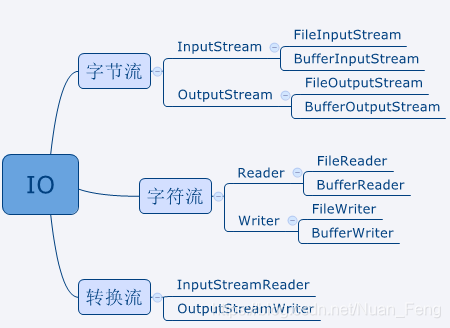
字节流
InputStream
public abstract class InputStream implements Closeable {
//最大可跳过字节数
private static final int MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE = 2048;
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
//读取一字节数据
int c = read();
//到达文件的末端返回-1
if (c == -1) {
return -1;
}
//赋值
b[off] = (byte)c;
//一个字节一个字节读取,填充到b数组
int i = 1;
try {
for (; i < len ; i++) {
c = read();
if (c == -1) {
break;
}
b[off + i] = (byte)c;
}
} catch (IOException ee) {
}
return i;
}
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
long remaining = n;
int nr;
if (n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
//最大创建MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE大小数组
int size = (int)Math.min(MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE, remaining);
byte[] skipBuffer = new byte[size];
//使用循环,尽量读取remaining大小数据
while (remaining > 0) {
nr = read(skipBuffer, 0, (int)Math.min(size, remaining));
//读到流的末端,则返回
if (nr < 0) {
break;
}
remaining -= nr;
}
return n - remaining;
}
//返回默认值
public int available() throws IOException {
return 0;
}
//标记一个位置,用于reset,当超过readlimit,则标记位置失效
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {}
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {
throw new IOException("mark/reset not supported");
}
//是否支持标记,默认不支持
public boolean markSupported() {
return false;
}
FilterInputStream
public class FilterInputStream extends InputStream {
//装饰器的代码特征:被装饰的对象一般是装饰器的成员变量
protected volatile InputStream in; //将要被装饰的字节输入流
protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in) { //通过构造方法传入此被装饰的流
this.in = in;
}
//下面这些方法,完成最小的装饰――0装饰,只是调用被装饰流的方法而已
public int read() throws IOException {
return in.read();
}
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return read(b, 0, b.length);
}
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
return in.read(b, off, len);
}
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
return in.skip(n);
}
public int available() throws IOException {
return in.available();
}
public void close() throws IOException {
in.close();
}
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {
in.mark(readlimit);
}
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {
in.reset();
}
public boolean markSupported() {
return in.markSupported();
}
}
ByteArrayInputStream
将内存中的数组装饰成InputStrean
public
class ByteArrayInputStream extends InputStream {
//包装的字节数组
protected byte buf[];
//读取位置
protected int pos;
//标记位置
protected int mark = 0;
//数组长度
protected int count;
public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[]) {
//装饰的数组
this.buf = buf;
//设置位置和长度
this.pos = 0;
this.count = buf.length;
}
public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[], int offset, int length) {
this.buf = buf;
this.pos = offset;
this.count = Math.min(offset + length, buf.length);
this.mark = offset;
}
public synchronized int read() {
return (pos < count) ? (buf[pos++] & 0xff) : -1;
}
public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) {
if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
//超过范围,返回-1
if (pos >= count) {
return -1;
}
//查看剩下可读字节大小
int avail = count - pos;
//超过限制,则默认查询剩下可读字节数
if (len > avail) {
len = avail;
}
if (len <= 0) {
return 0;
}
System.arraycopy(buf, pos, b, off, len);
pos += len;
return len;
}
public synchronized long skip(long n) {
long k = count - pos;
if (n < k) {
k = n < 0 ? 0 : n;
}
pos += k;
return k;
}
public synchronized int available() {
return count - pos;
}
public boolean markSupported() {
return true;
}
public void mark(int readAheadLimit) {
mark = pos;
}
/**
* Resets the buffer to the marked position. The marked position
* is 0 unless another position was marked or an offset was specified
* in the constructor.
