_name(testScene)
cols = table.ncols
resource_path = table.cell(0, 1).value # 文件路径
url = "http://" + host + resource_path # 访问的url
method = table.cell(1, 1).value # 请求方法
dict_params = {}
for i in range(cols):
dict_params[table.cell(2, i).value] = table.cell(caseNo+2, i).value
caseNo = dict_params.pop("caseNo")
caseName = dict_params.pop("caseName")
expectCode = dict_params.pop("expect_code")
expectCotent = dict_params.pop("expect_content")
testName = "TestCase" + caseNo + "_" + caseName
return method, url, caseNo, testName, dict_params, expectCode, expectCotent
def getTestCaseNum(testDataFile, testScene):
'''
获取testScene测试场景中的测试用例数
:param testDataFile: 测试数据文件
:param testScene: 测试场景
:return: 测试用例数
'''
data = xlrd.open_workbook(testDataFile)
table = data.sheet_by_name(testScene)
rows = table.nrows
return rows-3
def getTestHttpMethod(testDataFile, testScene):
'''
获取testScene测试场景的请求方法
:param testDataFile: 测试数据文件
:param testScene: 测试场景
:return: 请求方法
'''
data = xlrd.open_workbook(testDataFile)
table = data.sheet_by_name(testScene)
method = table.cell(1, 1).value # 请求方法
return methodCommon_Exec.py
主要负责根据测试数据批量构造pybot命令来调用robot执行测试。
# coding: utf-8
import requests
import os
import time
def batch_Call(robot_testSuite, robot_testCase, testScene, caseNum, testCaseReportPath, execTime):
'''
批量执行testScene测试场景下的用例
:param robot_testSuite: robot testSuite路径
:param robot_testCase: robot testCase路径
:param testScene: 测试场景
:param caseNum: 用例数
:param testCaseReportPath: 业务用例测试报告路径
:param execTime: 执行时间
:return:
'''
try:
for caseNo in range(caseNum):
testCase = ""
caseNo = caseNo + 1
testName = "testcase" + "_" + str(caseNo)
output_dir = "-d " + testCaseReportPath + "/result_{0}".format(testScene) # 输出目录
