Spring Aop编程
1、概念
Spring 的Aop编程核心是动态代理的开发
代理设计模式:通过代理类为原始对象增加额外功能
好处:可以通过动态字节码字节码技术进行创建对象
常见的两种动态代理方式为:
1、JDK代理
JDK:根据接口,通过动态字节码技术进行接口的实现,既保留原有功能,又增加了额外功能。
2、CGLIB代理
Cglib:根据原始类,通过动态字节码技术,创建原始类的子类,在子类的对应方法中,既保留原始功能,又增加额外功能
在我们学习设计模式的过程中,我们知道代理设计模式和装饰器设计模式UML图完全一样,那么他们有什么区别呢?
1、代理设计模式增加的是额外功能
2、装饰器设计模式增加的是本职功能
2、Aop开发步骤
1、原始对象 --------核心功能
2、额外功能
根据运行时机,原始方法之前、之后、抛出异常的时候
3、切入点
额外功能增加给哪些原始方法,这些是由切入点决定的
4、切面
Spring体系称为 Advisor
AspectJ体系注解开发AOP @Aspect
在Spring开发过程如果有接口默认采用的是JDK的动态代理,那么有没有什么办法修改成Cglib代理的?
有的,一般我们注解开发要添加:
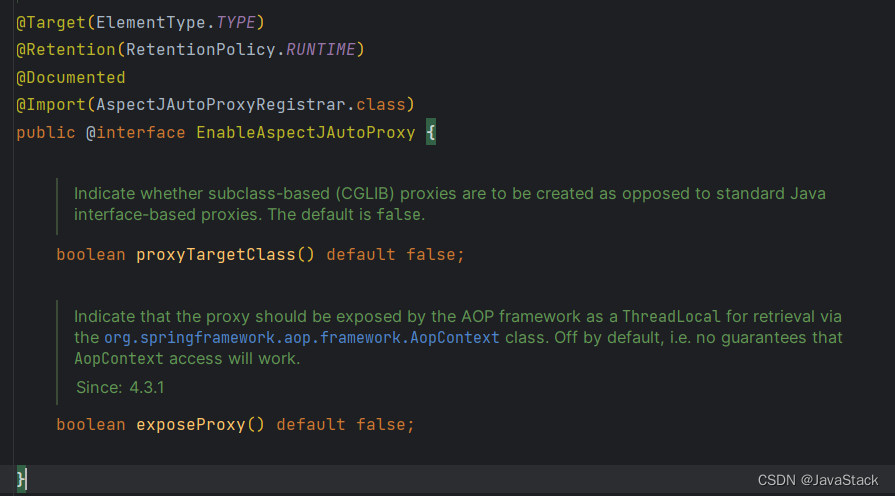
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
添加proxyTargetClass 可以将这次采用cglib动态代理
那么如果没有接口默认采用CGLIB,能否改为JDK代理呢?
不能
3、Aop编码
1、原始对象
public interface IUserService {
public void showName() ;
public void showAge();
}
//原始对象
@Service
public class UserService implements IUserService{
@Override
public void showName() {
System.out.println("UserService.showName");
}
@Override
public void showAge() {
System.out.println("UserService.showAge");
}
}
2、额外功能
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
/**
* 额外功能
*/
@Before("execution(* com.xiaohe.aop.UserService.*(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("------------------ before -------------------");
}
@After("execution(* com.xiaohe.aop.UserService.showAge(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("------------------ after --------------------");
}
}
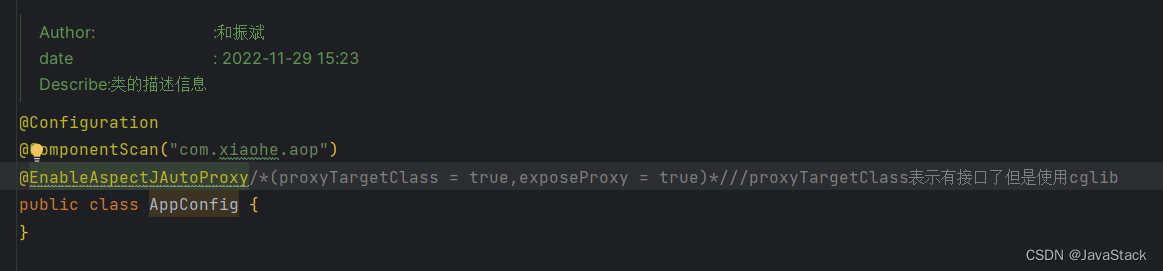
3、配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.xiaohe.aop")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy/*(proxyTargetClass = true,exposeProxy = true)*///proxyTargetClass表示有接口了但是使用cglib
public class AppConfig {
}
4、测试类
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
IUserService userService = (IUserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.showName();
}
}
4、Aop源码分析
4.1、代理对象的创建
AOP中两个比较重要的类:
- 1、CglibAopProxy
- 2、JdkDynamicAopProxy
- 3、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
4.1、从AppConfig中的@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
底层采用@Import引入AspectJAutoProxyRegister,以上我们已经解析过@Import引入的类会被Spring注册成为一个BeanDefinition
AspectJAutoProxyRegister实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,这个接口有一个
registerBeanDefinitions表示注册BeanDefinition的方法
class AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(
AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//1、 这个方法名不难判出这个方法是注册AspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreator的
AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
//2、解析@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解
AnnotationAttributes enableAspectJAutoProxy =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class);
//3、判断是否有@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,一般我们Aop开发是需要添加,因此走if分支
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy != null) {
//4、判断是否@EnableAspectJAutoProxy中的proxyTargetClass属性
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
//5、判断是否添加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy中的exposeProxy,这个当为True时Spring会将当前对象的代理对象放置在ThreadLocal中,可以从AopContext.currentProxy()获取当前类的代理类。
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("exposeProxy")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry);
}
}
}
}
AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry)
@Nullable
private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(
Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
//1、一般不走这里
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) {
int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName());
int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls);
if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) {
apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName());
}
}
return null;
}
//2、采用RootBeanDefinition构建BeanDifinition,cls为AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
beanDefinition.setSource(source);//source为null
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);//设置排序
//设置BeanDefinition的角色
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
//注册beanDefinition,重点
registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);
return beanDefinition;
}
注册完成后,在Spring在初始化过程中会调用AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类的postProcessAfterInitialization()实现代理的创建的。
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
//1、判断Bean的类型是否为BeanFactory,如果为BeanFactory则进行特殊处理
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
//2、判断是不是在循环引用中是否已经创建过代理,如果创建过则跳过
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
每一个在Spring中已经创建好的BeanDefinition都会进入这个方法
