本文来自OceanBase热心用户的实践分享。
本文主要是对OceanBase内存管理的实用技巧分享,而并非直接深入OceanBase的代码层面进行阐述。
阅读本文章你将了解:
- 重载运算符new 与malloc在返回值上区别?
- 在ceph 双向链表新用法,一个类定义时候 成员变量就是包含了 双向链表节点,可以通过该节点反推 类其他变量吗?
- 在stl中 中如何利用单链表存储申请批量对象?从对象中拿出固定字节就就可充当单链表?
- ob ob_allocator.h 与stl ob_allocator.h 分配器实现 有什么差别?
内存管理
C++中通过new和delete两个关键字进行动态内存管理。 c语言通过 malloc 和free 两个关键字进行动态内存管理
函数支持重载,运算符同样也支持重载
C++的提供了 重载运算符这一特性, 本质也是operators()函数重载,当遇到该运算符时就调用函数一样。
运算符重载的限制


小提示:Markdown左对,在原来基础上,后面一个空格就解决了 右对齐HTML css语法
重载运算符new
throwing (1) void* operator new (std::size_t size);
// throwing allocation ,On failure, it throws a bad_alloc exception
nothrow (2) void* operator new (std::size_t size, const std::nothrow_t& nothrow_value) noexcept;
//nothrow allocation on failure it returns a null pointer instead of throwing an exception
placement (3) void* operator new (std::size_t size, void* ptr) noexcept;
//placement Simply returns ptr (no storage is allocated).
// A pointer to an already-allocated memory block
代码示例
MyClass * p1 = new MyClass();
// allocates memory by calling: operator new (sizeof(MyClass))
// and then constructs an object at the newly allocated space
std::cout << "2: ";
MyClass * p2 = new (std::nothrow) MyClass();
// allocates memory by calling: operator new (sizeof(MyClass),std::nothrow)
// and then constructs an object at the newly allocated space
std::cout << "3: ";
new (p2) MyClass();//p2
delete p1;
delete p2;
malloc
https://en.cppreference.com/w/c/memory/malloc
void *malloc( size_t size );
Allocates size bytes of uninitialized storage,
alloc is thread-safe
Parameters
size - number of bytes to allocate
sizeof Queries size of the object or type.
On failure, returns a null pointer.
ob代码:ob_alter_table_resolver.cpp
//申请批量内存时候使用,
__MemoryContext__ *tmp = new (std::nothrow) __MemoryContext__();
abort_unless(tmp != nullptr); //
void *tmp_ptr = NULL;
common::ObIAllocator *allocator_;//分配器
if (NULL == (tmp_ptr = (ObAlterPrimaryArg *)allocator_->alloc(sizeof(obrpc::ObAlterPrimaryArg)))) {
} else {
alter_pk_arg = new (tmp_ptr) ObAlterPrimaryArg(); //这里没有使用delete
}
重载new运算符 使用场景
- 批量申请内容时候,使用std::nothrow 不抛出异常,通过返回值判断nullptr 来处理
- C++ placement new与内存池有关系,能帮助更节省内存吗?不清楚继续看
有些时候我们需要能够长时间运行的程序(例如监听程序,服务器程序)对于这些7*24运行的程序,我们不应该使用标准库提供的new 和 delete (malloc和free也算)。这是因为随着程序的运行,内存不断的被申请和被释放,频繁的申请和释放将会引发内存碎片、内存不足等问题,影响程序的正常运行。
更多的时候核心程序不允许内存申请失败,更不允许异常的出现,因此必须保证每次内存申请都是成功的(一般都是内核程序,当然不希望被中断的后台程序也是如此)。在这种极端要求下,内存池的好处就大大的凸现出来了。
在C++中,可以通过placement new 来实现内存池
如果分配能节省内存
内存池是很大概念,我平时用不到,上来不会说明原理,这是自己给自己挖坑,自己不会还要去自己讲清楚 先看一段代码,你发现什么错误吗?
一般定义链表,都有T 成员表示,但是ceph 中 定义 elist为什么没有,它怎么存储数据呢?
class Node
{
public:
int data; //存储数据
Node * last;
Node * next;
};
class DoubleNode
{
private:
Node * head; //头结点
Node * tail; //尾节点
};
一般定义链表,都有T 成员表示,但是elist为什么没有,它怎么存储数据呢?
完整代码:
https://lab.forgefriends.org/ceph/ceph/-/blob/wip-rgw-placement-rule-empty/src/include/elist.h
/*
* elist: embedded list. 这是一个双向链表,必须和类耦合起来。
* elist(embedded list)是一种特殊类型的链表,它允许将链表节点直接嵌入到用户定义的数据结构中。这种设计使得每个数据项可以作为链表的一部分
* requirements:
* - elist<T>::item be embedded in the parent class 定义类时候,必须使用 elist<T>::item 当作一个成员
* - items are _always_ added to the list via the same elist<T>::item at the same
* fixed offset in the class. //items 在类中偏移量
* - begin(), front(), back() methods take the member offset as an argument for traversal.
