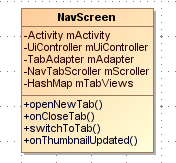
前面我们简单介绍了Tab和TabControl的大体结构,但是如果想要实现浏览器的多标签切换功能, 还需要一个用户交互界面, 这个界面在Android Browser中就是NavScreen了:
这里我们介绍一下下面这个UI的实现, 主要代码在NavScreen.java中.
我们知道, 在Android Browser中 用以和用户打交道的功能基本都被限制在了BaseUI中, 在手机上它的实现就是PhoneUI:
显示多窗口列表当然也是不例外的:PhoneUI::showNavScreen:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
|
//点击按钮显示多窗口列表
void
showNavScreen() {
mUiController.setBlockEvents(
true
);
//拦截多窗口外的其他操作
if
(mNavScreen ==
null
) {
mNavScreen =
new
NavScreen(mActivity, mUiController,
this
);
mCustomViewContainer.addView(mNavScreen, COVER_SCREEN_PARAMS);
}
else
{
mNavScreen.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mNavScreen.setAlpha(1f);
mNavScreen.refreshAdapter();
}
mActiveTab.capture();
if
(mAnimScreen ==
null
) {
//这是动画的视图 ,多标签窗口切换的动画师phoneui来实现的而不是 navscreen ,也就是说我点击一个tab 剩下的看到的其实是
//真正的web窗口
mAnimScreen =
new
AnimScreen(mActivity);
}
else
{
mAnimScreen.mMain.setAlpha(1f);
mAnimScreen.mTitle.setAlpha(1f);
mAnimScreen.setScaleFactor(1f);
}
//设置动画需要截图的view
mAnimScreen.set(getTitleBar(), getWebView());
if
(mAnimScreen.mMain.getParent() ==
null
) {
//如果animscreen 的main没有父亲, 说明是执行了 全屏模式
mCustomViewContainer.addView(mAnimScreen.mMain, COVER_SCREEN_PARAMS);
}
mCustomViewContainer.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mCustomViewContainer.bringToFront();
//把这个view放到顶层
mAnimScreen.mMain.layout(
0
,
0
, mContentView.getWidth(),
mContentView.getHeight());
//动画的宽度和contentview一样大
int
fromLeft =
0
;
int
fromTop = getTitleBar().getHeight();
int
fromRight = mContentView.getWidth();
int
fromBottom = mContentView.getHeight();
int
width = mActivity.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.nav_tab_width);
int
height = mActivity.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.nav_tab_height);
int
ntth = mActivity.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.nav_tab_titleheight);
int
toLeft = (mContentView.getWidth() - width) /
2
;
int
toTop = ((fromBottom - (ntth + height)) /
2
+ ntth);
int
toRight = toLeft + width;
int
toBottom = toTop + height;
float
scaleFactor = width / (
float
) mContentView.getWidth();
detachTab(mActiveTab);
mContentView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
AnimatorSet set1 =
new
AnimatorSet();
AnimatorSet inanim =
new
AnimatorSet();
//使用上下左右的位置 使得 tab的运动轨迹 从整个屏幕 位置缩小到tab,无论当前tab在哪里
ObjectAnimator tx = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mAnimScreen.mContent,
"left"
,
fromLeft, toLeft);
ObjectAnimator ty = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mAnimScreen.mContent,
"top"
,
fromTop, toTop);
ObjectAnimator tr = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mAnimScreen.mContent,
"right"
,
fromRight, toRight);
ObjectAnimator tb = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mAnimScreen.mContent,
"bottom"
,
fromBottom, toBottom);
ObjectAnimator title = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mAnimScreen.mTitle,
"alpha"
,
1f, 0f);
ObjectAnimator sx = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mAnimScreen,
"scaleFactor"
,
1f, scaleFactor);
ObjectAnimator blend1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mAnimScreen.mMain,
"alpha"
, 1f, 0f);
blend1.setDuration(
100
);
inanim.playTogether(tx, ty, tr, tb, sx, title);
inanim.setDuration(
200
);
set1.addListener(
new
AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public
void
onAnimationEnd(Animator anim) {
mCustomViewContainer.removeView(mAnimScreen.mMain);
finishAnimationIn();
mUiController.setBlockEvents(
false
);
}
});
set1.playSequentially(inanim, blend1);
//inanim播放ok后播放 blend1 也就是先缩放然后在透明
set1.start();
}
|
他的结构也不是很复杂, 拿到了Activity 和Controller的引用, 然后有一个NavTabScroller (继承自NavTabScroller )和 一个TabAdapter (继承自 BaseAdapter)的成员, 他们是多窗口列表view的具体实现和数据来源了. NavScreen有一些Tab的操作, 他们基本都需要通知到Controller, 因为NavScreen只不过是UI 真正的操作是Controller来做的.
