操作系统用户接口实验
一、实验目的
(1)熟悉登录Linux系统和退出系统的过程;
(2)使用Linux常用命令;
(3)用C语言编制一个小程序编译并执行。
二、实验原理
在vmware中虚拟一个linux环境 在蓝桥云中进行实验
三、实验过程
- 登录Linux系统和退出系统的过程
(类似于windows的登陆,输入密码即可)
(或者是输入用户名后再输入密码)

退出:输入exit即可
关机: shutdown
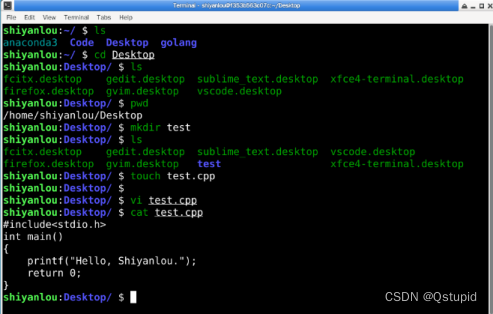
2. 使用Linux常用命令
ls 查看目录
cd:切换路径
rm:删除文件
touch:用于修改文件或者目录的时间属性,包括存取时间和更改时间。若文件不存在,系统会建立一个新的文件。
vi: 编辑文件
- 用C语言编制一个小程序编译并执行

四、实验结果
-
linux系统能够正常登录与登出
-
linux常见命令
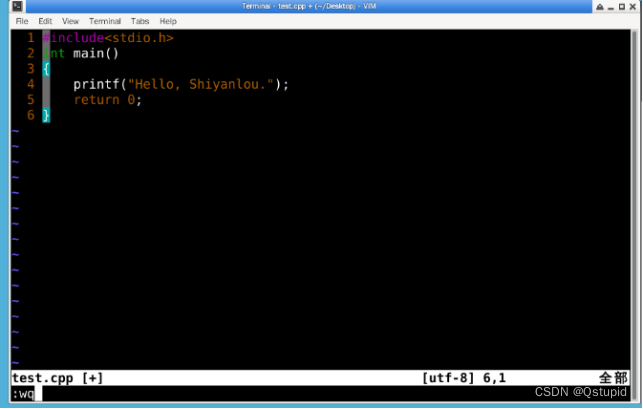
- 编译c文件

五、实验总结
Linux与windows之间仍有不小差别,本实验整体难度偏易,通过本实验可以逐步了解linux系统的基本命令操作,以及如何在linux系统中使用gcc对C程序进行编译,本程序是对linux操作系统学习的基础,熟练掌握linux的命令行可以帮助我们更好的适应linux。
进程控制
一、实验目的
(1)了解系统调用fork(), exex(), exit()等功能和实现过程;
(2)编写一段程序,使用系统调用fork()来创建两个子进程。
二、实验原理
1.使用系统调用fork()来创建两个子进程,并由父进程重复显示字符某字符串和自己的标识数,而子进程则重复显示某字符串和自己的标识数。
2.编写一段程序,使用系统调用fork()来创建一个子进程。子进程通过系统调用exec()更换自己的执行代码,显示新的代码后,调用exit()结束。
3.(1)getpid():获取本进程标识符
(2)getppid():获取父进程标识符
三、实验过程
调用fork()来创建两个子进程,父进程显示字符自己的标识数,子进程显示自己的标识数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void main()
{
pid_t childpid1;
pid_t childpid2;
childpid1 = fork();
childpid2 = fork();
if (childpid1 == 0)
{
printf("child1's id is %d\n", getpid());
}
else if (childpid2 == 0)
{
printf("child2's id is %d\n", getpid());
}
else
{
printf("parent id is %d\n", getpid());
}
}
系统调用fork(), exex(), exit()等功能
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
pid_t id;
id = fork();
if (id < 0)
{
printf("fork error");
}
else if (id == 0)
{
printf("child id is %d\n", getpid());
execl("./test", "./test", NULL);
exit(0);
}
else
{
printf("parent\n");
exit(0);
printf("no exec");
}
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
void main(){
printf("child\n");
}
四、实验结果


