1. 反转字符串
题目:编写一个函数,反转给定的字符串。
解答思路:
使用 StringBuilder 或 StringBuffer 的 reverse() 方法。
或者手动实现,通过交换字符串两端的字符
public String reverseString(String s) {
return new StringBuilder(s).reverse().toString();
// 或者手动实现
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
int left = 0, right = chars.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
char temp = chars[left];
chars[left] = chars[right];
chars[right] = temp;
left++;
right--;
}
return new String(chars);
}
2. 判断回文字符串
题目:编写一个函数,判断给定的字符串是否为回文。
解答思路:
将字符串反转后与原字符串比较。
或者使用双指针方法,从两端向中间比较字符。
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
int left = 0, right = s.length() - 1;
while (left < right) {
if (s.charAt(left) != s.charAt(right)) {
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
3. 斐波那契数列
题目:编写一个函数,计算斐波那契数列的第 n 项。
解答思路:
使用递归(注意效率问题)。
使用动态规划或迭代方法以提高效率。
public int fibonacci(int n) {
if (n <= 1) {
return n;
}
int a = 0, b = 1, c = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return c;
}
4. 数组去重
题目:编写一个函数,去除数组中的重复元素。
解答思路:使用 HashSet 来存储唯一元素。
或者使用双指针方法对已排序数组进行去重。
public int[] removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return new int[0];
}
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : nums) {
set.add(num);
}
int[] result = new int[set.size()];
int index = 0;
for (int num : set) {
result[index++] = num;
}
// 如果需要保持顺序,可以使用 LinkedHashSet
return result;
}
// 或者使用排序后的双指针方法
public int[] removeDuplicatesSorted(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return new int[0];
}
int i = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[j] != nums[i]) {
i++;
nums[i] = nums[j];
}
}
return Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0, i + 1);
}
5. 二分查找
题目:编写一个函数,在已排序的数组中查找给定的元素。
解答思路:
使用二分查找算法。
public int binarySearch(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
6.俩数之和
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int complement = target - nums[i];
if (map.containsKey(complement)) {
return new int[] {
map.get(complement), i };
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution");
}
7.反转列表
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode nextTemp = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nextTemp;
}
return prev;
}
8.LRU缓存实现
class LRUCache {
class DLinkedNode {
int key;
int value;
DLinkedNode prev;
DLinkedNode next;
}
private void addNode(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev = head;
node.next = head.next;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node) {
DLinkedNode prev = node.prev;
DLinkedNode next = node.next;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
}
private void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
removeNode(node);
addNode(node);
}
private DLinkedNode popTail() {
DLinkedNode res = tail.prev;
removeNode(res);
return res;
}
private Map<Integer, DLinkedNode> cache = new HashMap<>();
private int size;
private int capacity;
private DLinkedNode head, tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
head = new DLinkedNode();
tail = new DLinkedNode();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) return -1;
moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode();
newNode.key = key;
newNode.value = value;
cache.put(key, newNode);
addNode(newNode);
++size;
if (size > capacity) {
DLinkedNode tail = popTail();
cache.remove(tail.key);
--size;
}
} else {
node.value = value;
moveToHead(node);
}
}
}
9. 字母异位词分组
给你一个字符串数组,请你将 字母异位词 组合在一起。可以按任意顺序返回结果列表。
字母异位词 是由重新排列源单词的所有字母得到的一个新单词。

import java.util.*;
public class AnagramGrouper {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
// 使用 HashMap 来存储分组结果
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String str : strs) {
// 将字符串转换为字符数组并排序
char[] charArray = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(charArray);
// 将排序后的字符数组转换回字符串,作为哈希表的键
String sortedStr = new String(charArray);
// 如果哈希表中不存在该键,则创建一个新的列表
if (!map.containsKey(sortedStr)) {
map.put(sortedStr, new ArrayList<>());
}
// 将原始字符串添加到对应键的列表中
map.get(sortedStr).add(str);
}
// 返回哈希表中的所有值,即字母异位词的分组
return new ArrayList<>(map.values());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnagramGrouper grouper = new AnagramGrouper();
String[] strs = {
"eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"};
List<List<String>> groupedAnagrams = grouper.groupAnagrams(strs);
// 打印结果
for (List<String> group : groupedAnagrams) {
System.out.println(group);
}
}
}