*
*/
//计算成员变量在类中的偏移量
#define member_offset(cls, member) ((size_t)(&((cls*)1)->member) - 1)
template<typename T>
class elist {
public:
struct item {
item *_prev, *_next;
//通过偏移量
T get_item(size_t offset) {
ceph_assert(offset);
return (T)(((char *)this) - offset);
}
}; //elist<T>::item 是作为用户定义结构体的成员变量存在的。
//意味着 item 的内存是从用户结构体的内存中分配的,而不是独立分配。
private:
item _head;
size_t item_offset;
}
class iterator {
private:
item *head;
item *cur, *next;
size_t item_offset;
public:
T operator*() {
return cur->get_item(item_offset);
}
};
- c++ 内存模型 (了解)
GCC 或 Clang,你可以使用 __builtin_offsetof 函数来获取成员的偏移量:
#define member_offset(cls, member) ((size_t)(&((cls*)1)->member) - 1)
class Example {
public:
char a; // 1 byte
int b; // 4 bytes, aligned to 4 bytes
double c; // 8 bytes, aligned to 8 bytes
bool d; // 1 byte, but often padded to align with 'b'
};
size_t offset_a = __builtin_offsetof(Example, a);__
size_t offset_b = __builtin_offsetof(Example, b)
能否提供一个完整的示例,展示如何在一个复杂的类中嵌入 `elist` 并使用它?
https://kimi.moonshot.cn/share/cqqc6ga1n4gqsenn4ur0
https://kimi.moonshot.cn/share/cqqcdsdskq8g1pv5ces0
STL源码剖析 by 侯捷 提到一个同样技巧
资料:STL标准库与泛型编程
- what:关于STL中空间配置器中free_list的理解,理解不了_Obj 单链表将多个 对象组织起来?
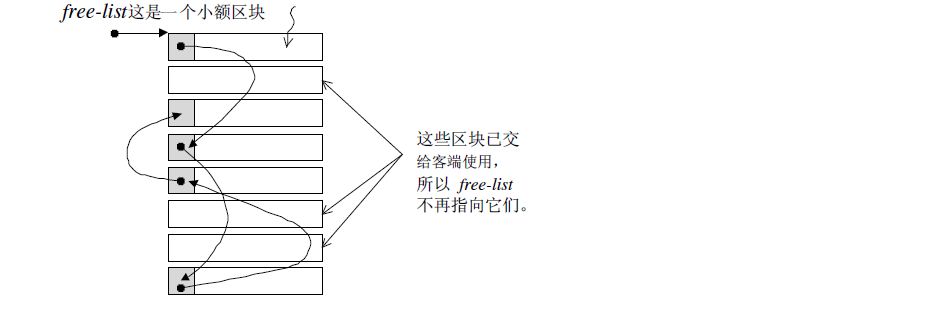
union _Obj {
union _Obj* _M_free_list_link; // 单链表
char _M_client_data[1]; /* The client sees this. */
}; 关于STL中空间配置器中free_list的理解
- how:参考资料
自己动手实现STL 01:内存配置器的实现(stl_alloc.h)
https://github.com/wangcy6/sgi-stl/blob/master/stl_alloc.h
https://www.cnblogs.com/wangjzh/p/4097355.html
https://github.com/wangcy6/STLSourceCodeNote
第一级配置器malloc_alloc 就是,直接调用系统的malloc分配内存
//第一级配置器malloc_alloc 就是,直接调用系统的malloc分配内存
typedef __malloc_alloc_template<0> malloc_alloc;
template <int __inst> //这个模板没啥意义,区分一级二级区别
class __malloc_alloc_template {
private:
static void* _S_oom_malloc(size_t);
static void* _S_oom_realloc(void*, size_t);
public:
static void* allocate(size_t __n)
{
void* __result = malloc(__n);
if (0 == __result) //malloc是否返回0
__result = _S_oom_malloc(__n); //分配失败继续分配
return __result;
}
static void deallocate(void* __p, size_t /* __n */)
{
free(__p);
}
}
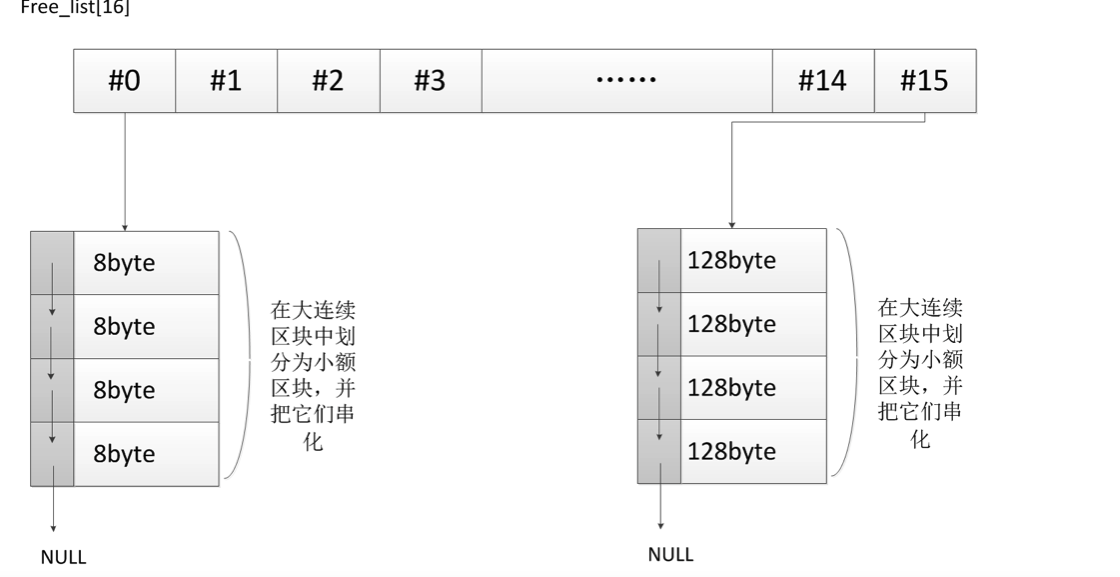