*/
public synchronized void reset() {
pos = mark;
}
public void close() throws IOException {
//什么操作都没有
}
}
//todo FileInputStream
BufferInputStream
public
class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
//默认缓冲区大小
private static int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192;
//缓冲区最大扩展容量
private static int MAX_BUFFER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
//缓冲数组
protected volatile byte buf[];
//用于CAS 修改数组
private static final
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<BufferedInputStream, byte[]> bufUpdater =
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater
(BufferedInputStream.class, byte[].class, "buf");
//缓冲区读取的个数
protected int count;
//当前读取位置
protected int pos;
//标记当前pos,用于reset,则重新开始从markpos读取
protected int markpos = -1;
//读取内容超过limit,markpos失效
protected int marklimit;
private InputStream getInIfOpen() throws IOException {
//获取封装输入流
InputStream input = in;
if (input == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
return input;
}
private byte[] getBufIfOpen() throws IOException {
///获取缓冲区数组
byte[] buffer = buf;
if (buffer == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
return buffer;
}
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {
//默认缓冲数组大小8192
this(in, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
}
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {
super(in);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
buf = new byte[size];
}
private void fill() throws IOException {
//获取缓冲数组
byte[] buffer = getBufIfOpen();
if (markpos < 0)
pos = 0; /* no mark: throw away the buffer */
//设置了标记位置,以及当前读取的位置超过缓存数据最大长度
else if (pos >= buffer.length) /* no room left in buffer */
//这一步相当于把markpos右边数据全部挪移到左边,因为标记的位置指不定需要reset,所以相当于保存一个进度点
if (markpos > 0) { /* can throw away early part of the buffer */
int sz = pos - markpos;
//将buffer数组从标记位置开始,复制sz个数到buffer
System.arraycopy(buffer, markpos, buffer, 0, sz);
//记录新的位置
pos = sz;
//标记位置回滚0
markpos = 0;
} else if (buffer.length >= marklimit) {
//当buffer长度超过marklimit时,mark失效
markpos = -1; /* buffer got too big, invalidate mark */
pos = 0; /* drop buffer contents */
} else if (buffer.length >= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE) {
//说明无法继续扩容缓冲数组容量了
throw new OutOfMemoryError("Required array size too large");
} else { /* grow buffer */
//扩容一倍容量
int nsz = (pos <= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE - pos) ?
pos * 2 : MAX_BUFFER_SIZE;
//太大则为marklimit大小
if (nsz > marklimit)
nsz = marklimit;
byte nbuf[] = new byte[nsz];
//将buffer数据copy扩容后的nbuf
System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, nbuf, 0, pos);
if (!bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, nbuf)) {
// Can't replace buf if there was an async close.
// Note: This would need to be changed if fill()
// is ever made accessible to multiple threads.
// But for now, the only way CAS can fail is via close.
// assert buf == null;
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
buffer = nbuf;
}
//设置下步没读取到数据,设置默认值
count = pos;
//从流中读取数据到缓冲数组
int n = getInIfOpen().read(buffer, pos, buffer.length - pos);
//读取到数据,则记录最新的缓冲数组大小
if (n > 0)
count = n + pos;
}
public synchronized int read() throws IOException {
//当前读取位置>=缓冲区最大容量,则重新从输入流获取数据
if (pos >= count) {
fill();
if (pos >= count)
return -1;
}
//缓冲读取一个字节
return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff;
}
private int read1(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {
//余下缓冲数组容量=buf数组长度-当前读取位置
int avail = count - pos;
//初次读取,又或者读取完缓冲数组
if (avail <= 0) {
//len超过缓冲数组的长度,则直接返回,不缓存
if (len >= getBufIfOpen().length && markpos < 0) {
return getInIfOpen().read(b, off, len);
}
//填充到缓冲数组
fill();
//返回读取个数
avail = count - pos;
if (avail <= 0) return -1;
}
//边界检查,最多只能获取缓冲数组最大容量的数据
int cnt = (avail < len) ? avail : len;
//缓冲数组获取数据
System.arraycopy(getBufIfOpen(), pos, b, off, cnt);
//记录当前读取位置
pos += cnt;
return cnt;
}
public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len)
throws IOException
{
//判断buffer是否打开
getBufIfOpen(); // Check for closed stream
//off=0 len=1024.则值为1024
//判断off+len < b.length 则越界异常
//也就是说从off开始读取len长度.