看一下NavTabScroller 是一个ScrollView, 多窗口之所以可以滑动就全靠他了, 他还实现了横向竖向滑动, 载入adapter的数据等功能:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
public
class
NavTabScroller
extends
ScrollerView {
static
final
int
INVALID_POSITION = -
1
;
static
final
float
[] PULL_FACTOR = {
2
.5f,
0
.9f };
interface
OnRemoveListener {
public
void
onRemovePosition(
int
position);
}
interface
OnLayoutListener {
public
void
onLayout(
int
l,
int
t,
int
r,
int
b);
}
private
ContentLayout mContentView;
//实际上是一个linearlayout
private
BaseAdapter mAdapter;
private
OnRemoveListener mRemoveListener;
private
OnLayoutListener mLayoutListener;
private
int
mGap;
private
int
mGapPosition;
private
ObjectAnimator mGapAnimator;
// after drag animation velocity in pixels/sec
private
static
final
float
MIN_VELOCITY =
1500
;
//最小的滑动
private
AnimatorSet mAnimator;
private
float
mFlingVelocity;
private
boolean
mNeedsScroll;
private
int
mScrollPosition;
DecelerateInterpolator mCubic;
int
mPullValue;
|
他装载数据的操作是setAdapter函数调用handleDataChanged函数实现的:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
//装载多窗口数据
void
handleDataChanged(
int
newscroll) {
int
scroll = getScrollValue();
//是x方向scroll 还是y
if
(mGapAnimator !=
null
) {
mGapAnimator.cancel();
//取消动画
}
mContentView.removeAllViews();
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < mAdapter.getCount(); i++) {
View v = mAdapter.getView(i,
null
, mContentView);
//从adapter中拿到view 添加到linearlayout上listview等其实也是这样实现的
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp =
new
LinearLayout.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
lp.gravity = (mHorizontal ? Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL : Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL);
mContentView.addView(v, lp);
//添加tabview到那个mContentView . 居中显示
if
(mGapPosition > INVALID_POSITION){
adjustViewGap(v, i);
}
}
if
(newscroll > INVALID_POSITION) {
newscroll = Math.min(mAdapter.getCount() -
1
, newscroll);
//newscroll 是从0 开始到 adapter.count的
mNeedsScroll =
true
;
mScrollPosition = newscroll;
requestLayout();
}
else
{
setScrollValue(scroll);
//滑动到顶部/左边
}
}
|
好 大体的UI就差不多这些了, 下面是其动画的实现:
其动画分为以下几个:
1.点击多窗口按钮  的时候, 整个浏览器窗口会缩小到多窗口列表, 然后显示出其他的窗口标签供作者选择
的时候, 整个浏览器窗口会缩小到多窗口列表, 然后显示出其他的窗口标签供作者选择
整个窗口会扩到到整个屏幕
3.在多窗口列表中左右滑动任何一个窗口, 整个窗口会渐变和移动 直到删除
4.其实这个"listview"还有回弹功能, 效果是使小窗口的间距缩小,不过效果不是很明显, 应该有点小bug
那就从第一个动画开始分析:
这个动画是在PhoneUI::showNavScreen()函数实现的, 其实就是一个animator动画:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
|
//点击按钮显示多窗口列表
void
showNavScreen() {
mUiController.setBlockEvents(
true
);
//拦截多窗口外的其他操作
if
(mNavScreen ==
null
) {
mNavScreen =
new
NavScreen(mActivity, mUiController,
this
);
mCustomViewContainer.addView(mNavScreen, COVER_SCREEN_PARAMS);
}
else
{
mNavScreen.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mNavScreen.setAlpha(1f);
mNavScreen.refreshAdapter();
}
mActiveTab.capture();
if
(mAnimScreen ==
null
) {
//这是动画的视图 ,多标签窗口切换的动画师phoneui来实现的而不是 navscreen ,也就是说我点击一个tab 剩下的看到的其实是
//真正的web窗口
mAnimScreen =
new
AnimScreen(mActivity);
}
else
{
mAnimScreen.mMain.setAlpha(1f);
mAnimScreen.mTitle.setAlpha(1f);
mAnimScreen.setScaleFactor(1f);
}
//设置动画需要截图的view
mAnimScreen.set(getTitleBar(), getWebView());
if
(mAnimScreen.mMain.getParent() ==
null
) {
//如果animscreen 的main没有父亲, 说明是执行了 全屏模式
mCustomViewContainer.addView(mAnimScreen.mMain, COVER_SCREEN_PARAMS);
