《C Primer Plus》第5章复习题与编程练习
复习题
1. 各变量的值
- x=(2+3)*6=30
- x=(12+6)/2*3=27
- y=x=(2+3)/4=1
- y=3+2*(x=7/2) ,x=3, y=9
2. 各变量的值
- x=(int)3.8+3.3=6
- x=(2+3)*10.5=52
- x=3/5*22.0=0
- x=22.0*3/5=13
3. 各表达式的值
- 37.5
- 1.5
- 35
- 37
- 37.5
- 35.0
4. 找程序的错误
原程序:
/* 5.10.4 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
int i = 1;
float n;
printf("Watch out! Here come a bunch of fractions!\n");
while (i < 30)
n = 1 / i;
printf(" %f", n);
printf("That's all, folks!\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
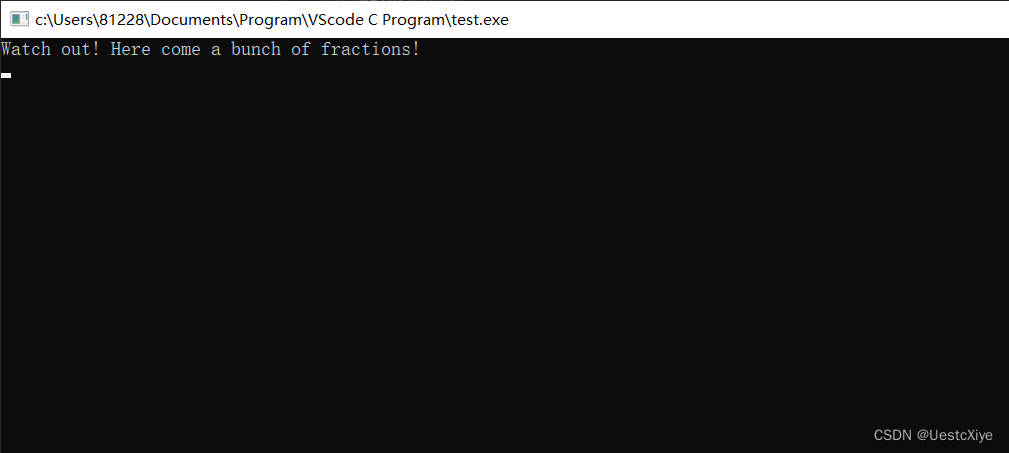
错误:程序打印Watch out! Here come a bunch of fractions!后,程序在下列代码中陷入死循环:
while (i < 30)
n = 1 / i;
运行截图:
修改后程序:
/* 5.10.4 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
int i = 1;
float n;
printf("Watch out! Here come a bunch of fractions!\n");
while (i < 30)
{
n = 1 / i;
printf(" %f", n);
i++;
}
printf("That's all, folks!\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行截图:
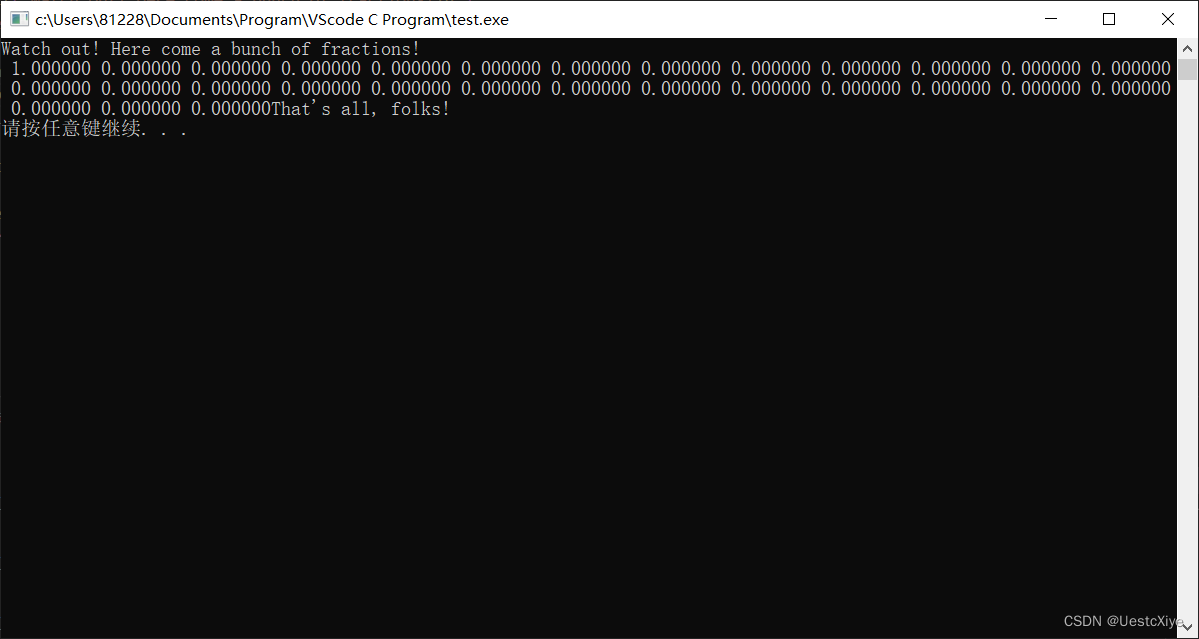
5. 找出不如原版之处
#include <stdio.h>
#define S_TO_M 60
int main(void)
{
int sec, min, left;
printf("This program converts seconds to minutes and ");
printf("seconds.\n");
printf("Just enter the number of seconds.\n");
printf("Enter 0 to end the program.\n");
while (sec > 0)
{
scanf("%d", &sec);
min = sec/S_TO_M;
left = sec % S_TO_M;
printf("%d sec is %d min, %d sec. \n", sec, min, left);
printf("Next input?\n");
}
printf("Bye!\n");
return 0;
}
原程序:
//5.9
#include <stdio.h>