10.最长连续序列
给定一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,找出数字连续的最长序列(不要求序列元素在原数组中连续)的长度。
请你设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。

import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class LongestConsecutiveSequence {
public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
Set<Integer> numSet = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : nums) {
numSet.add(num);
}
int longestStreak = 0;
for (int num : numSet) {
// 只有当 num 是序列的起点时才开始计算
if (!numSet.contains(num - 1)) {
int currentNum = num;
int currentStreak = 1;
while (numSet.contains(currentNum + 1)) {
currentNum += 1;
currentStreak += 1;
}
longestStreak = Math.max(longestStreak, currentStreak);
}
}
return longestStreak;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LongestConsecutiveSequence solution = new LongestConsecutiveSequence();
int[] nums = {
100, 4, 200, 1, 3, 2};
System.out.println("The length of the longest consecutive sequence is: " + solution.longestConsecutive(nums));
}
}

11. 移动零
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
请注意 ,必须在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。

public class MoveZeroes {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return;
}
int nonZeroIndex = 0; // 用于记录下一个非零元素应该放置的位置
// 遍历数组,将所有非零元素移动到前面
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
nums[nonZeroIndex] = nums[i];
nonZeroIndex++;
}
}
// 将剩余的位置填充为零
for (int i = nonZeroIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {
nums[i] = 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MoveZeroes solution = new MoveZeroes();
int[] nums = {
0, 1, 0, 3, 12};
solution.moveZeroes(nums);
// 打印结果
for (int num : nums) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
}
}

12.盛最多水的容器
给定一个长度为 n 的整数数组 height 。有 n 条垂线,第 i 条线的两个端点是 (i, 0) 和 (i, height[i]) 。
找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
返回容器可以储存的最大水量。
说明:你不能倾斜容器。
示例 1:

输入:[1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
输出:49
解释:图中垂直线代表输入数组 [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]。在此情况下,容器能够容纳水(表示为蓝色部分)的最大值为 49。
示例 2:
输入:height = [1,1]
输出:1
public class ContainerWithMostWater {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length < 2) {
return 0;
}
int left = 0;
int right = height.length - 1;
int maxArea = 0;
while (left < right) {
// 计算当前容器的面积
int currentArea = Math.min(height[left], height[right]) * (right - left);
// 更新最大面积
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, currentArea);
// 移动较短的线,尝试找到更大的面积
if (height[left] < height[right]) {
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
}
return maxArea;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ContainerWithMostWater solution = new ContainerWithMostWater();
int[] height = {
1, 8, 6, 2, 5, 4, 8, 3, 7};
System.out.println("Maximum area: " + solution.maxArea(height));
}
}

13.三数之和
给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
解释:
nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] = (-1) + 0 + 1 = 0 。
nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[4] = 0 + 1 + (-1) = 0 。
nums[0] + nums[3] + nums[4] = (-1) + 2 + (-1) = 0 。
不同的三元组是 [-1,0,1] 和 [-1,-1,2] 。
注意,输出的顺序和三元组的顺序并不重要。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1,1]
输出:[]
解释:唯一可能的三元组和不为 0 。
示例 3:
输入:nums = [0,0,0]
输出:[[0,0,0]]
解释:唯一可能的三元组和为 0 。
提示:
3 <= nums.length <= 3000
-105 <= nums[i] <= 105

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class ThreeSum {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length < 3) {
return result;
}
// 对数组进行排序
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 2; i++) {
// 跳过重复的元素
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
int left = i + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if (sum == 0) {
// 找到一个三元组
result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]));
// 跳过重复的元素
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) {
left++;
}
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) {
right--;
}
// 移动指针
left++;
right--;
} else if (sum < 0) {
// 如果和小于零,移动左指针以增加和
left++;
} else {
// 如果和大于零,移动右指针以减小和
right--;
}
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreeSum solution = new ThreeSum();
int[] nums = {
-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4};
List<List<Integer>> result = solution.threeSum(nums);
// 打印结果
for (List<Integer> triplet : result) {
System.out.println(triplet);
}
}
}