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
//1、判断BeanName是否为空,targetSourcedBeans资源bean中是否拥有这个Bean
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
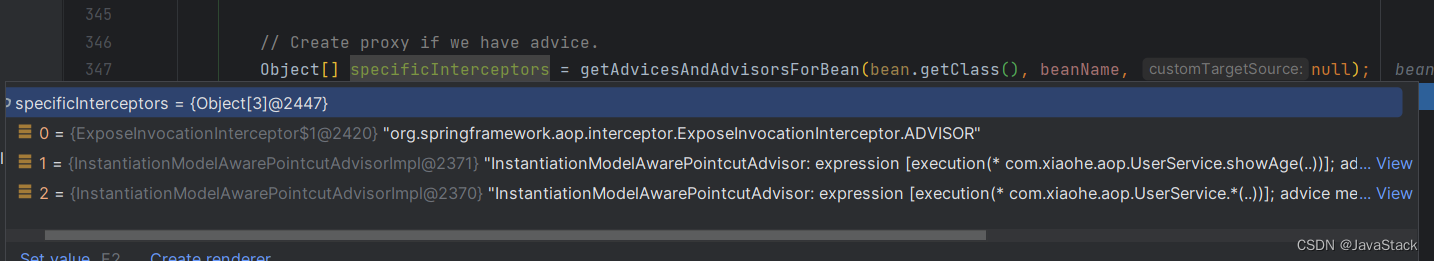
// 获取这次创建代理,所需要的所有切面
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
//因为在获取切面的过程中会有一个默认的,所以一般就走这个方法
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
//创建代理的方法
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
创建代理的方法Object proxy = createProxy()
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
//DefaultListableBeanFactory是ConfigurableListableBeanFactory的子类,一定走这个方法
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
//设置代理基类
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
//创建代理工厂,生产代理的
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);//指AbstractAutoProxyCreator,也就是当前类
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
//ProxyTargetClass设置为true的话,不管是否有接口都采用CGLib动态代理
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
//设置创建代理类所需要的 1、原始对象2、切面//
//切面
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
//原始对象
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
//重点,获取代理类的重点
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
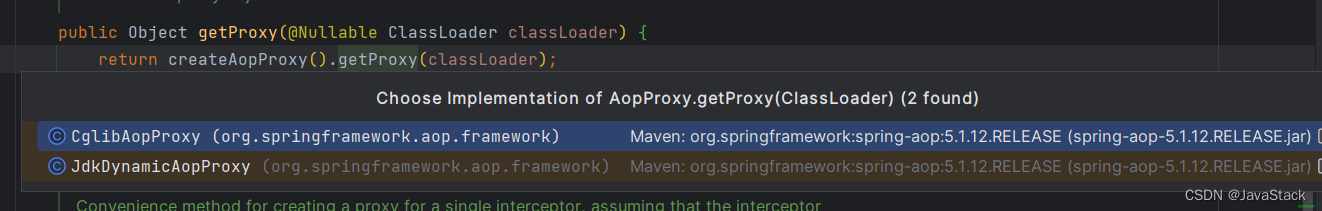
提供两个实现类:
- CglibAopProxy
- JdkDynamicAopProxy 如果有接口的话,默认采用JDK动态代理
JdkDynamicAopProxy.getProxy()
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);
findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);
//这个是创建代理的核心
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);
}
CglibAopProxy创建代理的核心
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(rootClass)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// Cglib创建代理的核心
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareUndeclaredThrowableStrategy(classLoader));
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}
至此代理创建完毕,在调用的时候,将不走原始对象的原有逻辑,而是走代理,将原始功能和额外功能整合在一起。以下即是代理运行过程中,原始对象的功能与额外功能的整合
4.2、代理的执行
代理的执行为原始功能与额外功能的融合
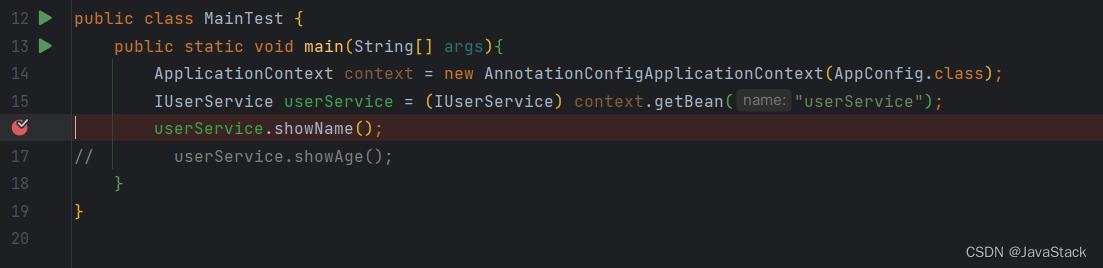
1、打断点到原始对象执行的过程
2、进入到代理对象执行的InvocationHandler方法,默认采用JDKDynamicAopProxy代理
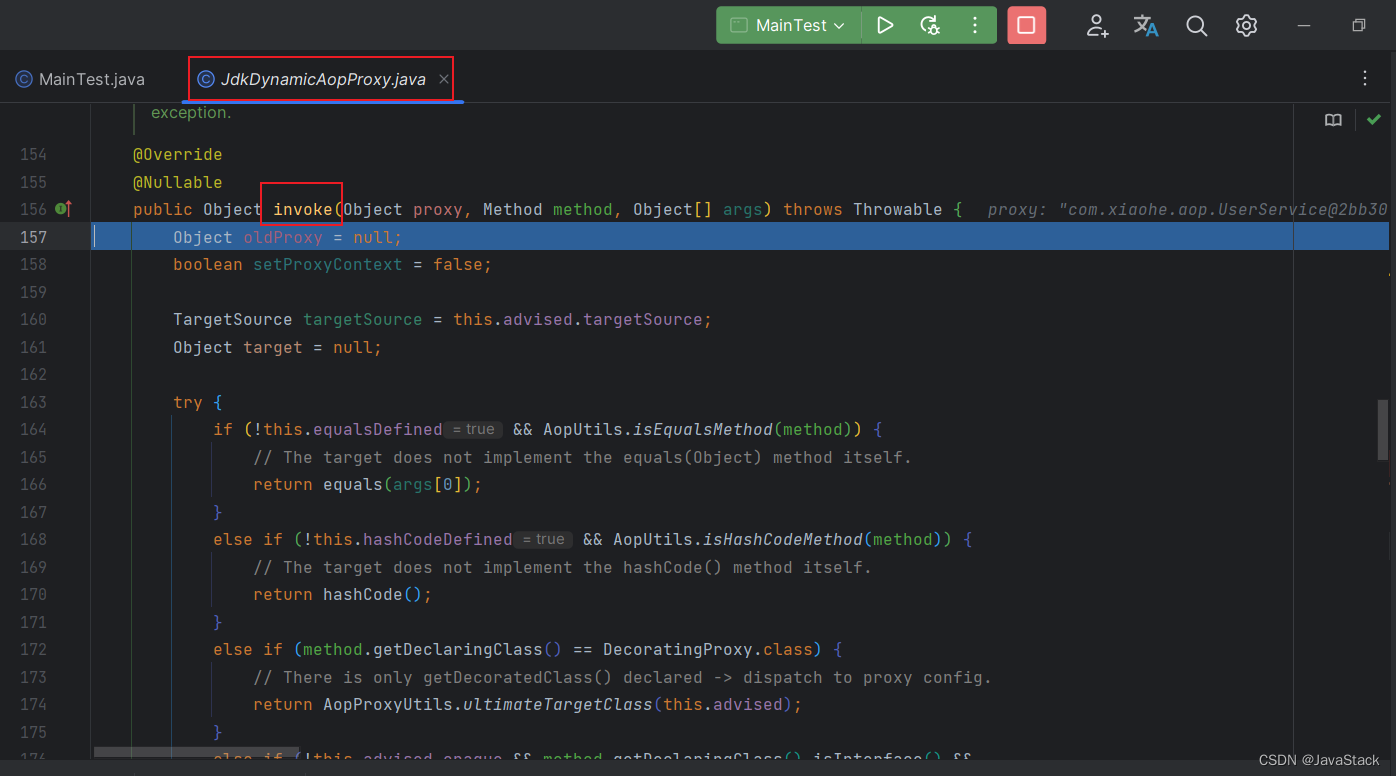
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Object target = null;
try {
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.
return equals(args[0]);
}