#define SEC_PER_MIN 60 // 1分钟60秒
int main(void)
{
int sec, min, left;
printf("Convert seconds to minutes and seconds!\n");
printf("Enter the number of seconds (<=0 to quit):\n");
scanf("%d", &sec); // 读取秒数
while (sec > 0)
{
min = sec / SEC_PER_MIN; // 截断分钟数
left = sec % SEC_PER_MIN; // 剩下的秒数
printf("%d seconds is %d minutes, %d seconds.\n", sec, min, left);
printf("Enter next value (<=0 to quit):\n");
scanf("%d", &sec);
}
printf("Done!\n");
return 0;
}
- sec没有进行初始化,内存位置上是一个垃圾值
- 当要结束输入的时候,仍然会输出一次0
6. 程序打印什么内容
#include <stdio.h>
#define FORMAT "%s! C is cool!\n"
int main(void)
{
int num = 10;
printf(FORMAT,FORMAT);
printf("%d\n", ++num);
printf("%d\n", num++);
printf("%d\n", num--);
printf("%d\n", num);
return 0;
}
%s! C is cool!
! C is cool!
11
11
12
11
7. 程序打印什么内容
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char c1, c2;
int diff;
float num;
c1 = 'S';
c2 = 'O';
diff = c1 - c2;
num = diff;
printf("%c%c%c:%d %3.2f\n", c1, c2, c1, diff, num);
return 0;
}
SOS:4 4.00
8. 程序打印什么内容
#include <stdio.h>
#define TEN 10
int main(void)
{
int n = 0;
while (n++ < TEN)
printf("%5d", n);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10(每个数字占5个单位长度)
9. 修改上一个程序,打印a~g
/* 5.10.4 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SEVEN 7
int main(void)
{
int n = 0;
char c = 'a';
while (n++ < SEVEN)
{
printf("%5c", c);
c++;
}
printf("\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
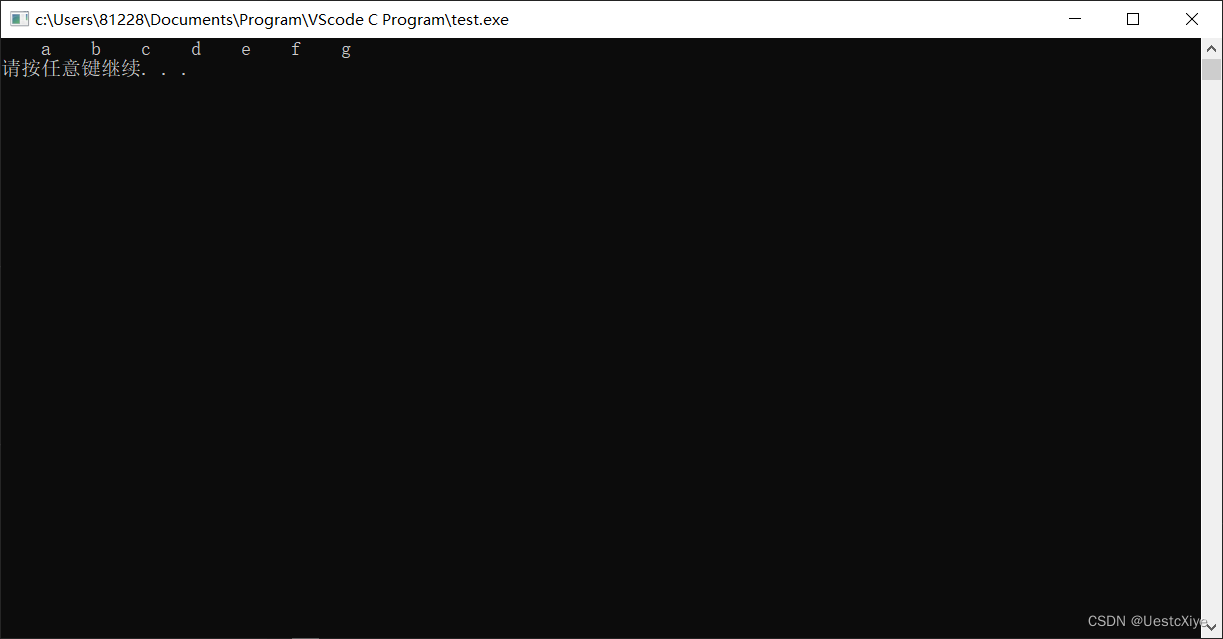
10. 打印什么内容
a.