五、实验总结
- 当调用fork()函数时,会创建一个进程,这个进程与当前的进程完全一样。
- 创建的子进程,不会从头开始执行程序,而是会沿着fork()函数向下执行程序,并得到一个返回值0。 若出错返回-1。
- fork()的实际意义:相当于复制当前程序并再次执行,所以每次输出都必然先输出parent进程符,两个字进程随机输出。
- exec函数族提供了一个在进程中启动另一个程序执行的方法。它可以根据指定的文件名或目录名找到可执行文件,并用它来取代原调用进程的数据段、代码段和堆栈段,在执行完之后,原调用进程的内容除了进程号外,其他全部被新的进程替换了。
- exit(0)函数,就是退出进程。exit是操作系统提供的(或者函数库中给出的),用于退出应用程序,删除进程使用的内存空间,并将应用程序的一个状态返回给OS(操作系统)。
exit(0):正常运行程序并退出程序;exit(1):非正常运行导致退出程序;
进程通信
一、实验目的
学习如何利用消息缓冲队列进行进程间的通信,并加深对消息缓冲队列通信机制的理解
(1)了解系统pipe(), msgsnd(),msgrcv()的功能和实现过程。
(2)编写一段程序,使其用管道来实现父子进程之间的进程通信。
二、实验原理
管道是连接读写进程的一个共享文件,允许进程以先进先出的方式写入和读出数据,并对读写操作进行同步。发送进程以字符流形式把大量数据送入管道尾部,接收进程从管道头部接收数据。
(1)管道应该互斥使用,管道读写不能同时进行。一个进程正在执行管道写入或读出操作时,另一进程必须等待。读写结束时,唤醒等待进程,自己应阻塞。
(2)读写双方必须能够知道对方是否存在,只有存在才能通信。系统发送SIGPIPE信号通知进程对方不存在。
(3)管道空间的大小通常是固定的,读写操作时需要考虑写满和读空问题。
三、实验过程
pipe函数 创建管道
msgsnd函数 功能:往队列中发送一个消息 返回值:成功返回0,失败返回-1;
msgrcv()函数 功能:读取消息,并且把消息队列中消息读完。 返回值:成功返回0,失败返回-1;
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
char buf[1024];
int fd[2];
char *p1 = "this is child.\nAnd child's id is:";//定义字符数组p1
if(-1==pipe(fd))
{printf("pipe error.");}
pid = fork();
if(pid<0)
{
printf("fork error.");
}
else if(pid==0)//子进程
{
int id = getpid();//获得子进程序列号
char *p2;
sprintf(p2,"%d",id);//用sprintf把子进程序列号从int型转为char型数组
close(fd[0]);//子进程关闭管道读端
write(fd[1],p1,strlen(p1));//子进程向管道写入p1、p2
write(fd[1],p2,strlen(p2));
close(fd[1]);
}
else
{
close(fd[1]);//父进程关闭管道写端
int len = read(fd[0],buf,sizeof(buf));
write(STDOUT_FILENO,buf,len);
close(fd[0]);
}
}
- 父进程先调用pipe()创建管道,得到两个文件描述符指向管道的读端和写端。
- 父进程fork()创建子进程,此时子进程也有两个文件描述符指向同一管道。
- 父进程关闭管道写端,子进程关掉管道读端,从而实现子进程向管道里面写入数据,父进程从管道里面读取数据,从而实现了进程间通信。
四、实验结果

