Nginx核心配置详解
全局配置
user nginx nginx;
worker_processes [number | auto];
worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010 00000100 00001000;
worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000;
error_log /apps/nginx/logs/error.log error;
pid /apps/nginx/logs/nginx.pid;
worker_priority 0;
worker_rlimit_nofile 65536;
[root@s2 ~]
daemon off;
master_process off|on;
events {
worker_connections 65536;
use epoll;
accept_mutex on;
multi_accept on;
}
http详细配置
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
location ~ /passwd.html {
deny all;
}
}
location /linux38/passwd.ht {
deny all;
}
核心配置示例
- 基于不同的IP、不同的端⼝以及不⽤得域名实现不同的虚拟主机,依赖于核⼼模块ngx_http_core_module实现。
//修改主配置文件设置,子配置文件路径
vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
//http块中添加,子配置文件路径
include /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/*.conf;
--------------------------
//新建编辑pc端子配置文件
vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf
//配置文件内容
server{
listen 80;
server_name www.pc.com;
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
}
}
---------------------------
//新建编辑mobile端子配置文件
vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/mobile.conf
//配置文件内容
server{
listen 80;
server_name www.mobile.com;
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/mobile;
}
}
-----------------------------
//创建测试页面
echo "this is pc web" > /data/nginx/html/pc/index.html
echo "this is mobile web" > /data/nginx/html/mobile/index.html
//重新加载配置文件
/apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
//修改windows中hosts文件内容添加
172.20.26.104 www.pc.com
172.20.26.104 www.mobile.com
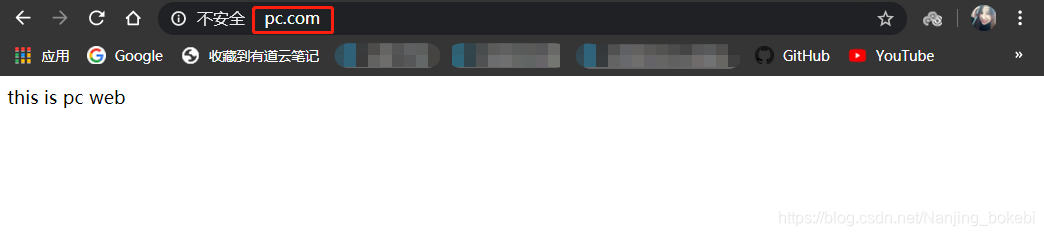
- 浏览器访问http://www.mobile.com/得
- root与alias
- root:指定web的家⽬录,在定义location的时候,⽂件的绝对路径等于 root+location,如:
//编辑pc端子配置文件
vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf
//配置文件如下
server{
listen 80;
server_name www.pc.com;
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
}
location /images{
root /data/nginx/html/pc
index index.html
}
}
----------------------------------------
//查看图片存放位置
tree /data/nginx/html/pc/images/
/data/nginx/html/pc/images/
└── ms.jpg
- 浏览器访问http://www.pc.com/images/ms.jpg得
- alias:定义路径别名,会把访问的路径重新定义到其指定的路径,如:
//编辑pc端子配置文件
vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf
server{
listen 80;
server_name www.pc.com;
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
}
location /images{
alias /data/nginx/html/pc
内容。
index index.html
}
}
-------------------------------------------
//查看图片存放位置
tree /data/nginx/html/pc/
/data/nginx/html/pc/
├── images
├── index.html
└── ms.jpg
- 浏览器访问http://www.pc.com/images/ms.jpg得