int x = 0;
while (++x < 3)
printf("%4d", x);
1 2
b.
int x = 100;
while (x++ < 103)
printf("%4d\n",x);
printf("%4d\n",x);
101
102
103
104
c.
char ch = 's';
while (ch < 'w')
{
printf("%c", ch);
ch++;
}
printf("%c\n",ch);
stuvw
11. 打印什么内容
#define MESG "COMPUTER BYTES DOG"
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int n = 0;
while ( n < 5 )
printf("%s\n", MESG);
n++;
printf("That's all.\n");
return 0;
}
重复打印 COMPUTER BYTES DOG 直到程序终止。
12. 分别编写一条语句,完成下列各任务(或者说,使其具有以下副作用):
a.将变量x的值增加10
x=x+10;
b.将变量x的值增加1
x++;
c.将a与b之和的两倍赋给c
c=(a+b)*2;
d.将a与b的两倍之和赋给c
c=a+b*2;
13. 分别编写一条语句,完成下列各任务:
a.将变量x的值减少1
x--;
b.将n除以k的余数赋给m
m=n%k;
c.q除以b减去a,并将结果赋给p
p=q/(b-a); // 有歧义
d.a与b之和除以c与d的乘积,并将结果赋给x
x=(a+b)/(c*d);
编程练习
1. 时间转换
编写一个程序,把用分钟表示的时间转换成用小时和分钟表示的时间。使用#define或const创建一个表示60的符号常量或const变量。通过while循环让用户重复输入值,直到用户输入小于或等于0的值才停止循环。
代码:
/* 5.11.1 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MINUTE 60