//把需要做动画的view添加到整个布局的上层
}
mCustomViewContainer.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mCustomViewContainer.bringToFront();
//把这个view放到顶层
mAnimScreen.mMain.layout(
0
,
0
, mContentView.getWidth(),
mContentView.getHeight());
//动画的宽度和contentview一样大
int
fromLeft =
0
;
int
fromTop = getTitleBar().getHeight();
int
fromRight = mContentView.getWidth();
int
fromBottom = mContentView.getHeight();
int
width = mActivity.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.nav_tab_width);
int
height = mActivity.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.nav_tab_height);
int
ntth = mActivity.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.nav_tab_titleheight);
int
toLeft = (mContentView.getWidth() - width) /
2
;
int
toTop = ((fromBottom - (ntth + height)) /
2
+ ntth);
int
toRight = toLeft + width;
int
toBottom = toTop + height;
float
scaleFactor = width / (
float
) mContentView.getWidth();
detachTab(mActiveTab);
mContentView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
AnimatorSet set1 =
new
AnimatorSet();
AnimatorSet inanim =
new
AnimatorSet();
//使用上下左右的位置 使得 tab的运动轨迹 从整个屏幕 位置缩小到屏幕的中心 ,无论当前tab在哪里, 不过轨迹是一样的
ObjectAnimator tx = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mAnimScreen.mContent,
"left"
,
fromLeft, toLeft);
ObjectAnimator ty = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mAnimScreen.mContent,
"top"
,
fromTop, toTop);
ObjectAnimator tr = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mAnimScreen.mContent,
"right"
,
fromRight, toRight);
ObjectAnimator tb = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mAnimScreen.mContent,
"bottom"
,
fromBottom, toBottom);
ObjectAnimator title = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mAnimScreen.mTitle,
"alpha"
,
1f, 0f);
ObjectAnimator sx = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mAnimScreen,
"scaleFactor"
,
1f, scaleFactor);
ObjectAnimator blend1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mAnimScreen.mMain,
"alpha"
, 1f, 0f);
blend1.setDuration(
100
);
inanim.playTogether(tx, ty, tr, tb, sx, title);
inanim.setDuration(
200
);
set1.addListener(
new
AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public
void
onAnimationEnd(Animator anim) {
mCustomViewContainer.removeView(mAnimScreen.mMain);
//把做动画的view删除
finishAnimationIn();
mUiController.setBlockEvents(
false
);
}
});
set1.playSequentially(inanim, blend1);
//inanim播放ok后播放 blend1 也就是先缩放然后在透明
set1.start();
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
|
/*
*其实动画是使用两个imageview在做, 这两个imageview 分别绘制了titlebar和webview
*/
static
class
AnimScreen {
private
View mMain;
private
ImageView mTitle;
private
ImageView mContent;
private
float
mScale;
private
Bitmap mTitleBarBitmap;
private
Bitmap mContentBitmap;
public
AnimScreen(Context ctx) {
mMain = LayoutInflater.from(ctx).inflate(R.layout.anim_screen,
null
);
mTitle = (ImageView) mMain.findViewById(R.id.title);
mContent = (ImageView) mMain.findViewById(R.id.content);
mContent.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.MATRIX);
mContent.setImageMatrix(
new
Matrix());
mScale =
1
.0f;
setScaleFactor(getScaleFactor());
}
/**
* 包titilebar和webview的截图画到动画的view上
* @param tbar
* @param web
*/
public
void
set(TitleBar tbar, WebView web) {
if
(tbar ==
null
|| web ==
null
) {
return
;
}
if