output_xml = "-o output_{0}_{1}.xml".format(testName, execTime)
output_log = "-l log_{0}_{1}.html".format(testName, execTime)
output_report = "-r report_{0}_{1}.html".format(testName, execTime)
variable = "-v caseNo:" + str(caseNo) + " -v testScene:" + testScene
testCase = "--test " + robot_testCase
pybot_cmd = "pybot " + output_dir + " " + output_xml + " " + output_log + " " + output_report + " " + variable + " " + " " + testCase + " " + robot_testSuite
os.system(pybot_cmd) # 执行pybot命令
return "done"
except Exception as e:
return "Error: " + str(e)
def send_HttpRequest(url, data=None, headers=None, method=None):
'''
发送http请求
:param url: 请求的url
:param data: 请求数据
:param headers: 请求头
:param method: 请求方法
:return: 响应码,响应内容
'''
if method == "get":
response = requests.get(url, data, headers=headers)
if method == "post":
response = requests.post(url, data, headers=headers)
code = str(response.status_code)
content = response.content.decode("utf-8") # 转码
return code, content
def cleanLogs(testScene, testCaseReportPath):
'''
删除硬盘中合并前的测试报告
:param testScene: 测试场景
:param testCaseReportPath: 业务用例测试报告路径
:return:
'''
testCaseReportPath = testCaseReportPath + "/result_{0}".format(testScene)
report_files = testCaseReportPath + "/report_testcase*"
xml_files = testCaseReportPath + "/output_testcase*"
log_files = testCaseReportPath + "/log_testcase*"
cmd = "del " + report_files + " " + xml_files + " " + log_files # windows
cmd = cmd.replace("/", "\\")
print(cmd)
os.system(cmd)
def getCurtime():
'''
获取当前时间
:return: 当前时间
'''
return time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S", time.localtime(time.time()))
def mergeReport(testScene, testCaseReportPath, execTime):
'''
# 合并报告
:param testScene: 测试场景
:param testCaseReportPath: 业务用例测试报告路径