if ((off | len | (off + len) | (b.length - (off + len))) < 0) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
//记录读取的总字节数
int n = 0;
for (;;) {
//读取到b数组,返回读取个数
int nread = read1(b, off + n, len - n);
//说明没读取到,则直接返回
if (nread <= 0)
return (n == 0) ? nread : n;
//累加读取字节数
n += nread;
//读取的总字节数>=读取长度,则直接返回
if (n >= len)
return n;
// if not closed but no bytes available, return
InputStream input = in;
//虽然读取的字节数<=读取长度,但是如果可以读取的字节数预估读完了,则直接返回
if (input != null && input.available() <= 0)
return n;
}
}
public synchronized long skip(long n) throws IOException {
getBufIfOpen(); // Check for closed stream
if (n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
//可以跳过的最大范围
long avail = count - pos;
//说明尚未读取,又或者已经读取填充完整个缓冲区
if (avail <= 0) {
// If no mark position set then don't keep in buffer
//尚未标记位置,则直接操作输入流跳过n
if (markpos <0)
return getInIfOpen().skip(n);
// Fill in buffer to save bytes for reset
//填充缓存数组
fill();
//获取填充之后的可跳过范围
avail = count - pos;
//依旧没,则返回
if (avail <= 0)
return 0;
}
//跳过的最大不能超过最大可以跳过的范围
long skipped = (avail < n) ? avail : n;
//记录新的位置
pos += skipped;
return skipped;
}
//该方法的返回值为缓存中的可读字节数目加流中可读字节数目的和
public synchronized int available() throws IOException {
int n = count - pos;
int avail = getInIfOpen().available();
return n > (Integer.MAX_VALUE - avail)
? Integer.MAX_VALUE
: n + avail;
}
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {
//标记位置无效之前可以读取的最大字节数
marklimit = readlimit;
//标记此输入流中的当前位置
markpos = pos;
}
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {
getBufIfOpen(); // Cause exception if closed
if (markpos < 0)
throw new IOException("Resetting to invalid mark");
pos = markpos;
}
//该流和ByteArrayInputStream一样都支持mark
public boolean markSupported() {
return true;
}
public void close() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer;
while ( (buffer = buf) != null) {
//CAS,清空缓冲流
if (bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, null)) {
InputStream input = in;
in = null;
if (input != null)
input.close();
return;
}
}
}
}
PipedInputStream
public class PipedInputStream extends InputStream {
//分别标记当前读管道,写管道的状态
boolean closedByWriter = false;
volatile boolean closedByReader = false;
//标记是否连接到写管道
boolean connected = false;
//读写2个线程
Thread readSide;
Thread writeSide;
//默认管道缓冲区大小
private static final int DEFAULT_PIPE_SIZE = 1024;
protected static final int PIPE_SIZE = DEFAULT_PIPE_SIZE;
protected byte buffer[];
//下一个写入字节位置 in=out则说明满了
protected int in = -1;
//下一个读取字节位置
protected int out = 0;
public PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream src) throws IOException {
this(src, DEFAULT_PIPE_SIZE);
}
public PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream src, int pipeSize)
throws IOException {
//初始化缓冲区大小,默认大小1024
initPipe(pipeSize);
//将当前对象传入PipedOutputStream
connect(src);
}
public PipedInputStream() {
//初始化缓冲区大小,默认大小1024
initPipe(DEFAULT_PIPE_SIZE);
}
public PipedInputStream(int pipeSize) {
//初始化指定大小的缓冲区
initPipe(pipeSize);
}
private void initPipe(int pipeSize) {
//初始化指定大小管道缓冲区
if (pipeSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Pipe Size <= 0");
}
buffer = new byte[pipeSize];
}
public void connect(PipedOutputStream src) throws IOException {
//管道连接
src.connect(this);
}
//接受output发送过来的数据
protected synchronized void receive(int b) throws IOException {
checkStateForReceive();
//获取当前线程
writeSide = Thread.currentThread();
//读满,则等待,通知其他读线程,我要开始写了
if (in == out)
awaitSpace();
//读满或初次读取,则重置下标
if (in < 0) {
in = 0;
out = 0;
}
//写入数据
buffer[in++] = (byte)(b & 0xFF);
//超过边界则从0开始
if (in >= buffer.length) {
in = 0;
}
}
synchronized void receive(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
//检查读写管道状态是否正常开放
checkStateForReceive();
writeSide = Thread.currentThread();
int bytesToTransfer = len;
while (bytesToTransfer > 0) {
//读满,则等待,通知其他读线程,我要开始写了
if (in == out)
awaitSpace();
int nextTransferAmount = 0;
//如果还有空间可以读取,则获取最大可读取大小
if (out < in) {
nextTransferAmount = buffer.length - in;
} else if (in < out) {
//读满或者初次读取则重置
if (in == -1) {
in = out = 0;
nextTransferAmount = buffer.length - in;
} else {
//读到这里说明in走了一圈,重置为0了
nextTransferAmount = out - in;
}
}
//读取空间足够
if (nextTransferAmount > bytesToTransfer)
nextTransferAmount = bytesToTransfer;
assert(nextTransferAmount > 0);
//写入范围数据到buffer
System.arraycopy(b, off, buffer, in, nextTransferAmount);