14.接雨水
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
示例 1:

输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出:6
解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
示例 2:
输入:height = [4,2,0,3,2,5]
输出:9
提示:
n == height.length
1 <= n <= 2 * 104
0 <= height[i] <= 105

public class TrappingRainWater {
public int trap(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length < 3) {
return 0;
}
int left = 0;
int right = height.length - 1;
int leftMax = 0;
int rightMax = 0;
int trappedWater = 0;
while (left < right) {
if (height[left] < height[right]) {
// 如果左侧柱子较低
if (height[left] >= leftMax) {
leftMax = height[left];
} else {
trappedWater += leftMax - height[left];
}
left++;
} else {
// 如果右侧柱子较低或相等
if (height[right] >= rightMax) {
rightMax = height[right];
} else {
trappedWater += rightMax - height[right];
}
right--;
}
}
return trappedWater;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TrappingRainWater solution = new TrappingRainWater();
int[] height = {
0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
System.out.println("Trapped water: " + solution.trap(height));
}
}


15.无重复字符的最长子串
给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长 子串 的长度。
示例 1:
输入: s = “abcabcbb”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “abc”,所以其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: s = “bbbbb”
输出: 1
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “b”,所以其长度为 1。
示例 3:
输入: s = “pwwkew”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “wke”,所以其长度为 3。
请注意,你的答案必须是 子串 的长度,“pwke” 是一个子序列,不是子串。
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
s 由英文字母、数字、符号和空格组成

import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingCharacters {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
Set<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
int maxLength = 0;
int left = 0;
for (int right = 0; right < s.length(); right++) {
// 如果字符已经存在于集合中,移动左指针直到移除重复字符
while (set.contains(s.charAt(right))) {
set.remove(s.charAt(left));
left++;
}
// 将当前字符添加到集合中
set.add(s.charAt(right));
// 更新最大长度
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, right - left + 1);
}
return maxLength;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingCharacters solution = new LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingCharacters();
String s = "abcabcbb";
System.out.println("Length of longest substring without repeating characters: " + solution.lengthOfLongestSubstring(s));
}
}


16.找到字符串中所有字母异位词
给定两个字符串 s 和 p,找到 s 中所有 p 的 异位词 的子串,返回这些子串的起始索引。不考虑答案输出的顺序。
示例 1:
输入: s = “cbaebabacd”, p = “abc”
输出: [0,6]
解释:
起始索引等于 0 的子串是 “cba”, 它是 “abc” 的异位词。
起始索引等于 6 的子串是 “bac”, 它是 “abc” 的异位词。
示例 2:
输入: s = “abab”, p = “ab”
输出: [0,1,2]
解释:
起始索引等于 0 的子串是 “ab”, 它是 “ab” 的异位词。
起始索引等于 1 的子串是 “ba”, 它是 “ab” 的异位词。
起始索引等于 2 的子串是 “ab”, 它是 “ab” 的异位词。
提示:
1 <= s.length, p.length <= 3 * 104
s 和 p 仅包含小写字母

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class FindAllAnagramsInAString {
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (s == null || p == null || s.length() < p.length()) {
return result;
}
int[] pCount = new int[26]; // 用于存储模式字符串 p 中每个字符的频率
int[] sCount = new int[26]; // 用于存储当前窗口中每个字符的频率
// 初始化模式字符串 p 的字符频率
for (char c : p.toCharArray()) {
pCount[c - 'a']++;
}
int pLength = p.length();
int sLength = s.length();
// 滑动窗口遍历字符串 s
for (int i = 0; i < sLength; i++) {
// 增加当前字符到窗口中
sCount[s.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
// 如果窗口大小超过 p 的长度,移除最左侧字符
if (i >= pLength) {
sCount[s.charAt(i - pLength) - 'a']--;
}
// 检查当前窗口是否与模式字符串 p 的字符频率相同
if (Arrays.equals(pCount, sCount)) {
result.add(i - pLength + 1);
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
FindAllAnagramsInAString solution = new FindAllAnagramsInAString();
String s = "cbaebabacd";
String p = "abc";
List<Integer> result = solution.findAnagrams(s, p);
System.out.println("Indices of anagrams: " + result);
}
}