:param execTime: 执行时间
:return:
'''
try:
output_dir = "-d " + testCaseReportPath + "/result_{0}".format(testScene) # 输出目录
output_xml = "-o output_{0}.xml".format(execTime)
output_log = "-l log_{0}.html".format(execTime)
output_report = "-r report_{0}.html".format(execTime)
# 被合并的报告
merge_report = testCaseReportPath + "/result_{0}".format(testScene) + "/output_testcase_*.xml"
name = "--name " + testScene
rebot_cmd = r"rebot " + output_dir + " " + output_xml + " " + output_log + " " + output_report + " " + name + " " + merge_report
os.system(rebot_cmd) # 执行rebot命令
return "done"
except Exception as e:
return "Error: " + str(e)report
该目录用于存放测试报告。其中report目录下的robot测试报告为测试Suite的测试报告,而TestCaseReport下会根据不同的测试场景生成对应该场景名称的测试报告文件夹,其下会包含该测试场景下所有用例的合并报告(即excel中的每一条case会生成一个报告,最后会将这些cases的报告合并为一个报告,作为该测试场景即该http接口的测试报告)。
rfcode
该目录下为robot的代码。
batch_Request.txt
batch_Request下包含要测试的各http接口对应的测试场景(即robot的测试用例)。在各测试场景中会设置${testScene}变量,通过该变量去excel文件中对应的sheet页获取相应的测试数据。
*** Settings ***
Library ../pycode/Common_Exec.py
Resource 关键字/关键字index.txt
Resource 配置信息/configIndex.txt
Library ../pycode/Common_Excel.py
*** Test Cases ***
test_showCityName
[Documentation] /areaplug/showCityName
# 测试场景
${testScene} Set Variable showCityName
# 请求方法
${method} getTestHttpMethod ${testDataFile} ${testScene}
执行测试 ${testScene} ${method}
test_getScheduleFlags
[Documentation] /ManageSchedule/getScheduleFlags
# 测试场景
${testScene} Set Variable getScheduleFlags
# 请求方法
${method} getTestHttpMethod ${testDataFile} ${testScene}
执行测试 ${testScene} ${method}
test_calendar
# 测试场景
${testScene} Set Variable calendar
# 请求方法
${method} getTestHttpMethod ${testDataFile} ${testScene}
执行测试 ${testScene} ${method}http_Request.txt