int main(void)
{
int minutes;
printf("Please input your minutes(>0): ");
scanf("%d", &minutes);
while (minutes > 0)
{
printf("%d minute(s) equal to %d hour(s) and %d minutes.\n", minutes, minutes / MINUTE, minutes % MINUTE);
printf("Try again: ");
scanf("%d", &minutes);
}
printf("Bye!\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
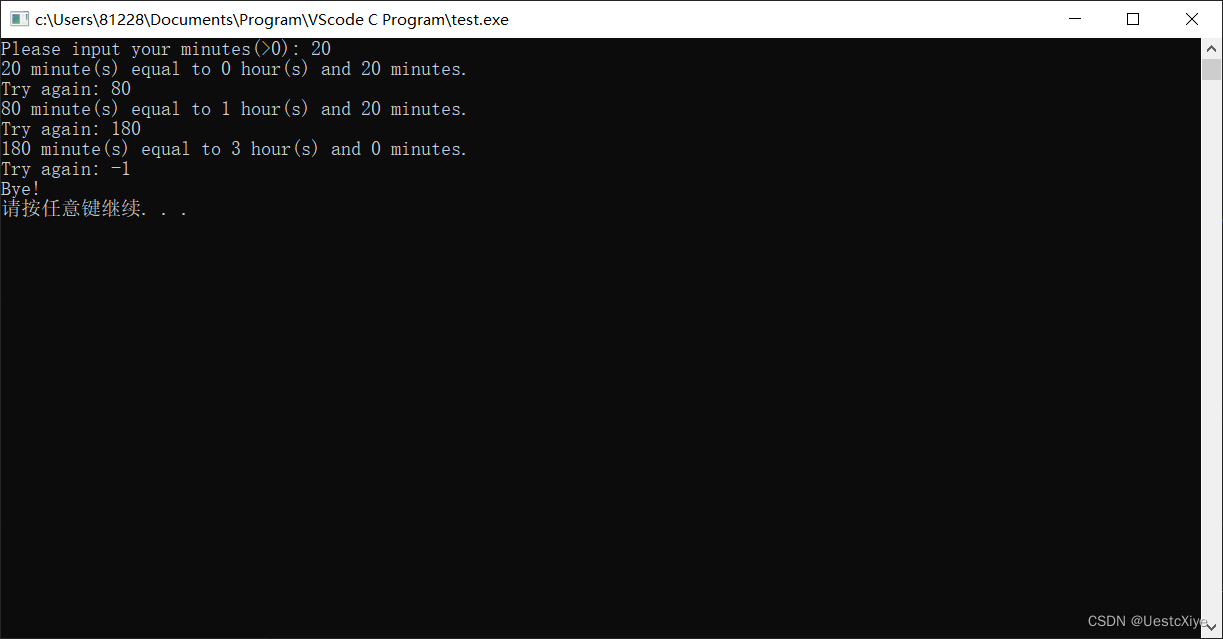
2. 打印数字
编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个整数,然后打印从该数到比该数大10的所有整数(例如,用户输入5,则打印5~15的所有整数,包括5和15)。要求打印的各值之间用一个空格、制表符或换行符分开。
代码:
/* 5.11.2 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
int n;
printf("Please input a integer: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<11;i++)
{
printf("%d ",n++);
}
printf("\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
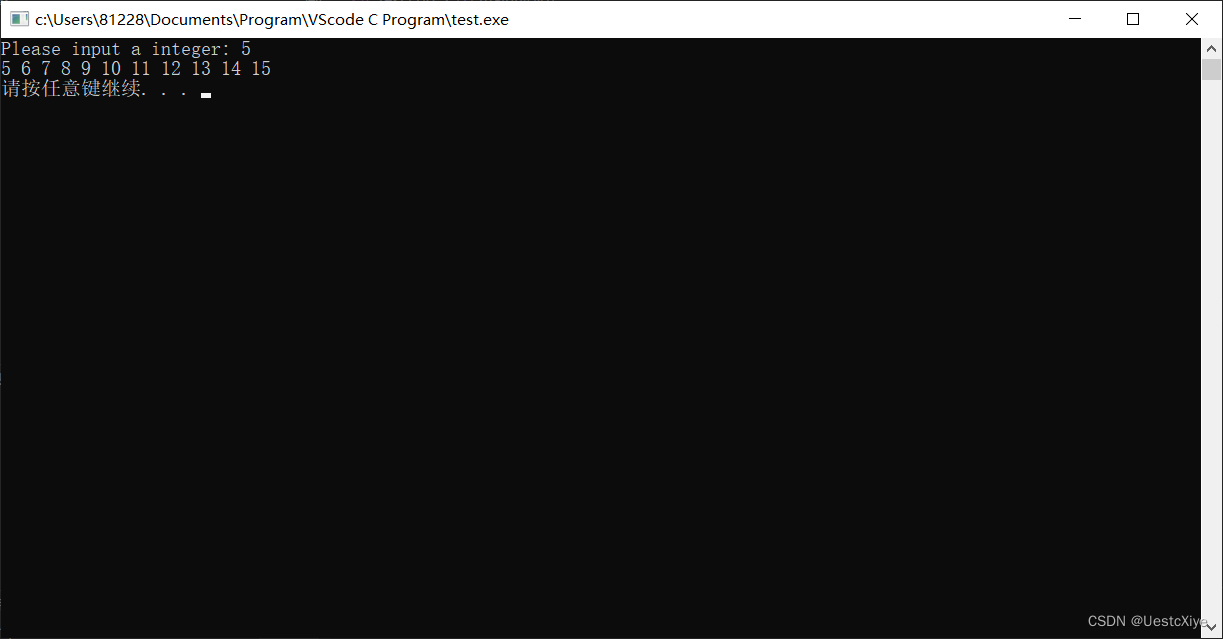
3. 天数转换
编写一个程序,提示用户输入天数,然后将其转换成周数和天数。例如,用户输入18,则转换成2周4天。以下面的格式显示结果:
18 days are 2 weeks, 4 days.
通过while循环让用户重复输入天数,当用户输入一个非正值时(如0或-20),循环结束。
代码:
/* 5.11.3 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define WEEK 7
int main(void)
{
int day;
printf("Please input your days(>0): ");
scanf("%d", &day);
while (day > 0)
{
printf("%d days are %d weeks, %d days.\n", day, day / WEEK, day % WEEK);
printf("Try again: ");
scanf("%d", &day);
}
printf("Bye!\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
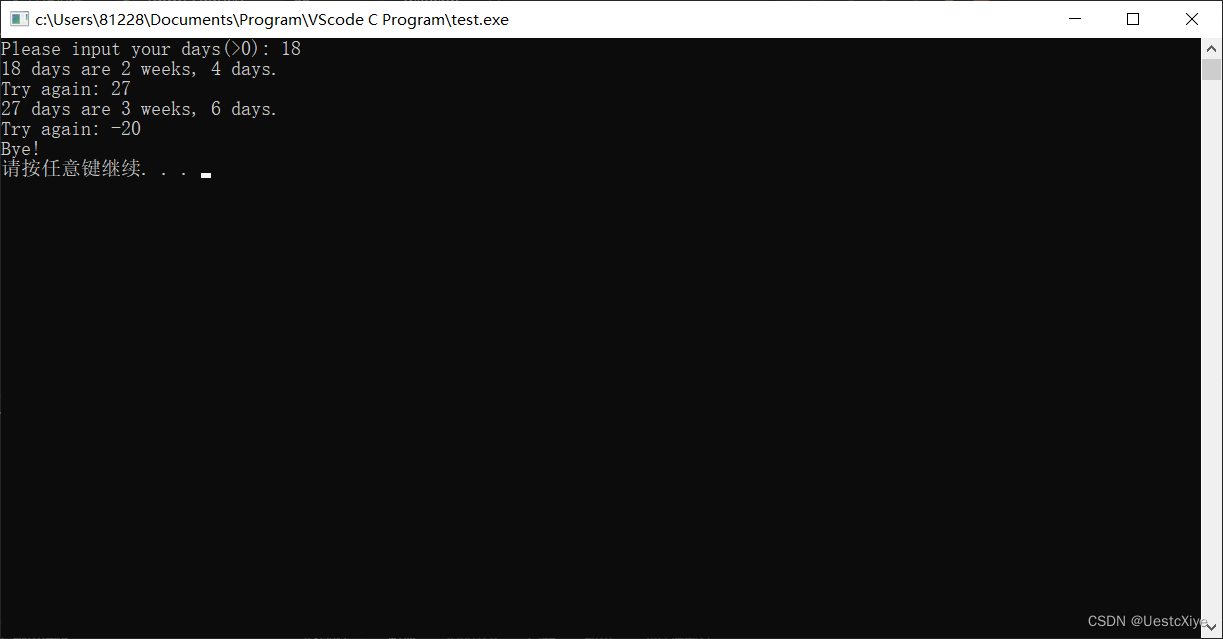
4. 身高转换
编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个身高(单位:厘米),并分别以厘米和英寸为单位显示该值,允许有小数部分。程序应该能让用户重复输入身高,直到用户输入一个非正值。其输出示例如下:
Enter a height in centimeters: 182
182.0 cm = 5 feet, 11.7 inches
Enter a height in centimeters (<=0 to quit): 168.7
168.0 cm = 5 feet, 6.4 inches
Enter a height in centimeters (<=0 to quit): 0
bye
代码:
/* 5.11.4 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
float m;