五、实验总结
管道应该互斥使用,管道读写不能同时进行。
读写双方必须能够知道对方是否存在,只有存在才能通信。
读写操作时需要考虑写满和读空问题。
使用动态优先权的进程调度算法的模拟
一、实验目的
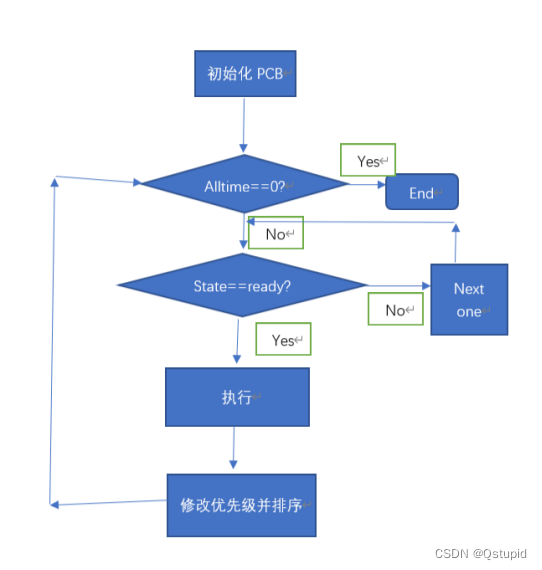
(1)实现对N个进程采用动态优先权算法的进程调度;
(2)每个用来标识进程控制块PCB用结构来描述;
(3)优先数改变的原则:进程在就绪队列中呆一个时间片,优先数增加1,进程每运行一个时间片优先数减3
二、实验原理
三、实验过程
PCB结构体:
typedef struct node
{
int id;
int priority;
int cputime;
int alltime; // last cpu time
int startblock; // wait to startblock
int blocktime; // wait blocktime then change to ready
char state[10];
struct node *next;
} PCB;
初始化队列
PCB *creat_queue(int num)
{
int i;
PCB *head, *temp1;
for (i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
temp1 = (PCB *)malloc(sizeof(PCB));
printf("the %d id priority cputime alltime startblock blocktime state\n", i);
scanf("%d %d %d %d %d %d %s", &temp1->id, &temp1->priority, &temp1->cputime, &temp1->alltime, &temp1->startblock, &temp1->blocktime, &temp1->state);
if (i == 0)
{
head = temp1;
head->next = NULL;
continue;
}
if (head->priority < temp1->priority) // find the head
{
temp1->next = head;
head = temp1;
continue;
}
PCB *t2, *t3;
t2 = head;
t3 = t2->next;
while (t3 != NULL && t3->priority >= temp1->priority) // find the correct place
{
t2 = t3;
t3 = t3->next;
}
t2->next = temp1;
temp1->next = t3;
}
return head;
}
修改优先级后插入队列中
PCB *Insert_queue(PCB *head, PCB *run)
{
PCB *t1, *t2;
if (head == NULL)
{
head = run;
head->next = NULL;
}
else if (head->priority < run->priority)
{
run->next = head;
head = run;
}
else
{
t1 = head;
t2 = head->next;
while (t2 != NULL && t2->priority >= run->priority)
{
t1 = t2;
t2 = t2->next;
}
t1->next = run;
run->next = t2;
}
return head;
}
格式化输出
void print(PCB *run, PCB *head, PCB *block)
{
if (run != NULL)
printf("running:%d\n", run->id);
else
printf("running:\n");
// ready start
printf("ready queue:");
PCB *t = head;
while (t != NULL)
{
printf("->%d", t->id);
t = t->next;
}
// ready end
printf("\n");
// block
printf("blocked queue:");
if (block != NULL)
{
printf("%d", block->id);
}
printf("\n");
// block end
// the ready info start
printf("-------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("id |\t priority |\t cputime |\t alltime |\t startblock |\t blocktime |\t state\n");
printf("%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%s\n", run->id, run->priority, run->cputime, run->alltime, run->startblock, run->blocktime, run->state);
t = head;
while (t != NULL)
{
printf("id |\t priority |\t cputime |\t alltime |\t startblock |\t blocktime |\t state\n");
printf("%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%s\n", t->id, t->priority, t->cputime, t->alltime, t->startblock, t->blocktime, t->state);
t = t->next;
}
// the ready info end
if (block != NULL)
{
printf("id |\t priority |\t cputime |\t alltime |\t startblock |\t blocktime |\t state\n");
printf("%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%d|\t\t%s\n", block->id, block->priority, block->cputime, block->alltime, block->startblock, block->blocktime, block->state);
}
printf("-------------------------------------------------------\n");
}
Main函数
int main()
{
int num;
int alltime = 0;
PCB *head, *temp;
PCB *run = NULL, *block = NULL;
printf("input the num:\n");
scanf("%d", &num);
head = creat_queue(num);
temp = head;
while (temp != NULL)
{
alltime += temp->alltime;
temp = temp->next;
}
while (alltime > 0)
{
if (head != NULL)
{
run = head;
head = head->next;
strcpy(run->state, "run");
run->next = NULL;
print(run, head, block);
// change the priority start
run->priority -= 3;
temp = head;
while (temp != NULL)
{
temp->priority += 1;
temp = temp->next;
}
// change the priority end
// change other start
run->cputime += 1;
run->alltime -= 1;
if (run->alltime != 0) // still run
{
if (run->startblock > 0)
{
run->startblock -= 1;
if (run->startblock == 0)
{
block = run;
strcpy(block->state, "block");
alltime--;
printf("\n");
continue;
}
}
strcpy(run->state, "ready");
head = Insert_queue(head, run); // find the correct place
run = NULL;
}
// change other end
alltime--;
}
else // head==NULL(may be have blocks)
{
print(NULL, NULL, block);
}
if (block != NULL)
{
block->blocktime -= 1;
if (block->blocktime == 0)
{
strcpy(block->state, "ready");
head = Insert_queue(head, block);
block = NULL;
}
}
}
}
四、实验结果

