一个生产者生产产品,这些产品将提供给若干个消费者去消费,为了使生产者和消费者能并发执行,在两者之间设置一个具有多个缓冲区的缓冲池,生产者将它生产的产品放入一个缓冲区中,消费者可以从缓冲区中取走产品进行消费,显然生产者和消费者之间必须保持同步,即不允许消费者到一个空的缓冲区中取产品,也不允许生产者向一个已经放入产品的缓冲区中再次投放产品。
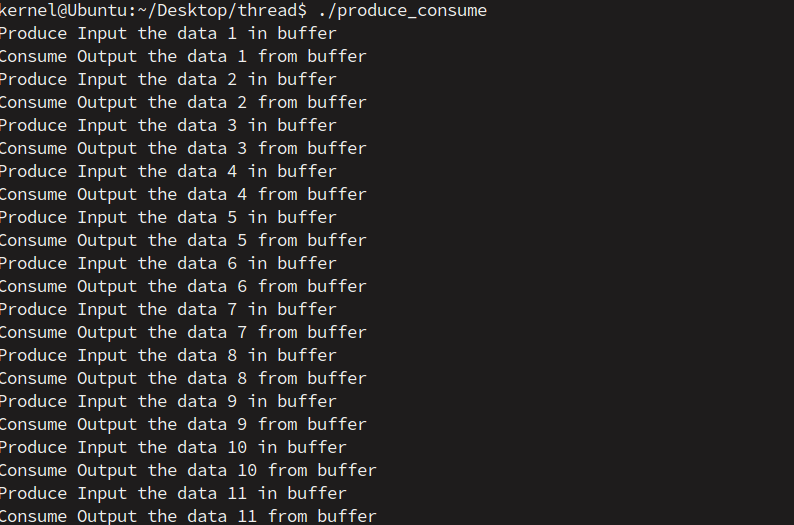
1. 一个消费者和一个生产者
消费者和生产者分别为两个不同线程,并且共享一个资源nitems。如果生产者拥有该资源,并且缓冲区为空,生产者向缓冲区生产产品,如果消费者拥有该资源,并且缓冲区有数据,消费者取出数据。为了使两个线程同步也就是互斥的读写共享资源,使用互斥锁,保持线程操作共享资源的原子性。
#include <cstdio>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int nitems;
int count;
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void* produce(void*);
void* consume(void*);
int main(void) {
pthread_t tid_produce, tid_consume;
int iRet = pthread_create(&tid_produce, NULL, produce, NULL);
if (iRet) {
printf("create produce thread error\n");
}
iRet = pthread_create(&tid_consume, NULL, consume, NULL);
if (iRet)
printf("create consume thread error\n");
pthread_join(tid_produce, NULL);
pthread_join(tid_consume, NULL);
return 0;
}
void* produce(void* arg) {
for(; ;) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if (nitems == 1) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
else {
nitems = 1;
printf("Produce Input the data %d in buffer\n", ++count);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
void* consume(void* arg) {
for (; ;) {
if (nitems == 1 && count != 0) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
nitems = 0;
printf("Consume Output the data %d from buffer\n", count);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
return 0;
}
2. 一个消费者和多个生产者
使用一个全局变量buff[MAXNITEMS],存放多个生产者的每次能够存放的最大条目。本次例子,只有当所有生产者都完成缓冲区的存放时,消费者取出条目。使用引用计数,统计每个生产者线程存放条目的数目。使用互斥锁,各个生产者线程对共享资源buff操作的原子性。
#include <cstdio>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXNITEMS 1000000
#define MAXTHREADS 100
#define min(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (b) : (a))
int nitems;
// 条目结构体
struct {
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
int buff[MAXNITEMS];
int nput; // buff下标
int nval; // buff下一个位置的元素
}shared = { PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER };
void* produce(void*);
void* consume(void*);
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
if(argc != 3) {
printf("usage: produce_consume <items> <threads> ");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
pthread_t tid_produce[MAXTHREADS], tid_consume;
nitems = min(atoi(argv[1]), MAXNITEMS);
int nthreads = min(atoi(argv[2]), MAXTHREADS);
int i, count[MAXTHREADS];
for (i = 0; i < nthreads; ++i) {
count[i] = 0;
int iRet = pthread_create(&tid_produce[i], NULL, produce, &count[i]); // 创建生产者线程
if (iRet) {
printf("create produce thread error\n");
}
}
for (i = 0; i < nthreads; ++i) {
pthread_join(tid_produce[i], NULL); // 回收生产者线程
printf("count[%d] = %d\n", i, count[i]);
}
int iRet = pthread_create(&tid_consume, NULL, consume, NULL); // 消费者线程
if (iRet)
printf("create consume thread error\n");
pthread_join(tid_consume, NULL);
return 0;
}
void* produce(void* arg) {
for(; ;) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex);