(tbar.getWidth() >
0
&& tbar.getEmbeddedHeight() >
0
) {
if
(mTitleBarBitmap ==
null
|| mTitleBarBitmap.getWidth() != tbar.getWidth()
|| mTitleBarBitmap.getHeight() != tbar.getEmbeddedHeight()) {
mTitleBarBitmap = safeCreateBitmap(tbar.getWidth(),
tbar.getEmbeddedHeight());
}
if
(mTitleBarBitmap !=
null
) {
Canvas c =
new
Canvas(mTitleBarBitmap);
tbar.draw(c);
c.setBitmap(
null
);
}
}
else
{
mTitleBarBitmap =
null
;
}
mTitle.setImageBitmap(mTitleBarBitmap);
mTitle.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
int
h = web.getHeight() - tbar.getEmbeddedHeight();
if
(mContentBitmap ==
null
|| mContentBitmap.getWidth() != web.getWidth()
|| mContentBitmap.getHeight() != h) {
mContentBitmap = safeCreateBitmap(web.getWidth(), h);
}
if
(mContentBitmap !=
null
) {
Canvas c =
new
Canvas(mContentBitmap);
int
tx = web.getScrollX();
int
ty = web.getScrollY();
c.translate(-tx, -ty - tbar.getEmbeddedHeight());
web.draw(c);
c.setBitmap(
null
);
}
mContent.setImageBitmap(mContentBitmap);
}
private
Bitmap safeCreateBitmap(
int
width,
int
height) {
if
(width <=
0
|| height <=
0
) {
Log.w(LOGTAG,
"safeCreateBitmap failed! width: "
+ width
+
", height: "
+ height);
return
null
;
}
return
Bitmap.createBitmap(width, height, Bitmap.Config.RGB_565);
}
/*
* 这个版本至显示content
*/
public
void
set(Bitmap image) {
mTitle.setVisibility(View.GONE);
mContent.setImageBitmap(image);
}
private
void
setScaleFactor(
float
sf) {
mScale = sf;
Matrix m =
new
Matrix();
m.postScale(sf,sf);
mContent.setImageMatrix(m);
}
private
float
getScaleFactor() {
return
mScale;
}
}
|
知道了第一个动画如何实现, 第二个动画就好理解了, 正好是第一个动画的反过来, 不过这次动画的轨迹可能不一样, 因为用户可能点击的是上面或者最底下的tab:当然, 通过navScreen就可以拿到选择tab的位置:整个操作调用的地方还是比较多的比如选择tab 新建tab等都会调用到这个和动画.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
|
//隐藏多窗口切换 动画基本同上面显示多标签
void
hideNavScreen(
int
position,
boolean
animate) {
if
(!showingNavScreen())
return
;
final
Tab tab = mUiController.getTabControl().getTab(position);
if
((tab ==
null
) || !animate) {
//似乎还有别的可以打开tab的方式但是还不是很清楚在哪里
if
(tab !=
null
) {
setActiveTab(tab);
}
else
if
(mTabControl.getTabCount() >
0
) {
// use a fallback tab
setActiveTab(mTabControl.getCurrentTab());
}
mContentView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
finishAnimateOut();
return
;
}
NavTabView tabview = (NavTabView) mNavScreen.getTabView(position);
if
(tabview ==
null
) {
if
(mTabControl.getTabCount() >
0
) {
// use a fallback tab
setActiveTab(mTabControl.getCurrentTab());
}
mContentView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
finishAnimateOut();
return
;
}
mUiController.setBlockEvents(
true
);
mUiController.setActiveTab(tab);
mContentView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
if
(mAnimScreen ==
null
) {
mAnimScreen =
new
AnimScreen(mActivity);
}
mAnimScreen.set(tab.getScreenshot());
mCustomViewContainer.addView(mAnimScreen.mMain, COVER_SCREEN_PARAMS);
//全屏模式
mAnimScreen.mMain.layout(
0
,
0
, mContentView.getWidth(),
mContentView.getHeight());
mNavScreen.mScroller.finishScroller();
ImageView target = tabview.mImage;
int
toLeft =
0
;
int
toTop = getTitleBar().getHeight();
int
toRight = mContentView.getWidth();
int
width = target.getDrawable().getIntrinsicWidth();
int
height = target.getDrawable().getIntrinsicHeight();
int
fromLeft = tabview.getLeft() + target.getLeft() - mNavScreen.mScroller.getScrollX();