17.和为 K 的子数组
给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你统计并返回 该数组中和为 k 的子数组的个数 。
子数组是数组中元素的连续非空序列。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,1], k = 2
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,2,3], k = 3
输出:2
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 104
-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000
-107 <= k <= 107

import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class SubarraySumEqualsK {
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int count = 0;
int sum = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> prefixSumCount = new HashMap<>();
// 初始化前缀和为0的情况,表示从数组开始到当前位置的子数组和为k的次数(即初始时有一个空子数组)
prefixSumCount.put(0, 1);
for (int num : nums) {
sum += num;
// 检查是否存在一个前缀和,使得当前前缀和减去该前缀和等于k
if (prefixSumCount.containsKey(sum - k)) {
count += prefixSumCount.get(sum - k);
}
// 更新当前前缀和的出现次数
prefixSumCount.put(sum, prefixSumCount.getOrDefault(sum, 0) + 1);
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SubarraySumEqualsK solution = new SubarraySumEqualsK();
int[] nums = {
1, 1, 1};
int k = 2;
System.out.println("Number of subarrays with sum " + k + ": " + solution.subarraySum(nums, k));
}
}


17.滑动窗口最大值
给你一个整数数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
返回 滑动窗口中的最大值 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3
输出:[3,3,5,5,6,7]
解释:
滑动窗口的位置 最大值
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3
1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3
1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5
1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5
1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6
1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1], k = 1
输出:[1]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
1 <= k <= nums.length

import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SlidingWindowMaximum {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 || k <= 0) {
return new int[0];
}
int n = nums.length;
int[] result = new int[n - k + 1];
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 移除不在窗口范围内的元素索引
if (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekFirst() < i - k + 1) {
deque.pollFirst();
}
// 移除所有比当前元素小的元素索引,因为它们不可能成为窗口的最大值
while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] < nums[i]) {
deque.pollLast();
}
// 添加当前元素的索引
deque.offerLast(i);
// 当窗口大小达到 k 时,记录当前窗口的最大值
if (i >= k - 1) {
result[i - k + 1] = nums[deque.peekFirst()];
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SlidingWindowMaximum solution = new SlidingWindowMaximum();
int[] nums = {
1, 3, -1, -3, 5, 3, 6, 7};
int k = 3;
int[] result = solution.maxSlidingWindow(nums, k);
System.out.println("Max values in sliding window: " + Arrays.toString(result));
}
}


18.最小覆盖子串
给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 “” 。
注意:
对于 t 中重复字符,我们寻找的子字符串中该字符数量必须不少于 t 中该字符数量。
如果 s 中存在这样的子串,我们保证它是唯一的答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = “ADOBECODEBANC”, t = “ABC”
输出:“BANC”
解释:最小覆盖子串 “BANC” 包含来自字符串 t 的 ‘A’、‘B’ 和 ‘C’。
示例 2:
输入:s = “a”, t = “a”
输出:“a”
解释:整个字符串 s 是最小覆盖子串。
示例 3:
输入: s = “a”, t = “aa”
输出: “”
解释: t 中两个字符 ‘a’ 均应包含在 s 的子串中,
因此没有符合条件的子字符串,返回空字符串。
提示:
m == s.length
n == t.length
1 <= m, n <= 105
s 和 t 由英文字母组成