在各测试场景中会根据excel中的测试用例记录数目去批量调用http_Request下的sendHttpRequest执行http接口测试。在sendHttpRequest中会根据caseNo去excel中查询相应测试数据,并发送对应的http请求到相应http接口中。收到响应后,与excel中的预期响应码和响应内容做比对。
*** Settings ***
Library ../pycode/Common_Exec.py
Library ../pycode/Common_Excel.py
Resource 关键字/关键字index.txt
*** Test Cases ***
sendHttpRequest
# 获取测试用例数据
${method} ${url} ${caseNo} ${testName} ${dict_params} ${expectCode} ${expectCotent}
... getTestData ${testDataFile} ${testScene} ${Host} ${caseNo}
# 设置用例说明
Set Test Documentation ${testName}
# 请求头
${headers} 获取请求头
#根据method发送对应的http请求
${actualCode} ${actualContent} send_HttpRequest ${url} ${dict_params} ${headers} ${method}
# 响应码比对
Should Be Equal ${actualCode} ${expectCode}
# 响应内容比对
Should Be Equal ${actualContent} ${expectCotent}关键字
关键字模块主要是对一些复用逻辑的封装。
*** Settings ***
Resource ../配置信息/configIndex.txt
Library ../../pycode/Common_Excel.py
Library ../../pycode/Common_Exec.py
*** Keywords ***
获取请求头
${dict_headers} Create Dictionary Host=${Host} User-Agent=${User-Agent} Accept=${Accept} Accept-Language=${Accept-Language} Accept-Encoding=${Accept-Encoding}
... Cookie=${Cookie} Connection=${Connection} Cache-Control=${Cache-Control}
Return From Keyword ${dict_headers}
执行测试
[Arguments] ${testScene} ${method} # 测试场景|请求方法
# 获取用例数目
${case_num} getTestCaseNum ${testDataFile} ${testScene}
# 获取当前时间
${execTime} getCurtime
#批量执行testScene测试场景下的用例
${status} batch_Call ${httpTestSuite} ${httpRequestTestCase} ${testScene} ${case_num} ${testCaseReportPath}
... ${execTime}
log ${status}
# 合并报告
${status} mergeReport ${testScene} ${testCaseReportPath} ${execTime}
log ${status}
# 清理合并前的报告
cleanLogs ${testScene} ${testCaseReportPath}配置信息
配置信息中存储配置信息以及通讯头的信息。通讯头中有cookie,保存有登录信息,通讯头的部分涉及隐私,故这部分数据不放出来了。
config.txt