else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.
return hashCode();
}
else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {
// There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.
return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);
}
else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
// in case it comes from a pool.
//1、获取原始对象
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// Get the interception chain for this method.
//结合切入点进行判断,是否对应的切面是否可以添加额外功能,返回值:符合切入点要求这些切面
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
//链条一般不会为空,因为默认系统有一个默认的
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
else {
// 原始对象和额外功能的整合
MethodInvocation invocation =
new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&
returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retVal = proxy;
}
else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// Must have come from TargetSource.
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
怎么判断原始方法执行是否添加额外功能呢?Spring提供了一个PointCut的接口
public interface Pointcut {
//1、校验类
ClassFilter getClassFilter();
//2、校验方法
MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher();
Pointcut TRUE = TruePointcut.INSTANCE;
}
ClassFilter提供了一个Match方法
public interface ClassFilter {
boolean matches(Class<?> clazz);
ClassFilter TRUE = TrueClassFilter.INSTANCE;
}
MethodMatcher 提供了校验方法的方法
public interface MethodMatcher {
boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass);
boolean isRuntime();
boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, Object... args);
MethodMatcher TRUE = TrueMethodMatcher.INSTANCE;
}
有了上面的基础我们看切入点的判断代码
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method);
List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey);
//第一次cache为空,会走if
if (cached == null) {
//这个是获取是否符合切入点的切面
cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
this, method, targetClass);
this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached);
}
return cached;
}
advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice()
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
Advised config, Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
// This is somewhat tricky... We have to process introductions first,
// but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list.