//记录剩下还需要写入的空间
bytesToTransfer -= nextTransferAmount;
off += nextTransferAmount;
in += nextTransferAmount;
//写入超限,重置
if (in >= buffer.length) {
in = 0;
}
}
}
private void checkStateForReceive() throws IOException {
//当前是否连接
if (!connected) {
throw new IOException("Pipe not connected");
} else if (closedByWriter || closedByReader) {
//当前读写管道是否关闭了
throw new IOException("Pipe closed");
} else if (readSide != null && !readSide.isAlive()) {
//当前线程死了
throw new IOException("Read end dead");
}
}
private void awaitSpace() throws IOException {
while (in == out) {
//检查读写管道状态是否正常开放
checkStateForReceive();
/* full: kick any waiting readers */
//通知
notifyAll();
try {
//等待
wait(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
throw new java.io.InterruptedIOException();
}
}
}
synchronized void receivedLast() {
//标记写管道流关闭
closedByWriter = true;
//通知所有等待的线程
notifyAll();
}
public synchronized int read() throws IOException {
//校验当前线程是否正常连接
if (!connected) {
throw new IOException("Pipe not connected");
} else if (closedByReader) {
//当前读管道是否关闭
throw new IOException("Pipe closed");
} else if (writeSide != null && !writeSide.isAlive()
&& !closedByWriter && (in < 0)) {
//写线程是否存活,以及是否关闭了写流
throw new IOException("Write end dead");
}
readSide = Thread.currentThread();
int trials = 2;
//等待写入
while (in < 0) {
//写入流关闭,则返回-1
if (closedByWriter) {
/* closed by writer, return EOF */
return -1;
}
//写线程已经不存活了,则抛异常
if ((writeSide != null) && (!writeSide.isAlive()) && (--trials < 0)) {
throw new IOException("Pipe broken");
}
/* might be a writer waiting */
//通知线程,开始读了
notifyAll();
try {
//等待
wait(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
throw new java.io.InterruptedIOException();
}
}
//读入数据
int ret = buffer[out++] & 0xFF;
//读到缓冲区上限则重置
if (out >= buffer.length) {
out = 0;
}
//读满则重置
if (in == out) {
/* now empty */
in = -1;
}
return ret;
}
public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
/* possibly wait on the first character */
//尝试读取一个字节
int c = read();
//没数据则直接返回
if (c < 0) {
return -1;
}
b[off] = (byte) c;
int rlen = 1;
while ((in >= 0) && (len > 1)) {
int available;
//获取可读取的范围
if (in > out) {
available = Math.min((buffer.length - out), (in - out));
} else {
//执行到这里,说明in写了一圈了.
available = buffer.length - out;
}
// A byte is read beforehand outside the loop
//可读取的空间足够,则直接读取len-1长度
if (available > (len - 1)) {
available = len - 1;
}
System.arraycopy(buffer, out, b, off + rlen, available);
out += available;
rlen += available;
len -= available;
//读到缓冲区上限则重置
if (out >= buffer.length) {
out = 0;
}
//读满则重置
if (in == out) {
/* now empty */
in = -1;
}
}
return rlen;
}
public synchronized int available() throws IOException {
//读满,或者第一次读取,则暂无字节可读取
if(in < 0)
return 0;
else if(in == out)
//读满,则重置范围
return buffer.length;
else if (in > out)
//还在一圈范围内
return in - out;
else
//读取一圈
return in + buffer.length - out;
}
public void close() throws IOException {
//标记当前读流关闭
closedByReader = true;
synchronized (this) {
in = -1;
}
}
}
//todo ObjectInputStream
OutputStream
public abstract class OutputStream implements Closeable, Flushable {
public abstract void write(int b) throws IOException;
public void write(byte b[]) throws IOException {
write(b, 0, b.length);
}
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
//非空,上下界限校验
if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if ((off < 0) || (off > b.length) || (len < 0) ||
((off + len) > b.length) || ((off + len) < 0)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return;
}
//一个字节一个字节写入
for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) {
write(b[off + i]);
}
}
//刷新此输出流并强制任何缓冲的输出字节被写出。
public void flush() throws IOException {
}
//关闭
public void close() throws IOException {
}
}
//todo FileOutputStream
BufferedOutputStream
Java IO中的管道为运行在同一个JVM中的两个线程提供了通信的能力。所以管道也可以作为数据源以及目标媒介
public
class BufferedOutputStream extends FilterOutputStream {
//记录缓冲大小,默认8192
protected byte buf[];
//记录缓冲数据个数
protected int count;
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) {
this(out, 8192);
}
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size) {
//使用父类装饰outputStream
super(out);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
//创建缓冲数组,默认大小8192
buf = new byte[size];
}
private void flushBuffer() throws IOException {
//当缓冲数组有数据,则刷新到输出流中,重置数组长度
if (count > 0) {
out.write(buf, 0, count);