int
fromTop = tabview.getTop() + target.getTop() - mNavScreen.mScroller.getScrollY();
//target就是选择的tab tab的顶部位置 为了给人以 从原来位置扩大到整个屏幕的感觉
int
fromRight = fromLeft + width;
int
fromBottom = fromTop + height;
float
scaleFactor = mContentView.getWidth() / (
float
) width;
int
toBottom = toTop + (
int
) (height * scaleFactor);
mAnimScreen.mContent.setLeft(fromLeft);
mAnimScreen.mContent.setTop(fromTop);
mAnimScreen.mContent.setRight(fromRight);
mAnimScreen.mContent.setBottom(fromBottom);
mAnimScreen.setScaleFactor(1f);
AnimatorSet set1 =
new
AnimatorSet();
ObjectAnimator fade2 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mAnimScreen.mMain,
"alpha"
, 0f, 1f);
ObjectAnimator fade1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mNavScreen,
"alpha"
, 1f, 0f);
set1.playTogether(fade1, fade2);
set1.setDuration(
100
);
//使用上下左右的位置 使得 tab的运动轨迹 从原来位置扩展到整个屏幕,无论整个tab在哪里
AnimatorSet set2 =
new
AnimatorSet();
ObjectAnimator l = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mAnimScreen.mContent,
"left"
,
fromLeft, toLeft);
ObjectAnimator t = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mAnimScreen.mContent,
"top"
,
fromTop, toTop);
ObjectAnimator r = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mAnimScreen.mContent,
"right"
,
fromRight, toRight);
ObjectAnimator b = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mAnimScreen.mContent,
"bottom"
,
fromBottom, toBottom);
ObjectAnimator scale = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mAnimScreen,
"scaleFactor"
,
1f, scaleFactor);
ObjectAnimator otheralpha = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mCustomViewContainer,
"alpha"
, 1f, 0f);
otheralpha.setDuration(
100
);
set2.playTogether(l, t, r, b, scale);
set2.setDuration(
200
);
AnimatorSet combo =
new
AnimatorSet();
combo.playSequentially(set1, set2, otheralpha);
combo.addListener(
new
AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public
void
onAnimationEnd(Animator anim) {
mCustomViewContainer.removeView(mAnimScreen.mMain);
//动画结束的时候把动画view 隐藏
finishAnimateOut();
//让当前窗口渐变消失
mUiController.setBlockEvents(
false
);
}
});
combo.start();
}
|
对于第三个动画, 左右滑动删除的动画, 其入口有二
a. Scrollview的onTouchEvent事件中调用的NavTabScroller::onOrthoDragFinished()函数, 其实最后还是调用到animateOut函数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
/*这是scrollview回调的一个函数,作用是 在用户左右滑动 tab之后 判断是否删除这个tab*/
@Override
protected
void
onOrthoDragFinished(View downView) {
if
(mAnimator !=
null
)
return
;
if
(mIsOrthoDragged && downView !=
null
) {
// offset
float
diff = mHorizontal ? downView.getTranslationY() : downView.getTranslationX();
if
(Math.abs(diff) > (mHorizontal ? downView.getHeight() : downView.getWidth()) /
2
) {
// remove it 达到了删除tab的调节,开始删除
animateOut(downView, Math.signum(diff) * mFlingVelocity, diff);
}
else
{
// snap back 没有达到条件,就让view回来
offsetView(downView,
0
);
}
}
}
|
在用户按住小tab移动的时候会执行offsetView函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
private
void
offsetView(View v,
float
distance) {
v.setAlpha(getAlpha(v, distance));
//setTranslationY 这个功能应该只有3.0以后才支持 让view左右滑动
if
(mHorizontal) {
v.setTranslationY(distance);
}
else
{
v.setTranslationX(distance);
}
}
|
b另一种调用动画的方式比较简单了,其实就是直接调用animateOut函数:
看一下这个函数到底做了什么吧:
1.需要删除窗口的平移和alpha渐变