import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MinimumWindowSubstring {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
if (s == null || t == null || s.length() == 0 || t.length() == 0) {
return "";
}
// 用于存储 t 中每个字符的频率
Map<Character, Integer> targetCount = new HashMap<>();
for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {
targetCount.put(c, targetCount.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
// 滑动窗口中的字符频率
Map<Character, Integer> windowCount = new HashMap<>();
int left = 0, right = 0;
int valid = 0; // 记录窗口中满足 t 字符频率的字符种类数
int start = 0, minLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while (right < s.length()) {
char c = s.charAt(right);
right++;
// 更新窗口中的字符频率
if (targetCount.containsKey(c)) {
windowCount.put(c, windowCount.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
if (windowCount.get(c).equals(targetCount.get(c))) {
valid++;
}
}
// 判断左侧窗口是否要收缩
while (valid == targetCount.size()) {
// 更新最小覆盖子串
if (right - left < minLength) {
start = left;
minLength = right - left;
}
char d = s.charAt(left);
left++;
// 更新窗口中的字符频率
if (targetCount.containsKey(d)) {
if (windowCount.get(d).equals(targetCount.get(d))) {
valid--;
}
windowCount.put(d, windowCount.get(d) - 1);
}
}
}
return minLength == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(start, start + minLength);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MinimumWindowSubstring solution = new MinimumWindowSubstring();
String s = "ADOBECODEBANC";
String t = "ABC";
System.out.println("Minimum window substring: " + solution.minWindow(s, t));
}
}


19. 最大子数组和
给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
子数组是数组中的一个连续部分。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
输出:6
解释:连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1]
输出:1
示例 3:
输入:nums = [5,4,-1,7,8]
输出:23
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104

public class MaximumSubarraySum {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0; // 或者抛出异常,根据需求处理
}
int currentSum = nums[0];
int maxSum = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 更新当前子数组的和
currentSum = Math.max(nums[i], currentSum + nums[i]);
// 更新最大子数组和
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, currentSum);
}
return maxSum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MaximumSubarraySum solution = new MaximumSubarraySum();
int[] nums = {
-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4};
System.out.println("Maximum subarray sum: " + solution.maxSubArray(nums)); // 输出: 6
}
}

20.合并区间
以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回 一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间 。
示例 1:
输入:intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
输出:[[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
解释:区间 [1,3] 和 [2,6] 重叠, 将它们合并为 [1,6].
示例 2:
输入:intervals = [[1,4],[4,5]]
输出:[[1,5]]
解释:区间 [1,4] 和 [4,5] 可被视为重叠区间。
提示:
1 <= intervals.length <= 104
intervals[i].length == 2
0 <= starti <= endi <= 104

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class MergeIntervals {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
if (intervals == null || intervals.length == 0) {
return new int[0][0];
}
// Step 1: Sort intervals based on the start time
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0], b[0]));
List<int[]> merged = new ArrayList<>();
int[] currentInterval = intervals[0];
merged.add(currentInterval);
for (int[] interval : intervals) {
int currentEnd = currentInterval[1];
int nextStart = interval[0];
int nextEnd = interval[1];
if (currentEnd >= nextStart) {
// Overlapping intervals, merge them
currentInterval[1] = Math.max(currentEnd, nextEnd);
} else {
// Non-overlapping interval, add it to the list
currentInterval = interval;
merged.add(currentInterval);
}
}
// Convert List<int[]> to int[][]
return merged.toArray(new int[merged.size()][]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MergeIntervals solution = new MergeIntervals();
int[][] intervals = {
{
1, 3}, {
2, 6}, {
8, 10}, {
15, 18}};
int[][] mergedIntervals = solution.merge(intervals);
for (int[] interval : mergedIntervals) {
System.out.println("[" + interval[0] + ", " + interval[1] + "]");
}
}
}

21.轮转数组
给定一个整数数组 nums,将数组中的元素向右轮转 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 3
输出: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
解释:
向右轮转 1 步: [7,1,2,3,4,5,6]
向右轮转 2 步: [6,7,1,2,3,4,5]
向右轮转 3 步: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [-1,-100,3,99], k = 2
输出:[3,99,-1,-100]
解释:
向右轮转 1 步: [99,-1,-100,3]
向右轮转 2 步: [3,99,-1,-100]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
0 <= k <= 105

public class RotateArray {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 || k <= 0) {
return;
}
int n = nums.length;
k = k % n; // 处理 k 大于数组长度的情况
// 辅助方法:反转数组的指定部分
reverse(nums, 0, n - 1); // 反转整个数组
reverse(nums, 0, k - 1); // 反转前 k 个元素
reverse(nums, k, n - 1); // 反转剩余的元素
}
private void reverse(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
while (start < end) {
int temp = nums[start];
nums[start] = nums[end];
nums[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RotateArray solution = new RotateArray();
int[] nums = {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
int k = 3;
solution.rotate(nums, k);
// 输出旋转后的数组
for (int num : nums) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
// 输出: 5 6 7 1 2 3 4
}
}