printf("Enter a height in centimeters:");
while (~scanf("%f", &m) && m > 0)
{
int f = m / 31; //不用int型接收的话,用%d打印float类型会因为字节截断输出而出现问题
printf("%.1f cm = %d feet, %.1f inches\n", m, f, m * 0.39370 - f * 12);
printf("Enter a height in centimeters (<=0 to quit):");
}
printf("bye\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
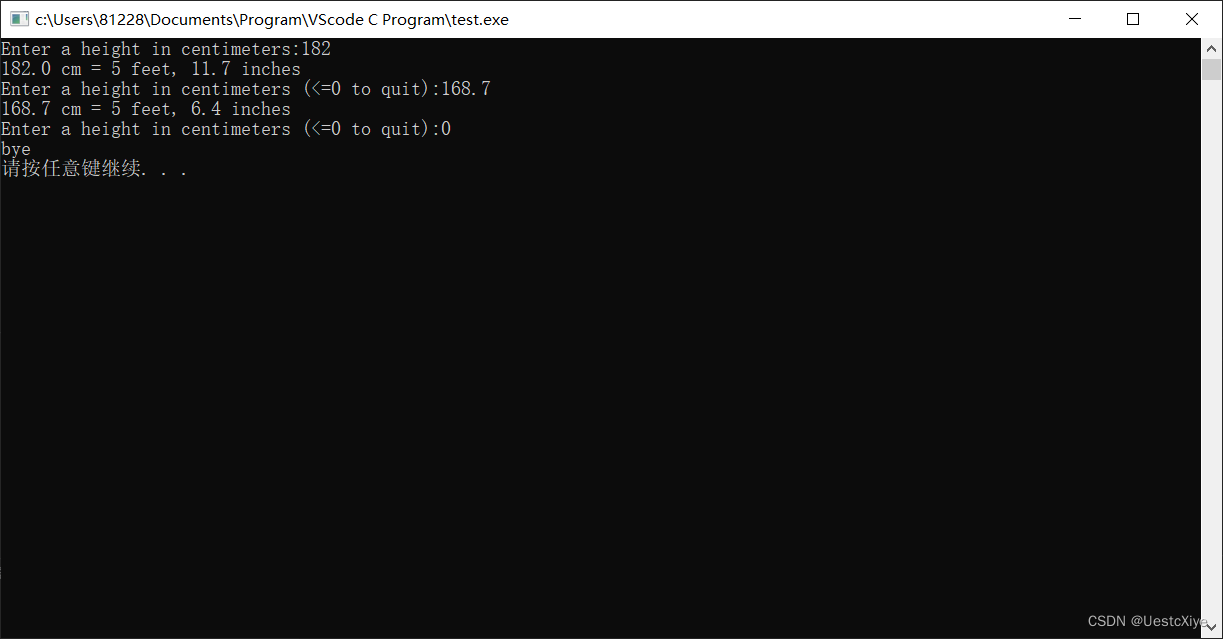
5. 打印赚钱数
修改程序addemup.c(程序清单5.13),你可以认为addemup.c是计算20天里赚多少钱的程序(假设第1天赚$1、第2天赚$2、第3天赚$3,以此类推)。修改程序,使其可以与用户交互,根据用户输入的数进行计算(即,用读入的一个变量来代替20)。
代码:
/* 5.11.5 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int count, sum, d;
count = 0;
sum = 0;
printf("input d: ");
scanf("%d", &d);
while (count++ < d)
{
sum = sum + count;
}
printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
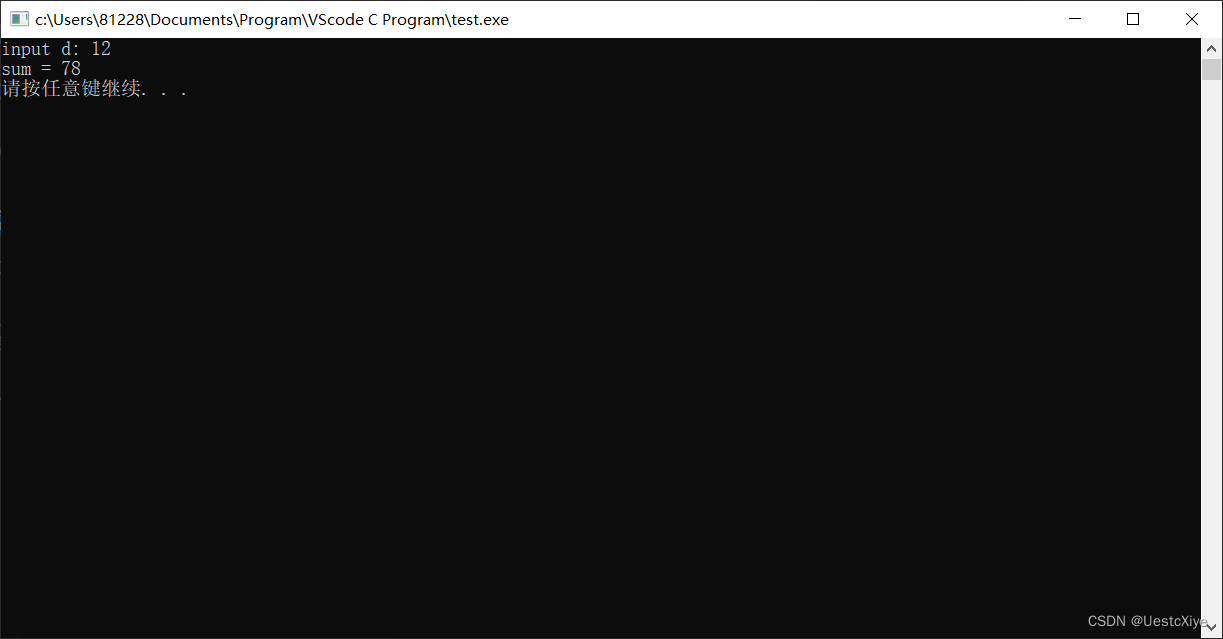
6. 修改程序5
修改编程练习5的程序,使其能计算整数的平方和(可以认为第1天赚$1、第2天赚$4、第3天赚$9,以此类推,这看起来很不错)。C没有平方函数,但是可以用n * n来表示n的平方。
代码:
/* 5.11.6 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int count, sum, d;
count = 0;
sum = 0;
printf("input d: ");
scanf("%d", &d);
while (count++ < d)
{
sum = sum + count * count;
}
printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
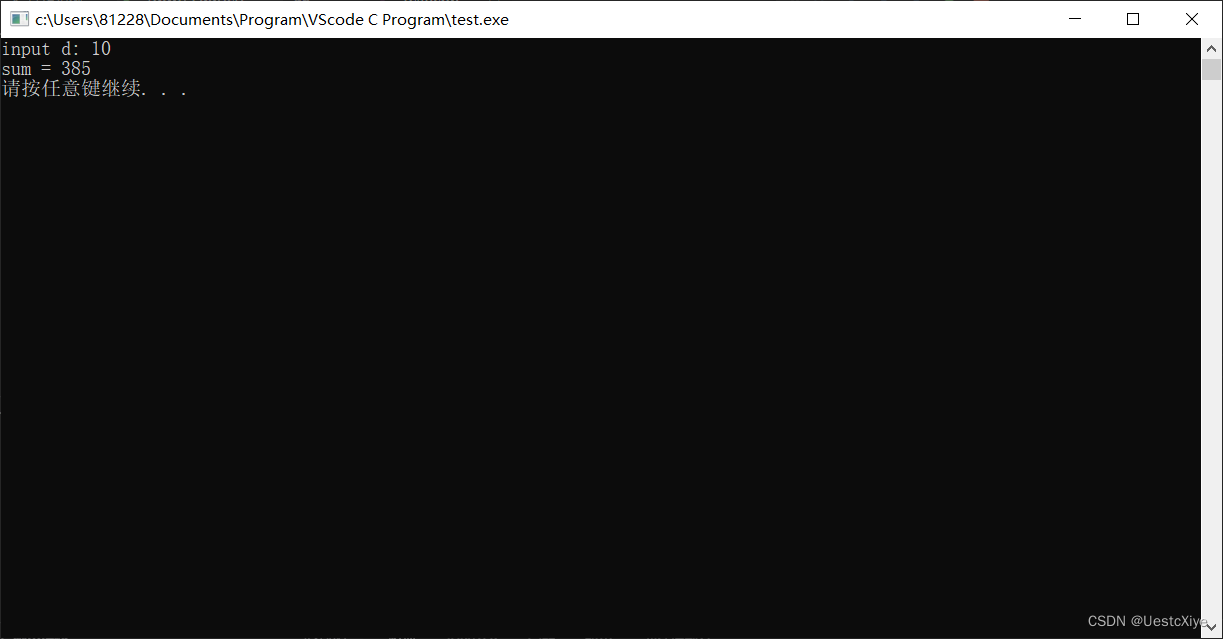
7. 打印立方值
编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个double类型的数,并打印该数的立方值。自己设计一个函数计算并打印立方值。main()函数要把用户输入的值传递给该函数。
代码:
/* 5.11.7 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void func(double x)
{
printf("%lf\n", x * x * x);
}
int main()
{
double x;
printf("Please input a number: ");
scanf("%lf", &x);
func(x);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
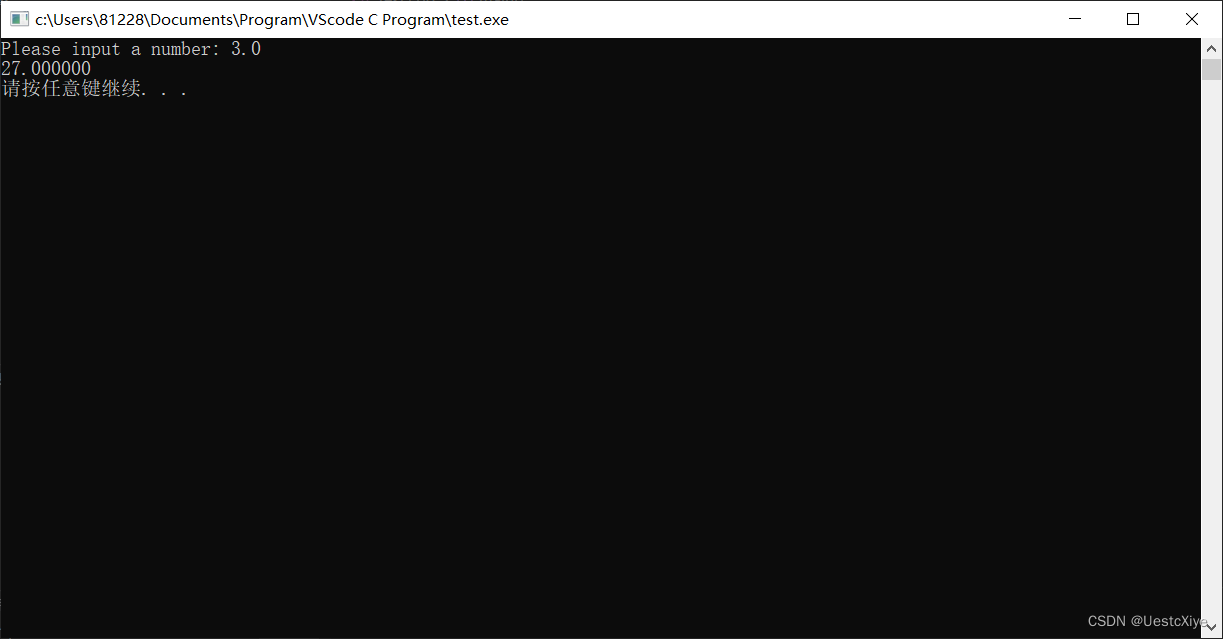
8. 打印求模运算结果
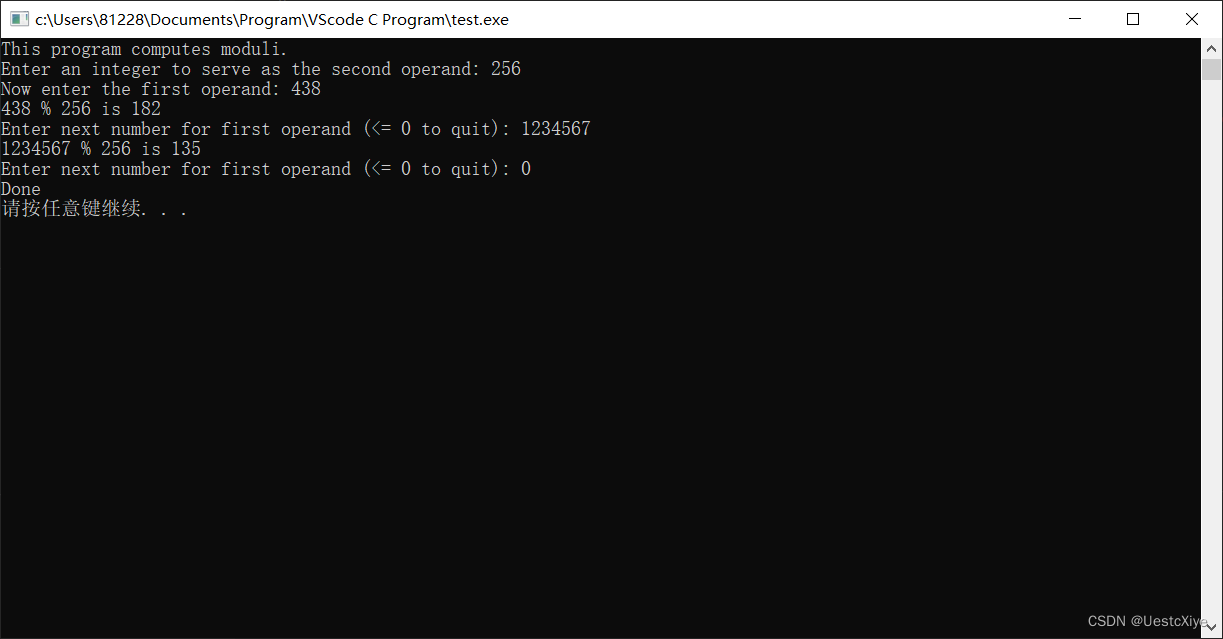
编写一个程序,显示求模运算的结果。把用户输入的第1个整数作为求模运算符的第2个运算对象,该数在运算过程中保持不变。用户后面输入的数是第1个运算对象。当用户输入一个非正值时,程序结束。其输出示例如下:
This program computes moduli.