第二级配置器(Second-level allocator):。
default_alloc 尝试通过分配大块内存(称为 "chunks")来减少内存碎片,并使用这些大块内存来满足较小的内存请求。 它使用一个自由列表(free list)机制来管理这些大块内存中的小块内存。
default_alloc 可以是线程安全的,并且提供了更好的内存局部性和缓存性能。
//第二级配置器
typedef __default_alloc_template<__NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS, 0> alloc;
template <bool threads, int inst>
class __default_alloc_template {
union _Obj {
union _Obj* _M_free_list_link;
char _M_client_data[1]; /* The client sees this. */
};
}
_S_refill(size_t __n)
{
// 定义分配的对象数量为20,这个值可以根据需要调整。
int __nobjs = 20;
// 调用 _S_chunk_alloc 函数分配足够存储 __nobjs 个大小为 __n 的对象的内存块。
char* __chunk = _S_chunk_alloc(__n, __nobjs);
// __my_free_list 指向适当大小的自由列表的指针。
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list;
// __result 指向新分配的内存块的起始位置,将被返回给调用者。
_Obj* __result;
// __current_obj 和 __next_obj 用于遍历和设置对象链表的指针。
_Obj* __current_obj;
_Obj* __next_obj;
// __i 是循环计数器。
int __i;
// 如果只分配了一个对象,就直接返回这个对象的内存。
if (1 == __nobjs) return(__chunk);
// 计算并获取对应大小的自由列表。
__my_free_list = _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__n);
// 构建内存块内的自由链表。
// __result 初始化为指向内存块的起始位置。
__result = (_Obj*)__chunk;
// 第一个对象之后的对象地址设置为自由链表的头。
*__my_free_list = __next_obj = (_Obj*)(__chunk + __n);
// 循环将内存块分割成多个对象,并用 _M_free_list_link 将它们链接起来。
for (__i = 1; ; __i++) {
// __current_obj 指向当前正在处理的对象。
__current_obj = __next_obj;
// 计算下一个对象的地址。
__next_obj = (_Obj*)((char*)__next_obj + __n);
// 如果这是分配的最后一个对象,将其 _M_free_list_link 设置为 NULL,结束链表。
if (__nobjs - 1 == __i) {
__current_obj -> _M_free_list_link = 0;
break;
} else {
// 否则,将当前对象的 _M_free_list_link 设置为指向下一个对象。
__current_obj -> _M_free_list_link = __next_obj;
}
}
// 返回可以立即使用的首个对象的地址。
return(__result);
}
OceanBase怎么做的
- 先看例子
ParseNode *key_child_node;
key_child_node = static_cast<ParseNode*>(allocator.alloc(sizeof(ParseNode))) //
key_child_node = new(key_child_node) ParseNode;
oceanbase/deps/oblib/src/lib/allocator/ob_allocator.h
class ObAllocator : public ObIAllocator//直接看看发狂,概念太多,还是stl看着舒服//
- 参考:从0到1 OceanBase原生分布式数据库内核实战进阶版























 1076
1076

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