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();
//获取所有切面
Advisor[] advisors = config.getAdvisors();
//创建一个切面数组
List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<>(advisors.length);
Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass());
Boolean hasIntroductions = null;
//遍历所有的切面
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
//PointcutAdvisor实现Advisor
if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
//将原来的切面类型包装成PointcutAdvisor类型
PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
//类型匹配和方法匹配,判断该切面是否匹配当前方法的执行
if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
boolean match;
if (mm instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
if (hasIntroductions == null) {
hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(advisors, actualClass);
}
match = ((IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) mm).matches(method, actualClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
match = mm.matches(method, actualClass);
}
if (match) {
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
if (mm.isRuntime()) {
// Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method
// isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains.
for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm));
}
}
else {
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
}
}
else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
else {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
//将匹配的切面放置到数组中进行返回
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
return interceptorList;
}
查找到符合的切面后,执行原来的方法
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Object target = null;
try {
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.
return equals(args[0]);
}
else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.
return hashCode();
}
else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {
// There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.
return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);
}
else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
// in case it comes from a pool.
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// 获取符合条件的切面
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
//不会为空
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
else {
MethodInvocation invocation =
new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&
returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retVal = proxy;
}
else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// Must have come from TargetSource.
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
前置通知执行
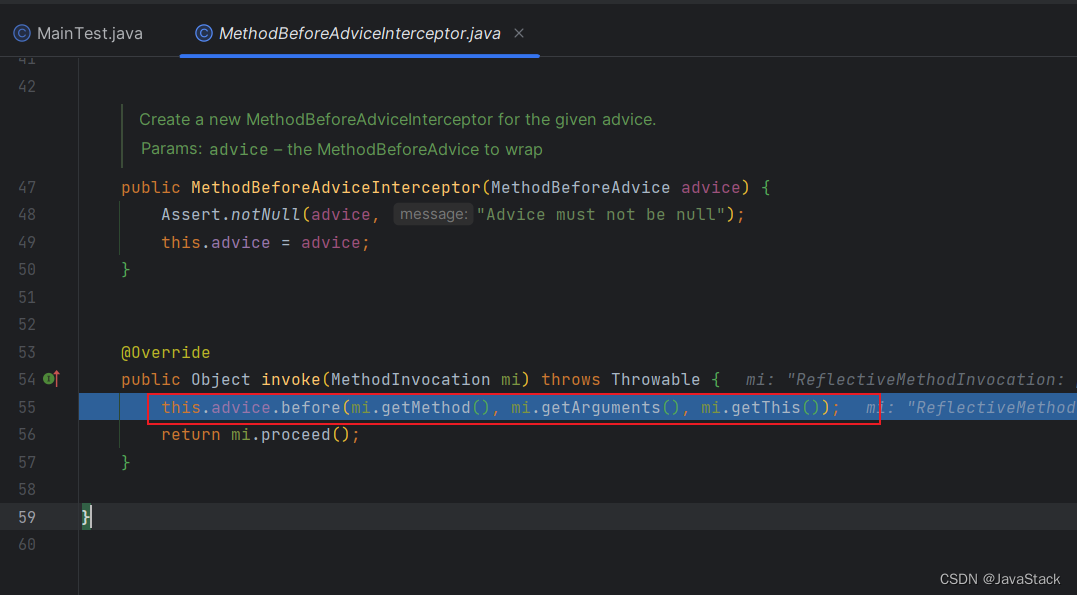
综上所述:AOP代理分析结束
面试如果文到Spring-Aop可以这样给面试官说:
Spring 的生命周期首先可以说一下,Spring分为对象创建、属性填充、初始化,在初始化的过程中会调用BeanPostProcessor中的PostProcessorsBeforeInitialization和BeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization,而Spring Aop分为代理的创建和执行代理对象时原始功能和额外功能的整合,代理对象的创建依赖于我们写的注解@EnableAspectJAutoProxy其是采用@Import的方式实现
向容器注入了AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class,当对象初始化过程中会回调AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类中的postProcessAfterInitialization中的creatProxt()进行代理的创建,代理的创建依赖于ProxyFactory,然后设置切面和原始类进行代理的创建,代理创建依赖于 proxyFactory.getProxy()方法,这个方法主要有两个实现类JdkDynamicAopProxy和CglibAopProxy的getProxy()进行代理的创建,在执行getBean()过程中到达初始化过程的时候会回调BeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization进行代理的创建。然后执行代理的invoke方法进行额外功能与原始功能,其大概逻辑就是根据类和方法获取所有的切面,然后将切面和原始方法进行整合。























 660
660











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