Enter an integer to serve as the second operand: 256
Now enter the first operand: 438
438 % 256 is 182
Enter next number for first operand (<= 0 to quit): 1234567
1234567 % 256 is 135
Enter next number for first operand (<= 0 to quit): 0
Done
代码:
/* 5.11.8 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int mod;
int num;
printf("This program computes moduli.\nEnter an integer to serve as the second operand: ");
scanf("%d", &mod);
printf("Now enter the first operand: ");
while (~scanf("%d", &num) && num > 0)
{
printf("%d %% %d is %d\n", num, mod, num % mod);
printf("Enter next number for first operand (<= 0 to quit): ");
}
printf("Done\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
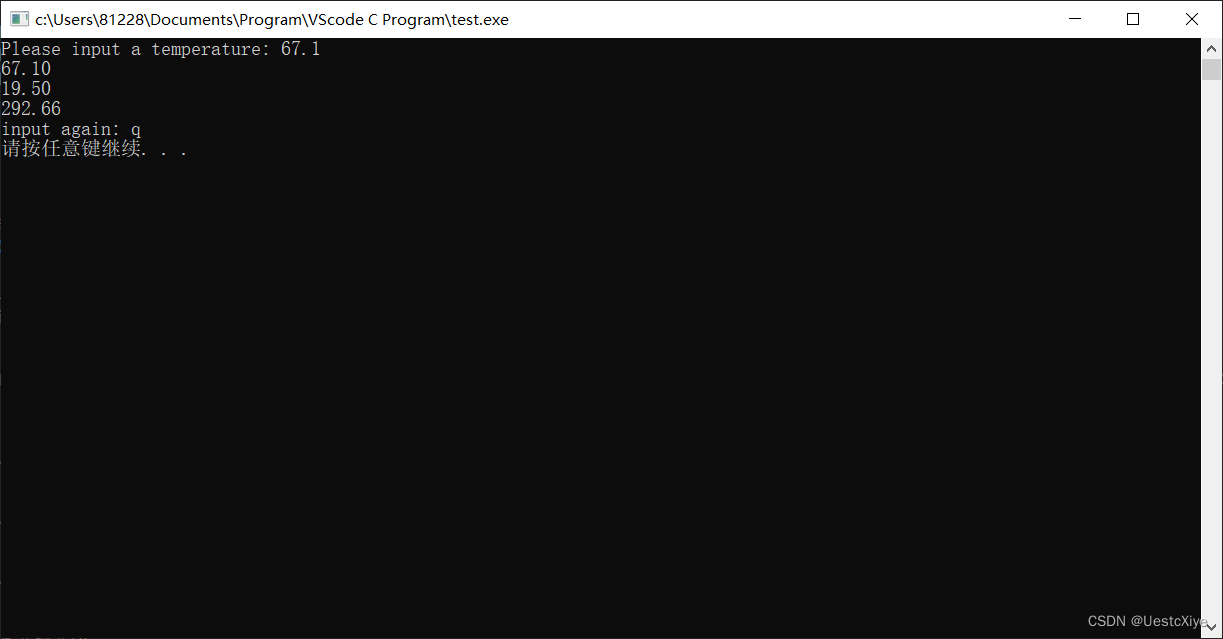
9. 温度转换
编写一个程序,要求用户输入一个华氏温度。程序应读取double类型的值作为温度值,并把该值作为参数传递给一个用户自定义的函数Temperatures()。该函数计算摄氏温度和开氏温度,并以小数点后面两位数字的精度显示3种温度。要使用不同的温标来表示这3个温度值。下面是华氏温度转摄氏温度的公式:
摄氏温度 = 5.0 / 9.0 * (华氏温度 - 32.0)
开氏温标常用于科学研究,0表示绝对零,代表最低的温度。下面是摄氏温度转开氏温度的公式:
开氏温度 = 摄氏温度 + 273.16
Temperatures()函数中用const创建温度转换中使用的变量。在main()函数中使用一个循环让用户重复输入温度,当用户输入 q 或其他非数字时,循环结束。scanf()函数返回读取数据的数量,所以如果读取数字则返回1,如果读取q则不返回1。可以使用==运算符将scanf()的返回值和1作比较,测试两值是否相等。
代码:
/* 5.11.9 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void Temperatures(double t)
{
const double w0 = 5.0 / 9.0;
const double w1 = 32.0;
const double k = 273.16;
printf("%.2lf\n", t);
printf("%.2lf\n", w0 * (t - w1));
printf("%.2lf\n", k + w0 * (t - w1));
}
int main()
{
double t;
printf("Please input a temperature: ");
while (scanf("%lf", &t) == 1)
{
Temperatures(t);
printf("input again: ");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:






















 563
563











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