count = 0;
}
}
public synchronized void write(int b) throws IOException {
//写入长度超过缓冲数组长度,则刷新一遍
if (count >= buf.length) {
flushBuffer();
}
//记录
buf[count++] = (byte)b;
}
public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
//写入长度,超过缓冲数组长度,则刷新一遍,写入输出流
if (len >= buf.length) {
flushBuffer();
out.write(b, off, len);
return;
}
//写入长度,超过余下缓冲数组长度,刷新输出流一次
if (len > buf.length - count) {
flushBuffer();
}
//写入缓冲数组
System.arraycopy(b, off, buf, count, len);
///累加数组记录字节数
count += len;
}
public synchronized void flush() throws IOException {
//缓冲数据写入输出流
flushBuffer();
//输出流刷新
out.flush();
}
}
PipedOutputStream
public
class PipedOutputStream extends OutputStream {
private PipedInputStream sink;
public PipedOutputStream(PipedInputStream snk) throws IOException {
//管道连接
connect(snk);
}
public PipedOutputStream() {
}
public synchronized void connect(PipedInputStream snk) throws IOException {
if (snk == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if (sink != null || snk.connected) {
throw new IOException("Already connected");
}
sink = snk;
//标记初次写入
snk.in = -1;
//读取起始位置
snk.out = 0;
//标记状态为连接
snk.connected = true;
}
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
if (sink == null) {
throw new IOException("Pipe not connected");
}
//往input写入数据
sink.receive(b);
}
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (sink == null) {
throw new IOException("Pipe not connected");
} else if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if ((off < 0) || (off > b.length) || (len < 0) ||
((off + len) > b.length) || ((off + len) < 0)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return;
}
//往input写入指定范围数据
sink.receive(b, off, len);
}
//强制唤醒所有阻塞状态
public synchronized void flush() throws IOException {
if (sink != null) {
synchronized (sink) {
//通知其他
sink.notifyAll();
}
}
}
public void close() throws IOException {
//标记当前管道已经关闭
if (sink != null) {
sink.receivedLast();
}
}
}
//todo ObjectOutputStream
字符流
Reader
public abstract class Reader implements Readable, Closeable {
/**
* The object used to synchronize operations on this stream. For
* efficiency, a character-stream object may use an object other than
* itself to protect critical sections. A subclass should therefore use
* the object in this field rather than <tt>this</tt> or a synchronized
* method.
*/
//锁,默认当前对象
protected Object lock;
/**
* Creates a new character-stream reader whose critical sections will
* synchronize on the reader itself.
*/
protected Reader() {
this.lock = this;
}
/**
* Creates a new character-stream reader whose critical sections will
* synchronize on the given object.
*
* @param lock The Object to synchronize on.
*/
protected Reader(Object lock) {
if (lock == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
this.lock = lock;
}
/**
* Attempts to read characters into the specified character buffer.
* The buffer is used as a repository of characters as-is: the only
* changes made are the results of a put operation. No flipping or
* rewinding of the buffer is performed.
*
* @param target the buffer to read characters into
* @return The number of characters added to the buffer, or
* -1 if this source of characters is at its end
* @throws IOException if an I/O error occurs
* @throws NullPointerException if target is null
* @throws java.nio.ReadOnlyBufferException if target is a read only buffer
* @since 1.5
*/
public int read(java.nio.CharBuffer target) throws IOException {
int len = target.remaining();
char[] cbuf = new char[len];
int n = read(cbuf, 0, len);
if (n > 0)
target.put(cbuf, 0, n);
return n;
}
/**
* Reads a single character. This method will block until a character is
* available, an I/O error occurs, or the end of the stream is reached.
*
* <p> Subclasses that intend to support efficient single-character input
* should override this method.
*
* @return The character read, as an integer in the range 0 to 65535
* (<tt>0x00-0xffff</tt>), or -1 if the end of the stream has
* been reached
*
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
public int read() throws IOException {
//创建容量为一字符的数组
char cb[] = new char[1];
//读取一个字符
if (read(cb, 0, 1) == -1)
return -1;
else
return cb[0];
}
/**
* Reads characters into an array. This method will block until some input
* is available, an I/O error occurs, or the end of the stream is reached.