if (shared.nput >= nitems) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
return 0;
}
else {
shared.buff[shared.nput] = shared.nval;
printf("thread id %lu : Produce Input the data %d in buffer\n", pthread_self(), shared.buff[shared.nput]);
++shared.nput;
++shared.nval;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
*((int*)arg) += 1;
}
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
void* consume(void* arg) {
int i;
pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex);
if (shared.nput < nitems) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
return 0;
}
if (shared.nput >= nitems) {
for(i = 0; i < nitems; ++i)
printf("Consume Output the data %d from buffer\n", shared.buff[i]);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
return 0;
}注:当消费者取出缓冲区条目时,由于先创建了多生产者线程,由于线程之间的竞争,消费者线程不一定会在生产者线程全部运行完之后才运行,因此需要生产者线程全部回收后,在创建消费者线程完成取值。
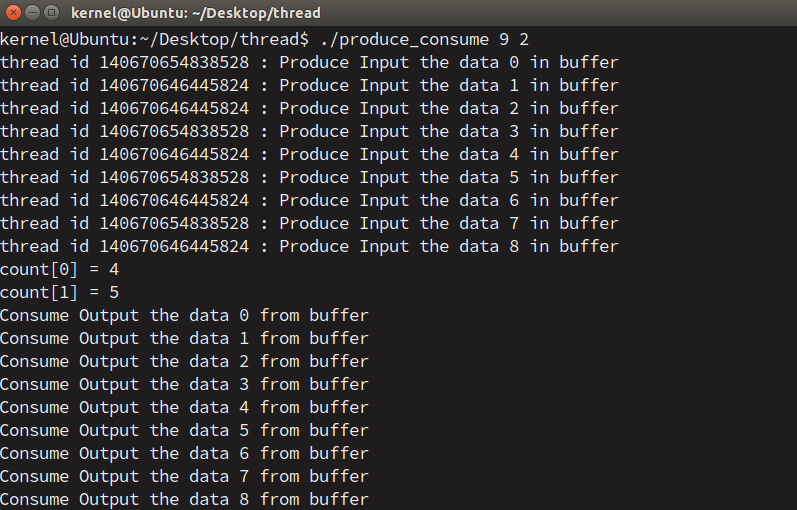
最大条目数为9,分两个生产者线程完成产品的生产。所有条目生产完毕后,消费者从中取出产品。
3. 多生产者和多消费者
如果无产品生产出来,如果通过轮询的方式让消费者等待,过于浪费CPU,因此可以采用条件变量,当无产品时,消费者进入睡眠,当生产者生产出产品时,产生信号,通知阻塞在条件变量的消费者线程,唤醒该线程。该线程等待生产者释放互斥锁,然后消费者线程获取互斥锁。获取产品,直到产品为0,继续阻塞条件变量睡眠。
在唤醒时,由于pthread_cond_signal在多处理器下,可能唤醒多个阻塞在条件变量的消费者线程,可能会产生虚假唤醒。于是需要改成如下形式:
while(等待条件)
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
这样就可以避免由于虚假唤醒造成对后面的错误处理。
消费者:当产品数量由0变为1时,pthread_cond_signal产生信号通知阻塞在条件变量,唤醒消费者线程(在临界区)。消费者线程获取产品,产品数量减一。
void* consume(void* arg) {
for (; ;) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&nready.mutex);
if (shared.nput >= nitems && nready.ready == 0) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&nready.mutex);
return 0;
}
while (nready.ready == 0) {
printf("consume wait the items\n");
pthread_cond_wait(&nready.cond, &nready.mutex);
}
printf("Consume id %lu : Consume Output the data %d from buffer\n", pthread_self(), shared.buff[count]);
++count;
--nready.ready;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&nready.mutex);
*((int*)arg) += 1;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}生产者:当产品数量由无到有的时候,通知消费者。由于pthread_cond_signal函数无任何线程阻塞在条件变量也会唤醒,因此加入条件,只有当产品数量由0变为1时才通知消费者处理。
void* produce(void* arg) {
for(; ;) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex);
if (shared.nput >= nitems) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
return 0;
}
else {
shared.buff[shared.nput] = shared.nval;
printf("Produce id %lu : Produce Input the data %d in buffer\n", pthread_self(), shared.buff[shared.nput]);
++shared.nput;
++shared.nval;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
*((int*)arg) += 1;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&nready.mutex);
if (nready.ready == 0)
pthread_cond_signal(&nready.cond);
++nready.ready;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&nready.mutex);
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}完整代码如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXNITEMS 1000000
#define MAXTHREADS 100
#define min(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (b) : (a))
int nitems;
int count;
struct {