Nginx四层访问控制
location /about {
alias /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
deny 192.168.1.1;
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
allow 10.1.1.0/16;
allow 2001:0db8::/32;
deny all;
}
Nginx账户认证功能
//安装httpd工具包
yum -y install httpd-tools
apt -y isntall apache2-utils
//设置用户1以及密码
htpasswd -cbm /apps/nginx/conf/.htpasswd bokebi1 123456
Adding password for user bokebi1
//设置用户2以及密码
htpasswd -bm /apps/nginx/conf/.htpasswd bokebi2 123456
Adding password for user bokebi2
//查看密码文件
tail /apps/nginx/conf/.htpasswd
user1:$apr1$Rjm0u2Kr$VHvkAIc5OYg.3ZoaGwaGq/
user2:$apr1$nIqnxoJB$LR9W1DTJT.viDJhXa6wHv.
//编辑pc端子配置文件
vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf
location = /login/ {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
auth_basic "login password";
auth_basic_user_file /apps/nginx/conf/.htpasswd;
}
重启nginx并访问测试
自定义错误页面
listen 80;
server_name www.magedu.net;
error_page 500 502 503 504 404 /error.html;
location = /error.html {
root html;
}
重启nginx并访问不存在的⻚⾯进⾏测试
自定义访问日志
[root@s2 ~]
listen 80;
server_name www.magedu.net;
error_page 500 502 503 504 404 /error.html;
access_log /data/nginx/logs/www-magedu-net_access.log;
error_log /data/nginx/logs/www-magedu-net_error.log;
location = /error.html {
root html;
}
重启nginx并访问不存在的⻚⾯进⾏测试并验证是在指定⽬录⽣成新的⽇志⽂件
检测文件是否存在
- try_files会按顺序检查⽂件是否存在,返回第⼀个找到的⽂件或⽂件夹(结尾加斜线表⽰为⽂件夹),如果所有⽂件或⽂件夹都找不到,会进⾏⼀个内部重定向到最后⼀个参数。只有最后⼀个参数可以引起⼀个内部重定向,之前的参数只设置内部URI的指向。最后⼀个参数是回退URI且必须存在,否则会出现内部500错误。
location /about {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
try_files $uri $uri/index.html $uri.html =489;
}
[root@s2 ~]
重启nginx并测试,当访问到http://www.pc.com/about/xx.html等不存在的uri会显⽰default,如果
是⾃定义的状态码则会显⽰在返回数据的状态码中,如:
[root@s2 about]
HTTP/1.1 489
Server: nginx
Date: Thu, 21 Feb 2019 00:11:40 GMT
Content-Length: 0
Connection: keep-alive
Keep-Alive: timeout=65
长连接配置
- keepalive_timeout number; #设定保持连接超时时⻓,0表⽰禁⽌⻓连接,默认为75s,通常配置在http字段作为站点全局配置 keepalive_requests number; #在⼀次⻓连接上所允许请求的资源的最⼤数量,默认为100次
keepalive_requests 3;
keepalive_timeout 65 65;
开启⻓连接后,返回客⼾端的会话保持时间为60s,单次⻓连接累计请求达到指定次数请求或65秒就会被断开,后⾯的
60为发送给客⼾端应答报⽂头部中显⽰的超时时间设置为60s:如不设置客⼾端将不显⽰超时时间。
Keep-Alive:timeout=60
如果设置为0表⽰关闭会话保持功能,将如下显⽰:
Connection:close
//使⽤命令测试:
telnet www.magedu.net 80
Trying 172.18.200.102...
Connected to www.pc.com
Escape character is '^]'.
GET / HTTP/1.1
HOST: www.pc.com
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.14.2
Date: Thu, 14 Mar 2019 17:23:46 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 7
Last-Modified: Thu, 14 Mar 2019 14:54:50 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Keep-Alive: timeout=60
ETag: "5c8a6b3a-7"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
pc web
作为下载服务器配置
//创建所需目录
mkdir /data/nginx/html/pc/download
//编辑配置文件
vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf
location /download {
autoindex on;
autoindex_exact_size on;
gb)
autoindex_localtime on;
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
}
limit_rate rate;
限速与不限速的对⽐:
limit_rate 10k;
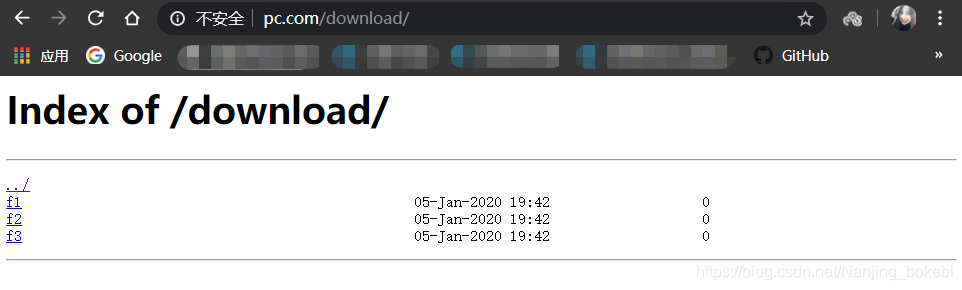
- 浏览器访问http://www.pc.com/download/得
作为上传服务器配置
client_max_body_size 1m;
client_body_buffer_size size;
此⼤⼩时,其将被暂存到磁盘上的由下⾯client_body_temp_path指令所定义的位置
client_body_temp_path path [level1 [level2 [level3]]];
值从后往前截取1位、2位、2位作为⽂件名:
[root@s3 ~]
95f6f65f498c74938064851b1bb 96 3d 4 /data/nginx/html/pc/index.html
1级⽬录占1位16进制,即2^4=16个⽬录 0-f
2级⽬录占2位16进制,即2^8=256个⽬录 00-ff
3级⽬录占2位16进制,即2^8=256个⽬录 00-ff
配置⽰例(一般作为默认配置,所以放置在主配置文件里):
client_max_body_size 10m;
client_body_buffer_size 16k;
client_body_temp_path /apps/nginx/temp 1 2 2;
其他配置
limit_except
- 限制客户端使用除了指定的请求方法之外的其它方法,只能用在location上下文。

GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, DELETE
MKCOL, COPY, MOVE, OPTIONS, PROPFIND,
PROPPATCH, LOCK, UNLOCK, PATCH
limit_except GET HEAD POST {
deny 192.168.111.200
allow 192.168.111.0/24;
deny all;
}
- 表示除了GET、HEAD、POST方法其他方法都限制,
- 主机范围为:禁止192.168.111.200、允许192.168.111.0/24、禁止所有。
- 即仅允许192.168.111.0网段访问,但是禁止192.168.111.200的地址访问
aio

- linux 2.6以上内核提供以下⼏个系统调⽤来⽀持aio:
- 1、SYS_io_setup:建⽴aio 的context
- 2、SYS_io_submit: 提交I/O操作请求
- 3、SYS_io_getevents:获取已完成的I/O事件
- 4、SYS_io_cancel:取消I/O操作请求
- 5、SYS_io_destroy:毁销aio的context
directio
- 是否同步写磁盘

- 操作完全和aio相反,aio是读取⽂件⽽directio是写⽂件到磁盘
- 启⽤直接I/O,默认为关闭,当⽂件⼤于等于给定⼤⼩时,例如directio 4m,同步(直接)写磁盘,⽽⾮写缓存。
open_file_cache
- 是否缓存打开过的⽂件信息

- nginx可以缓存以下三种信息:
(1) ⽂件元数据:⽂件的描述符、⽂件⼤⼩和最近⼀次的修改时间
(2) 打开的⽬录结构
(3) 没有找到的或者没有权限访问的⽂件的相关信息 - max=N:可缓存的缓存项上限数量;达到上限后会使⽤LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使⽤)算法实现
管理 - inactive=time:缓存项的⾮活动时⻓,在此处指定的时⻓内未被命中的或命中的次数少于
open_file_cache_min_uses指令所指定的次数的缓存项即为⾮活动项,将被删除
open_file_cache_errors
- 是否缓存查找时发⽣错误的⽂件⼀类的信息(默认值为off)

open_file_cache_min_uses
- open_file_cache指令的inactive参数指定的时⻓内,⾄少被命中此处指定的次数⽅可被归类为活动项(默认值为1)

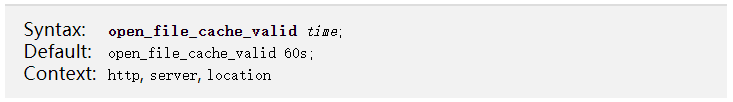
open_file_cache_valid
- 缓存项有效性的检查验证频率(默认值为60s)
- 示例
aio on;
directio 4m;
open_file_cache max=1000 inactive=20s;
open_file_cache_valid 30s;
open_file_cache_min_uses 2;
open_file_cache_errors on;




































 185
185

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