22.除自身以外数组的乘积
给你一个整数数组 nums,返回 数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 等于 nums 中除 nums[i] 之外其余各元素的乘积 。
题目数据 保证 数组 nums之中任意元素的全部前缀元素和后缀的乘积都在 32 位 整数范围内。
请 不要使用除法,且在 O(n) 时间复杂度内完成此题。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,4]
输出: [24,12,8,6]
示例 2:
输入: nums = [-1,1,0,-3,3]
输出: [0,0,9,0,0]
提示:
2 <= nums.length <= 105
-30 <= nums[i] <= 30
输入 保证 数组 answer[i] 在 32 位 整数范围内

直观实现(使用辅助数组)
public class ProductOfArrayExceptSelf {
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n == 0) return new int[0];
int[] leftProducts = new int[n];
int[] rightProducts = new int[n];
int[] result = new int[n];
// 计算前缀乘积
leftProducts[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
leftProducts[i] = leftProducts[i - 1] * nums[i - 1];
}
// 计算后缀乘积并同时计算结果
int[] rightProducts = new int[n];
rightProducts[n - 1] = 1; // 初始化最后一个元素的右侧乘积为1(因为右侧没有元素)
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
rightProducts[i] = rightProducts[i + 1] * nums[i + 1];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
result[i] = leftProducts[i] * rightProducts[i];
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProductOfArrayExceptSelf solution = new ProductOfArrayExceptSelf();
int[] nums = {
1, 2, 3, 4};
int[] result = solution.productExceptSelf(nums);
for (int num : result) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
// 输出: 24 12 8 6
}
}
优化为常数空间
为了进一步优化空间复杂度,我们可以不使用额外的数组,而是通过两个变量来存储当前位置左侧和右侧的乘积:
public class ProductOfArrayExceptSelfOptimized {
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] result = new int[n];
// 初始化结果数组为1(因为乘法的单位元是1)
int[] leftProducts = new int[n];
int[] rightProducts = new int[n];
int[] resultOptimized = new int[n]; // 或者直接在 resultOptimized 上操作,避免额外数组
// 初始化左侧乘积数组(这里用一个变量代替数组来优化)
int leftProduct = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
resultOptimized[i] = leftProduct; // 先赋值当前结果为左侧乘积
leftProduct *= nums[i]; // 更新左侧乘积(用于下一个位置)
}
// 从右向左计算右侧乘积并直接乘以左侧乘积
int rightProduct = 1; // 右侧乘积初始化为1
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
resultOptimized[i] *= rightProduct; // 先计算右侧乘积的累积
rightProduct *= (i + 1 < n ? nums[i + 1] : 1; // 避免越界
}
// 或者使用两个变量在单次遍历中完成(更高效):
int[] result = new int[nums.length];
int leftProduct = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
result[i] = leftProduct;
leftProduct *= nums[i]; // 在赋值后更新左侧乘积,用于下一个位置
}
// 重置左侧乘积为1从右向左计算(或直接在上述循环中从右向左结合右侧值)
leftProduct = 1; // 重置为1用于从右向左计算
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result[i] *= leftProduct; // 直接在原result数组上操作(或新建数组)
leftProduct *= (i > 0 ? nums[i] : 1); // 避免i=0时nums[i]越界
}
return result; // 如果使用result数组,否则返回直接构建的结果数组
}
// 示例使用(展示如何结合第一个实现逻辑,但实际建议直接用上面优化后的单次遍历逻辑
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProductOfArrayExceptSelfOptimized solution = new ProductOfArrayExceptSelfOptimized();
int[] nums = {
1, 2, 3, 4};
int[] result = solution.productExceptSelf(nums);
for (int num : result) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
// 输出: 24 12 8 6
}
}