*** Settings ***
*** Variables ***
${testDataFile} E:/llf_58TestSuites/jz_webIntergration/robot_code/testData/testData.xlsx # 测试数据
${httpRequestTestCase} sendHttpRequest # http请求用例模板
${httpTestSuite} E:/llf_58TestSuites/jz_webIntergration/robot_code/rfcode/http_Request.txt # http请求测试套件
${testCaseReportPath} E:/llf_58TestSuites/jz_webIntergration/robot_code/report/TestCaseReport # 业务用例测试报告路径RequestHeaders.txt
*** Settings ***
Documentation 请求头信息
*** Variables ***
${Host} ******* # 服务器主机
${User-Agent} Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:56.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/56.0 # 浏览器代理
${Accept} text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
${Accept-Language} en-US,en;q=0.5
${Accept-Encoding} gzip, deflate
${Cookie} ************
${Connection} keep-alive
${Cache-Control} max-age=0
${Upgrade-Insecure-Requests} ***- testData
该目录下存放测试数据excel文件。
执行测试
pybot -d E:/llf_58TestSuites/jz_webIntergration/robot_code/report -o output.xml -l log.html -r report.html E:\llf_58TestSuites\jz_webIntergration\robot_code\rfcode\batch_Request.txt
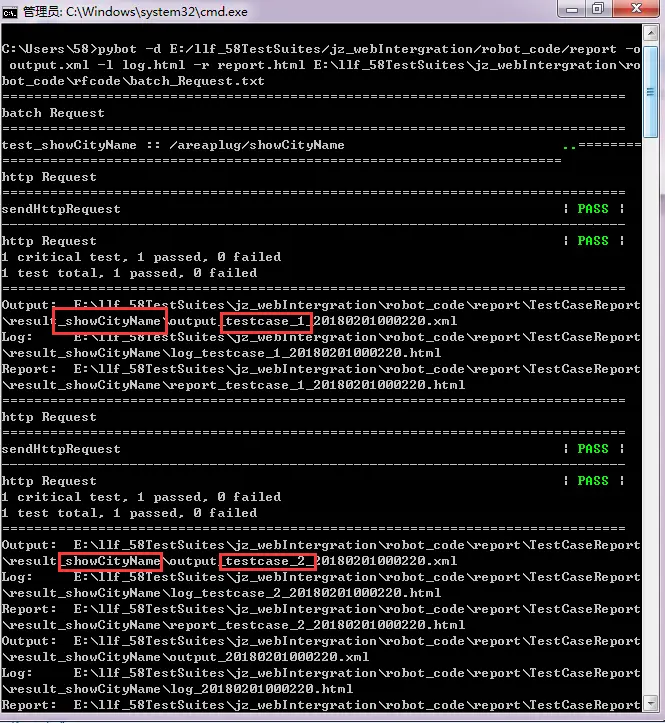
执行测试
可见,showCityName测试场景已根据excel中的用例条数批量执行了测试。
进入TestCaseReport目录,可以看到已根据测试场景分别生成了对应目录的测试报告:
各测试场景的报告存在相应目录中
进入showCityName目录,打开最新生成的该场景测试报告:
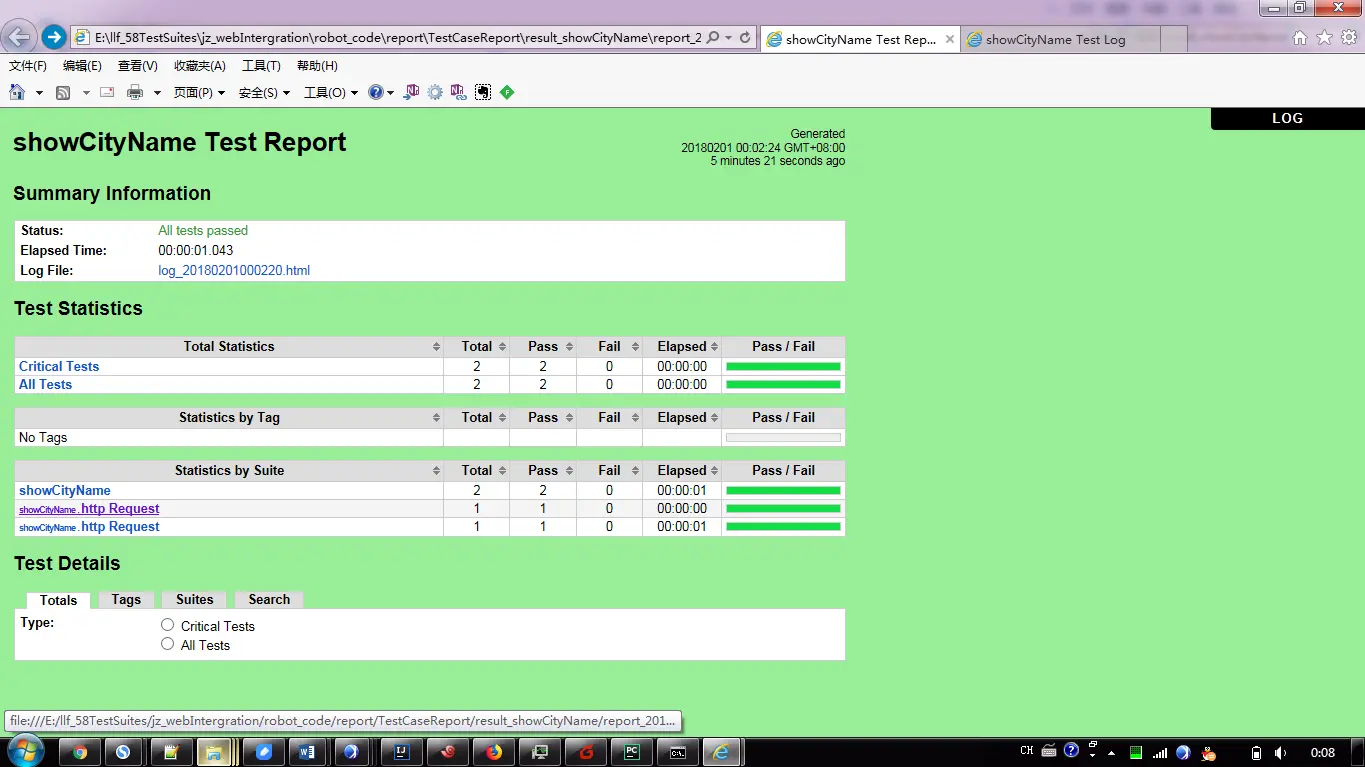
showCityName场景测试报告
 根据说明列辨别是哪条用例的报告数据
根据说明列辨别是哪条用例的报告数据
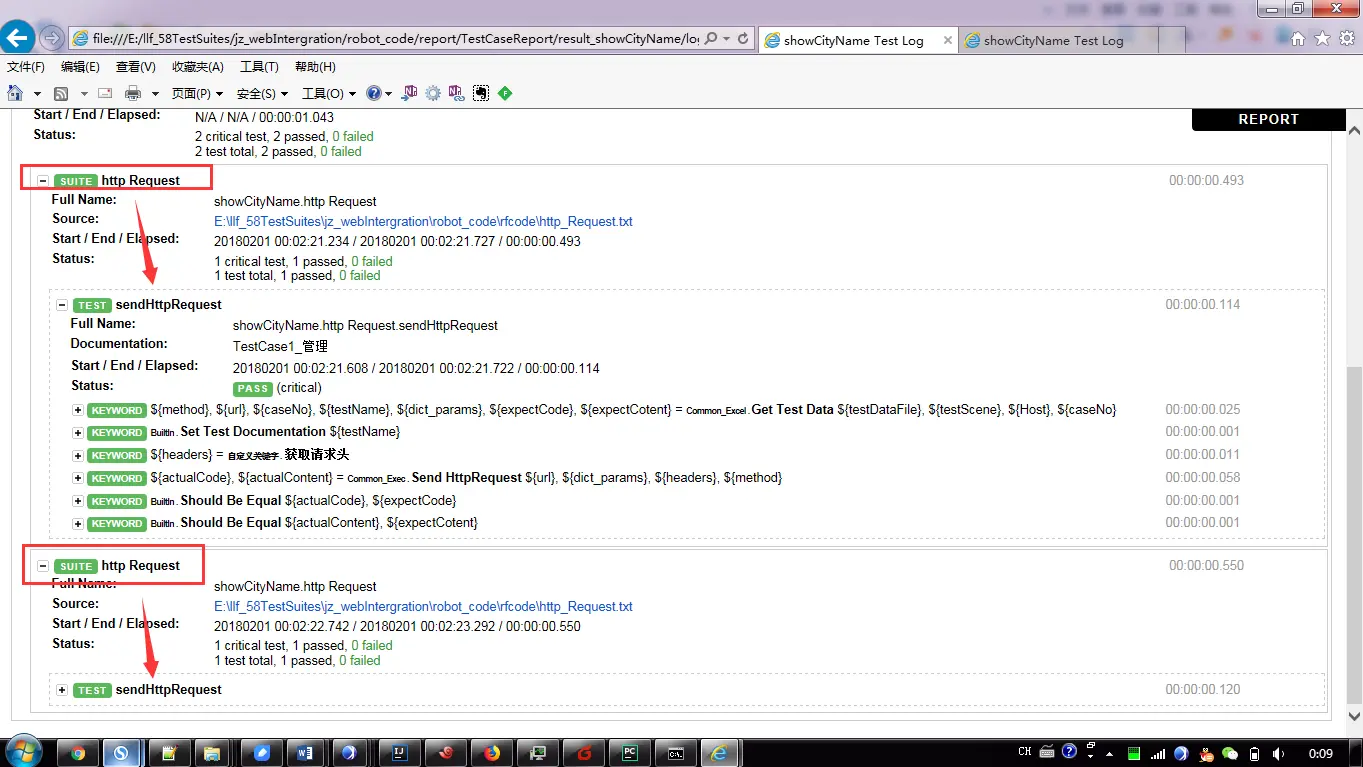
sendHttpRequest被批量调用
总结
经过了上一个项目吃过的亏,这次在http接口测试需求前,提前把自动化框架搭好了,便于测试后期的回归测试。其实http接口自动化测试框架可以很方便的搭建,之所以这么费劲用robot去实现,也是为了后续用例管理以及集成到平台实现工具化的考虑结果。希望这篇文章可以对其他同学有所帮助。
最后感谢每一个认真阅读我文章的人,礼尚往来总是要有的,虽然不是什么很值钱的东西,如果你用得到的话可以直接拿走:
这些资料,对于【软件测试】的朋友来说应该是最全面最完整的备战仓库,这个仓库也陪伴上万个测试工程师们走过最艰难的路程,希望也能帮助到你!























 2155
2155

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