*
* @param cbuf Destination buffer
*
* @return The number of characters read, or -1
* if the end of the stream
* has been reached
*
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
public int read(char cbuf[]) throws IOException {
return read(cbuf, 0, cbuf.length);
}
/**
* Reads characters into a portion of an array. This method will block
* until some input is available, an I/O error occurs, or the end of the
* stream is reached.
*
* @param cbuf Destination buffer
* @param off Offset at which to start storing characters
* @param len Maximum number of characters to read
*
* @return The number of characters read, or -1 if the end of the
* stream has been reached
*
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
abstract public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
/** Maximum skip-buffer size */
private static final int maxSkipBufferSize = 8192;
/** Skip buffer, null until allocated */
private char skipBuffer[] = null;
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
if (n < 0L)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("skip value is negative");
//默认最大只能跳过8192字节
int nn = (int) Math.min(n, maxSkipBufferSize);
synchronized (lock) {
//新建记录跳过的字符
if ((skipBuffer == null) || (skipBuffer.length < nn))
skipBuffer = new char[nn];
long r = n;
while (r > 0) {
int nc = read(skipBuffer, 0, (int)Math.min(r, nn));
if (nc == -1)
break;
r -= nc;
}
return n - r;
}
}
/**
* Tells whether this stream is ready to be read.
*
* @return True if the next read() is guaranteed not to block for input,
* false otherwise. Note that returning false does not guarantee that the
* next read will block.
*
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
//告诉这个流是否准备好被读取。
public boolean ready() throws IOException {
return false;
}
/**
* Tells whether this stream supports the mark() operation. The default
* implementation always returns false. Subclasses should override this
* method.
*
* @return true if and only if this stream supports the mark operation.
*/
//不支持标记
public boolean markSupported() {
return false;
}
/**
* Marks the present position in the stream. Subsequent calls to reset()
* will attempt to reposition the stream to this point. Not all
* character-input streams support the mark() operation.
*
* @param readAheadLimit Limit on the number of characters that may be
* read while still preserving the mark. After
* reading this many characters, attempting to
* reset the stream may fail.
*
* @exception IOException If the stream does not support mark(),
* or if some other I/O error occurs
*/
public void mark(int readAheadLimit) throws IOException {
throw new IOException("mark() not supported");
}
/**
* Resets the stream. If the stream has been marked, then attempt to
* reposition it at the mark. If the stream has not been marked, then
* attempt to reset it in some way appropriate to the particular stream,
* for example by repositioning it to its starting point. Not all
* character-input streams support the reset() operation, and some support
* reset() without supporting mark().
*
* @exception IOException If the stream has not been marked,
* or if the mark has been invalidated,
* or if the stream does not support reset(),
* or if some other I/O error occurs
*/
public void reset() throws IOException {
throw new IOException("reset() not supported");
}
/**
* Closes the stream and releases any system resources associated with
* it. Once the stream has been closed, further read(), ready(),
* mark(), reset(), or skip() invocations will throw an IOException.
* Closing a previously closed stream has no effect.
*
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
abstract public void close() throws IOException;
}
//todo FileReader
BufferedReader
public class BufferedReader extends Reader {
private Reader in;
//缓冲区
private char cb[];
//缓冲区缓存数据个数
private int nChars,
//下一个字符的位置
nextChar;
private static final int INVALIDATED = -2;
private static final int UNMARKED = -1;
private int markedChar = UNMARKED;
private int readAheadLimit = 0; /* Valid only when markedChar > 0 */
/** If the next character is a line feed, skip it */
private boolean skipLF = false;
/** The skipLF flag when the mark was set */
private boolean markedSkipLF = false;
private static int defaultCharBufferSize = 8192;
private static int defaultExpectedLineLength = 80;
/**
* Creates a buffering character-input stream that uses an input buffer of
* the specified size.
*
* @param in A Reader
* @param sz Input-buffer size
*
* @exception IllegalArgumentException If {@code sz <= 0}
*/
public BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz) {
//当前锁对象为in流
super(in);
if (sz <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
this.in = in;
//默认缓冲区大小8192
cb = new char[sz];
//数组总个数和下一个字符索引默认0
nextChar = nChars = 0;
}
/**
* Creates a buffering character-input stream that uses a default-sized
* input buffer.