动态分区分配方式的模拟
一、实验目的
(1)用C或其他语言分别实现采用首次适应算法和最佳适应算法的动态分区分配过程和回收过程。
二、实验原理

三、实验过程
初始化分区
Status Initblock()
{
block_first = (DuLinkList)malloc(sizeof(DuLNode));
block_last = (DuLinkList)malloc(sizeof(DuLNode));
block_first->prior = NULL;
block_first->next = block_last;
block_last->prior = block_first;
block_last->next = NULL;
block_last->data.address = 0;
block_last->data.size = Max_block_size;
block_last->data.state = Free;
return SUCCEED;
}
定义分配函数
Status alloc(int ch)
{
int request = 0;
cout << "Enter the size(KB) of main memory to be allocated:\n";
cin >> request;
if (request <= 0)
{
cout << "allocate error!Please enter again.\n"
<< endl;
return ERROR;
}
if (ch == 1)
{
if (First_fit(request) == SUCCEED)
cout << "allocation success." << endl;
else
{
cout << "allocation fail." << endl;
return ERROR;
}
return SUCCEED;
}
else
{
if (Best_fit(request) == SUCCEED)
{
cout << "allocation success." << endl;
return SUCCEED;
}
else
{
cout << "allocation fail." << endl;
return ERROR;
}
}
}
定义释放函数
Status free(int block_id)
{
DuLNode *p = block_first;
for (int i = 0; i <= block_id; i++)
{
if (p != NULL)
p = p->next;
else
return ERROR;
}
p->data.state = Free;
/*merge with the previous free block*/
if (p->prior != block_first && p->prior->data.state == Free)
{
p->prior->data.size += p->data.size;
p->prior->next = p->next;
p->next->prior = p->prior;
p = p->prior;
}
/*merge with the following free block*/
if (p->next != block_last && p->next->data.state == Free)
{
p->data.size += p->next->data.size;
p->next->next->prior = p;
p->next = p->next->next;
}
/*merge with the last free block*/
if (p->next == block_last && p->next->data.state == Free)
{
p->data.size += p->next->data.size;
p->next = NULL;
}
return SUCCEED;
}
定义首次适应算法
Status First_fit(int request)
{
DuLinkList temp = (DuLinkList)malloc(sizeof(DuLNode));
temp->data.size = request;
temp->data.state = Busy;
DuLNode *p = block_first->next;
while (p)
{
if (p->data.state == Free && p->data.size == request)
{
p->data.state = Busy;
return SUCCEED;
break;
}
if (p->data.state == Free && p->data.size > request) // the first place
{ // insert p
temp->prior = p->prior;
temp->next = p;
temp->data.address = p->data.address;
p->prior->next = temp;
p->prior = temp;
p->data.address = temp->data.address + temp->data.size;
p->data.size -= request;
return SUCCEED;
break;
}
p = p->next;
}
return ERROR; // cant find the place
}
定义最佳适应算法