2.删除窗口后,其他窗口的上移,这是比较复杂的一个逻辑 ,大体是通过改变mGap这个参数实现,动画也是使用了animator:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
|
/*删除 tab 动画 (左右滑动删除 )的显示*/
private
void
animateOut(
final
View v,
float
velocity,
float
start) {
if
((v ==
null
) || (mAnimator !=
null
))
return
;
//有其他动画就不要执行这个动画
final
int
position = mContentView.indexOfChild(v);
int
target =
0
;
if
(velocity <
0
) {
//动画结束的位置
target = mHorizontal ? -getHeight() : -getWidth();
}
else
{
target = mHorizontal ? getHeight() : getWidth();
}
int
distance = target - (mHorizontal ? v.getTop() : v.getLeft());
long
duration = (
long
) (Math.abs(distance) *
1000
/ Math.abs(velocity));
//动画持续时间
int
scroll =
0
;
int
translate =
0
;
int
gap = mHorizontal ? v.getWidth() : v.getHeight();
int
centerView = getViewCenter(v);
//获取view的中心
int
centerScreen = getScreenCenter();
//获取屏幕的中心
int
newpos = INVALID_POSITION;
if
(centerView < centerScreen - gap /
2
) {
// top view删除的是上面的view
scroll = - (centerScreen - centerView - gap);
translate = (position >
0
) ? gap :
0
;
newpos = position;
}
else
if
(centerView > centerScreen + gap /
2
) {
// bottom view 删除的是底部的view
scroll = - (centerScreen + gap - centerView);
if
(position < mAdapter.getCount() -
1
) {
translate = -gap;
}
}
else
{
// center view 删除的是中间的view
scroll = - (centerScreen - centerView);
if
(position < mAdapter.getCount() -
1
) {
translate = -gap;
}
else
{
scroll -= gap;
}
}
mGapPosition = position;
final
int
pos = newpos;
ObjectAnimator trans = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(v,
(mHorizontal ? TRANSLATION_Y : TRANSLATION_X), start, target);
//控制待删除view的水平 移动
ObjectAnimator alpha = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(v, ALPHA, getAlpha(v,start),
//控制待删除view的透明变化
getAlpha(v,target));
AnimatorSet set1 =
new
AnimatorSet();
set1.playTogether(trans, alpha);
set1.setDuration(duration);
mAnimator =
new
AnimatorSet();
ObjectAnimator trans2 =
null
;
ObjectAnimator scroll1 =
null
;
if
(scroll !=
0
) {
if
(mHorizontal) {
//调整scrollview的scroll位置
scroll1 = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(
this
,
"scrollX"
, getScrollX(), getScrollX() + scroll);
}
else
{
scroll1 = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(
this
,
"scrollY"
, getScrollY(), getScrollY() + scroll);
}
}
if
(translate !=
0
) {
trans2 = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(
this
,
"gap"
,
0
, translate);
//删除view会留下一个空白,需要让上面的view补充上 这里gap是 负值,因为view少了,坐标也就小了
}
final
int
duration2 =
200
;
if
(scroll1 !=
null
) {
if
(trans2 !=
null
) {
AnimatorSet set2 =
new
AnimatorSet();
set2.playTogether(scroll1, trans2);
set2.setDuration(duration2);
mAnimator.playSequentially(set1, set2);
}
else
{
scroll1.setDuration(duration2);
mAnimator.playSequentially(set1, scroll1);
}
}
else
{
if
(trans2 !=
null
) {
trans2.setDuration(duration2);
mAnimator.playSequentially(set1, trans2);
}
}
mAnimator.addListener(
new
AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
public
void
onAnimationEnd(Animator a) {
if
(mRemoveListener !=
null
) {
mRemoveListener.onRemovePosition(position);
//通知移除tab
mAnimator =
null
;
mGapPosition = INVALID_POSITION;
mGap =
0
;
handleDataChanged(pos);
}
}
});
mAnimator.start();
}
|
至于切换就简单了,是在controller::setActiveTab()函数进行处理.
原文地址:http://my.oschina.net/sfshine/blog/198727
























 2531
2531

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