*
* @param in A Reader
*/
public BufferedReader(Reader in) {
this(in, defaultCharBufferSize);
}
/** Checks to make sure that the stream has not been closed */
private void ensureOpen() throws IOException {
if (in == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
private void fill() throws IOException {
int dst;
//没有设置标记点,则默认0开始读取
if (markedChar <= UNMARKED) {
/* No mark */
dst = 0;
} else {
/* Marked */
int delta = nextChar - markedChar;
//超过标记限制,则清除标记状态
//markedChar~readAheadLimit范围还在余下缓冲区空间中
if (delta >= readAheadLimit) {
/* Gone past read-ahead limit: Invalidate mark */
markedChar = INVALIDATED;
readAheadLimit = 0;
dst = 0;
} else {
//markedChar右边数据移动到最左边,然后重置markedChar=0
//markedChar~readAheadLimit余下缓冲区大小无法满足,但是数组最大容量可以满足
if (readAheadLimit <= cb.length) {
/* Shuffle in the current buffer */
System.arraycopy(cb, markedChar, cb, 0, delta);
markedChar = 0;
dst = delta;
} else {
//数组最大容量满足不了,只好扩容到readAheadLimit大小了
/* Reallocate buffer to accommodate read-ahead limit */
//扩容,容量最大范围为readAheadLimit
//markedChar右边数据移动到扩容数组的最左边,然后重置markedChar=0
char ncb[] = new char[readAheadLimit];
System.arraycopy(cb, markedChar, ncb, 0, delta);
cb = ncb;
markedChar = 0;
dst = delta;
}
nextChar = nChars = delta;
}
}
int n;
//一口气读取到cb数组
do {
n = in.read(cb, dst, cb.length - dst);
} while (n == 0);
//读取到值
if (n > 0) {
//记录当前读取总个数
nChars = dst + n;
//记录读取的起始位置
nextChar = dst;
}
}
/**
* Reads a single character.
*
* @return The character read, as an integer in the range
* 0 to 65535 (<tt>0x00-0xffff</tt>), or -1 if the
* end of the stream has been reached
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
public int read() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
//判断是否开启
ensureOpen();
for (;;) {
//当下一个字节超过当前缓冲区数据个数大小,则重新从0覆盖缓冲区数据
if (nextChar >= nChars) {
fill();
//说明没读取到数据,则返回-1
if (nextChar >= nChars)
return -1;
}
//遇到换行
if (skipLF) {
skipLF = false;
//下标移动到下一行
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n') {
nextChar++;
continue;
}
}
return cb[nextChar++];
}
}
}
/**
* Reads characters into a portion of an array, reading from the underlying
* stream if necessary.
*/
private int read1(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) throws IOException {
//老规矩,读到最后,则重新从0覆盖读取到缓冲区
if (nextChar >= nChars) {
/* If the requested length is at least as large as the buffer, and
if there is no mark/reset activity, and if line feeds are not
being skipped, do not bother to copy the characters into the
local buffer. In this way buffered streams will cascade
harmlessly. */
//一次性读取的数据范围超过缓冲区大小,且尚未标记点,且没遇到换行,则直接从流中获取数据
if (len >= cb.length && markedChar <= UNMARKED && !skipLF) {
return in.read(cbuf, off, len);
}
fill();
}
//执行到这里,说明要么没越界,要么越界了但是没读到数据,则直接返回-1
if (nextChar >= nChars) return -1;
//执行到这里说明没越界
if (skipLF) {
//重置没换行
skipLF = false;
//换行,则下标+1,移动到下一行
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n') {
nextChar++;
//如果移动下一行后,超过最大容量,则再次加载缓冲区
if (nextChar >= nChars)
fill();
//如果加载缓冲区,没读到数据,则直接返回-1
if (nextChar >= nChars)
return -1;
}
}
//一次获取的最大容量不超过缓冲区剩余大小
int n = Math.min(len, nChars - nextChar);
System.arraycopy(cb, nextChar, cbuf, off, n);
nextChar += n;
return n;
}
public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
//检验流是否开启
ensureOpen();
//范围校验
if ((off < 0) || (off > cbuf.length) || (len < 0) ||
((off + len) > cbuf.length) || ((off + len) < 0)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
//获取数据
int n = read1(cbuf, off, len);
//没数据直接返回
if (n <= 0) return n;
//保证获取数据容量偏向于len
while ((n < len) && in.ready()) {
//再次从off+n开始获取数据
int n1 = read1(cbuf, off + n, len - n);
//没读取则跳出循环
if (n1 <= 0) break;
n += n1;
}
return n;
}
}
/**
* Reads a line of text. A line is considered to be terminated by any one
* of a line feed ('\n'), a carriage return ('\r'), or a carriage return
* followed immediately by a linefeed.