Status Best_fit(int request)
{
DuLinkList temp = (DuLinkList)malloc(sizeof(DuLNode));
temp->data.size = request;
temp->data.state = Busy;
DuLNode *p = block_first->next;
DuLNode *q = NULL; // record the best insert position
while (p) // initialize the min_size and the best positon
{
if (p->data.state == Free && (p->data.size) >= request)
{
if (q == NULL)
{
q = p;
}
else if (q->data.size > p->data.size)
{
q = p;
}
}
p = p->next;
}
if (q == NULL)
{
return ERROR;
}
else if (q->data.size == request)
{
q->data.state = Busy;
return SUCCEED;
}
else
{
temp->prior = q->prior;
temp->next = q;
temp->data.address = q->data.address;
q->prior->next = temp;
q->prior = temp;
q->data.address = q->data.address + request;
q->data.size = q->data.size - request;
return SUCCEED;
}
}
定义输出函数
void print()
{
int block_id = 0;
cout << "\nMain memory allocation:\n";
cout << "=============================================================\n\n";
DuLNode *p = block_first->next;
cout << "block_id\t start_address\t block_size\t block_state\n\n";
while (p)
{
cout << " " << block_id++ << "\t\t";
cout << " " << p->data.address << "\t\t";
cout << " " << p->data.size << "KB\t\t";
if (p->data.state == Free)
cout << "free\n\n";
else
cout << "busy\n\n";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "=============================================================\n\n";
}
Main函数
int main()
{
int ch;
cout << "Please enter the memory allocation algorithm used:\n";
cout << "1.First Fit\n2.Best Fit\n";
cin >> ch;
while (ch < 1 || ch > 2)
{
cout << "input error,please enter again!" << endl;
cin >> ch;
}
Initblock();
int choice; // operation choice
while (1)
{
print();
cout << "\n 1.allocate\n 2.free\n 3.exit\n";
cin >> choice;
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
alloc(ch);
break;
case 2:
int block_id;
cout << "Please enter the block id which you want to free." << endl;
cin >> block_id;
free(block_id);
break;
case 3:
return 0;
default:
cout << "wrong input!Please do it again." << endl;
continue;
}
}
return 0;
}
四、实验结果
1.首次适应算法
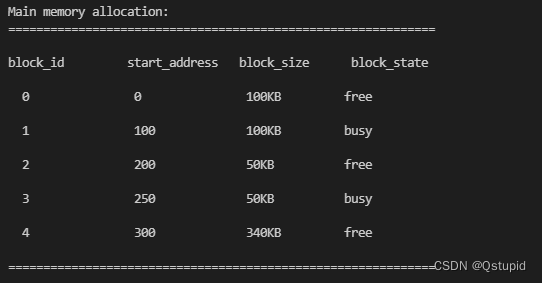
再次分配50kb,得到

- 最佳适应算法

分配50kb:

分配30kb:
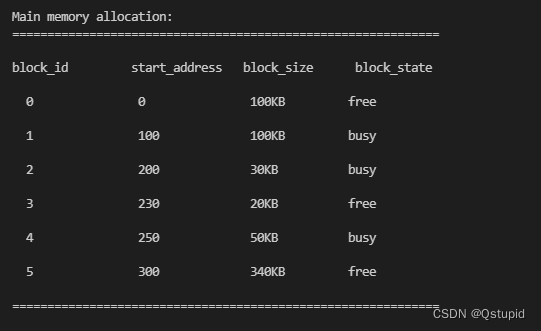
实现了首次适应算法和最佳适应算法
五、实验总结
本来用char[]来表示块状态是free或busy的,发现状态的传化挺麻烦的,得用strcpy,判断状态是否为free或busy不能简单用==判断.因此改用enum.
Block想用一个next指针和双指针实现,但是难度有点大,但是用prior和next两个























 6261
6261

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