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
int buff[MAXNITEMS];
int nput;
int nval;
}shared = { PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER };
struct {
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
int ready;
} nready = { PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER, PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER };
void* produce(void*);
void* consume(void*);
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
if(argc != 4) {
printf("usage: produce_consume <items> <produce_threads> <consume_threads>\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
pthread_t tid_produce[MAXTHREADS], tid_consume[MAXTHREADS];
nitems = min(atoi(argv[1]), MAXNITEMS);
int produce_threads = min(atoi(argv[2]), MAXTHREADS);
int consume_threads = min(atoi(argv[3]), MAXTHREADS);
int i, produce_count[MAXTHREADS], consume_count[MAXTHREADS];
int iRet;
for (i = 0; i < produce_threads; ++i) {
produce_count[i] = 0;
iRet = pthread_create(&tid_produce[i], NULL, produce, &produce_count[i]);
if (iRet) {
printf("create produce thread error\n");
}
}
sleep(1);
for (i = 0; i < consume_threads; ++i) {
consume_count[i] = 0;
iRet = pthread_create(&tid_consume[i], NULL, consume, &consume_count[i]);
}
sleep(1);
for(i = 0; i < consume_threads; ++i) {
pthread_join(tid_consume[i], NULL);
printf("Consume id %lu consume_count[%d] = %d\n", tid_consume[i], i, consume_count[i]);
}
for (i = 0; i < produce_threads; ++i) {
pthread_join(tid_produce[i], NULL);
printf("produce id %lu produce_count[%d] = %d\n", tid_produce[i], i, produce_count[i]);
}
return 0;
}
void* produce(void* arg) {
for(; ;) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex);
if (shared.nput >= nitems) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
return 0;
}
else {
shared.buff[shared.nput] = shared.nval;
printf("Produce id %lu : Produce Input the data %d in buffer\n", pthread_self(), shared.buff[shared.nput]);
++shared.nput;
++shared.nval;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
*((int*)arg) += 1;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&nready.mutex);
if (nready.ready == 0)
pthread_cond_signal(&nready.cond);
++nready.ready;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&nready.mutex);
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
void* consume(void* arg) {
for (; ;) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&nready.mutex);
if (shared.nput >= nitems && nready.ready == 0) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&nready.mutex);
return 0;
}
while (nready.ready == 0) {
printf("consume wait the items\n");
pthread_cond_wait(&nready.cond, &nready.mutex);
}
printf("Consume id %lu : Consume Output the data %d from buffer\n", pthread_self(), shared.buff[count]);
++count;
--nready.ready;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&nready.mutex);
*((int*)arg) += 1;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}





















 1758
1758

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