*
* @param ignoreLF If true, the next '\n' will be skipped
*
* @return A String containing the contents of the line, not including
* any line-termination characters, or null if the end of the
* stream has been reached
*
* @see java.io.LineNumberReader#readLine()
*
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
//ignoreLF=true 则跳过下一个\n
String readLine(boolean ignoreLF) throws IOException {
StringBuffer s = null;
int startChar;
synchronized (lock) {
//校验流是否打开
ensureOpen();
//是否跳过\n或\r\n
boolean omitLF = ignoreLF || skipLF;
bufferLoop:
for (;;) {
if (nextChar >= nChars)
//数据填充缓冲区
fill();
//越界,则直接返回
if (nextChar >= nChars) { /* EOF */
if (s != null && s.length() > 0)
return s.toString();
else
return null;
}
boolean eol = false;
char c = 0;
//记录下一个\r or \n 下标
int i;
/* Skip a leftover '\n', if necessary */
//跳过换行,并移动到下一行
if (omitLF && (cb[nextChar] == '\n'))
nextChar++;
//执行到这一步,说明没换行,或者已经跳过换行,则重置状态
skipLF = false;
omitLF = false;
//遍历查找到\r or \n下标赋值给i
charLoop:
for (i = nextChar; i < nChars; i++) {
c = cb[i];
if ((c == '\n') || (c == '\r')) {
eol = true;
break charLoop;
}
}
//分别标记读取的数据的开始结束位置
startChar = nextChar;
nextChar = i;
//遇到换行或者空行情况
if (eol) {
String str;
if (s == null) {
//s为空,则新建对象
str = new String(cb, startChar, i - startChar);
} else {
//s有数据则累加
s.append(cb, startChar, i - startChar);
str = s.toString();
}
//因为换行了,所以自增,移动到下一行
nextChar++;
if (c == '\r') {
//标记遇到换行
skipLF = true;
}
return str;
}
//没遇到换行情况
if (s == null)
s = new StringBuffer(defaultExpectedLineLength);
s.append(cb, startChar, i - startChar);
}
}
}
public String readLine() throws IOException {
//不跳过换行
return readLine(false);
}
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
if (n < 0L) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("skip value is negative");
}
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
long r = n;
while (r > 0) {
if (nextChar >= nChars)
fill();
if (nextChar >= nChars) /* EOF */
break;
if (skipLF) {
skipLF = false;
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n') {
nextChar++;
}
}
long d = nChars - nextChar;
if (r <= d) {
nextChar += r;
r = 0;
break;
}
else {
r -= d;
nextChar = nChars;
}
}
return n - r;
}
}
public boolean ready() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
if (skipLF) {
/* Note that in.ready() will return true if and only if the next
* read on the stream will not block.
*/
//越界且同时流准备好,再次加载
if (nextChar >= nChars && in.ready()) {
fill();
}
//针对下一个下标换行的处理
if (nextChar < nChars) {
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n')
nextChar++;
skipLF = false;
}
}
return (nextChar < nChars) || in.ready();
}
}
/**
* Tells whether this stream supports the mark() operation, which it does.
*/
public boolean markSupported() {
return true;
}
public void mark(int readAheadLimit) throws IOException {
if (readAheadLimit < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Read-ahead limit < 0");
}
synchronized (lock) {
//检查流是否开启
ensureOpen();
this.readAheadLimit = readAheadLimit;
markedChar = nextChar;
markedSkipLF = skipLF;
}
}
public void reset() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
if (markedChar < 0)
throw new IOException((markedChar == INVALIDATED)
? "Mark invalid"
: "Stream not marked");
nextChar = markedChar;
skipLF = markedSkipLF;
}
}
public void close() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
if (in == null)
return;
try {
//关闭流
in.close();
} finally {
//释放流和缓冲区GC
in = null;
cb = null;
}
}
}
public Stream<String> lines() {
Iterator<String> iter = new Iterator<String>() {
String nextLine = null;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if (nextLine != null) {
return true;
} else {
try {
nextLine = readLine();
return (nextLine != null);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new UncheckedIOException(e);
}
}
}
@Override
public String next() {
if (nextLine != null || hasNext()) {
String line = nextLine;
nextLine = null;
return line;
} else {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
};
return StreamSupport.stream(Spliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(
iter, Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.NONNULL), false);
}
}






















 898
898

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