23.缺失的第一个正数
给你一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,请你找出其中没有出现的最小的正整数。
请你实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 并且只使用常数级别额外空间的解决方案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,0]
输出:3
解释:范围 [1,2] 中的数字都在数组中。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,4,-1,1]
输出:2
解释:1 在数组中,但 2 没有。
示例 3:
输入:nums = [7,8,9,11,12]
输出:1
解释:最小的正数 1 没有出现。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1

public class FirstMissingPositive {
public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
// 将每个正整数 x 放置在索引 x-1 的位置上
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= n && nums[nums[i] - 1] != nums[i]) {
// 交换 nums[i] 和 nums[nums[i] - 1]
int temp = nums[nums[i] - 1];
nums[nums[i] - 1] = nums[i];
nums[i] = temp;
}
}
// 找到第一个位置 i 使得 nums[i] != i + 1
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != i + 1) {
return i + 1;
}
}
// 如果所有位置都正确,则返回 n + 1
return n + 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
FirstMissingPositive solution = new FirstMissingPositive();
int[] nums1 = {
1, 2, 0};
int[] nums2 = {
3, 4, -1, 1};
int[] nums3 = {
7, 8, 9, 11, 12};
System.out.println(solution.firstMissingPositive(nums1)); // 输出: 3
System.out.println(solution.firstMissingPositive(nums2)); // 输出: 2
System.out.println(solution.firstMissingPositive(nums3)); // 输出: 1
}
}

24.矩阵置零
给定一个 m x n 的矩阵,如果一个元素为 0 ,则将其所在行和列的所有元素都设为 0 。请使用 原地 算法。
示例 1:

输入:matrix = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
输出:[[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]]
示例 2:

输入:matrix = [[0,1,2,0],[3,4,5,2],[1,3,1,5]]
输出:[[0,0,0,0],[0,4,5,0],[0,3,1,0]]
提示:
m == matrix.length
n == matrix[0].length
1 <= m, n <= 200
-231 <= matrix[i][j] <= 231 - 1

public class SetMatrixZeroes {
public void setZeroes(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return;
}
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
boolean firstRowZero = false;
boolean firstColZero = false;
// 检查第一行是否有零
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (matrix[0][j] == 0) {
firstRowZero = true;
break;
}
}
// 检查第一列是否有零
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (matrix[i][0] == 0) {
firstColZero = true;
break;
}
}
// 使用第一行和第一列作为标记
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 0) {
matrix[i][0] = 0;
matrix[0][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// 根据标记置零
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
if (matrix[i][0] == 0 || matrix[0][j] == 0) {
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// 如果第一行需要置零
if (firstRowZero) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
matrix[0][j] = 0;
}
}
// 如果第一列需要置零
if (firstColZero) {
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
matrix[i][0] = 0;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SetMatrixZeroes solution = new SetMatrixZeroes();
int[][] matrix = {
{
1, 1, 1},
{
1, 0, 1},
{
1, 1, 1}
};
solution.setZeroes(matrix);
// 输出结果
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}

25.螺旋矩阵
给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
示例 1:
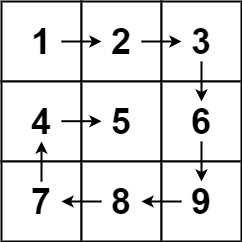
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
输出:[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
示例 2:

输入:matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]
输出:[1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
提示:
m == matrix.length
n == matrix[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 10
-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class SpiralMatrix {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return result;
}
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
int top = 0;
int bottom = m - 1;
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;
while (top <= bottom && left <= right) {
// 从左到右遍历
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
result.add(matrix[top][i]);
}
top++;
// 从上到下遍历
for (int i = top; i <= bottom; i++) {
result.add(matrix[i][right]);
}
right--;
// 从右到左遍历(需要检查是否仍然在有效范围内)
if (top <= bottom) {
for (int i = right; i >= left; i--) {
result.add(matrix[bottom][i]);
}
bottom--;
}
// 从下到上遍历(需要检查是否仍然在有效范围内)
if (left <= right) {
for (int i = bottom; i >= top; i--) {
result.add(matrix[i][left]);
}
left++;
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpiralMatrix solution = new SpiralMatrix();
int[][] matrix = {
{
1, 2, 3},
{
4, 5, 6},
{
7, 8, 9}
};
List<Integer




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 887
887

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








