链表的题目注意画图辅助思考防止断链;如果需要构造新的链表使用伪头结点(dummyHead)可以简化操作;双指针(快慢指针,左右指针)。
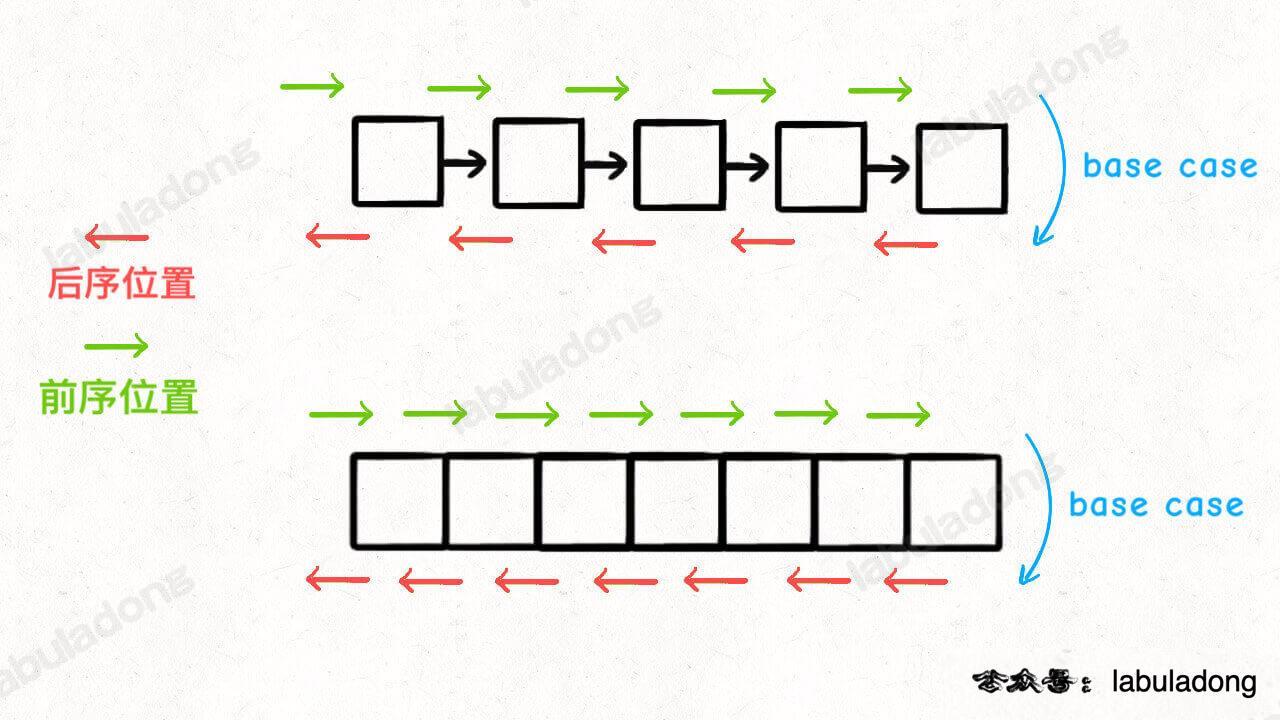
链表的递归算法:只要是递归形式的遍历,都可以有前序位置和后序位置,分别在递归之前和递归之后。所谓前序位置,就是刚进入一个节点(元素)的时候,后序位置就是即将离开一个节点(元素)的时候,那么进一步,你把代码写在不同位置,代码执行的时机也不同:
链表数据结构定义:
public class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode() {}
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
public class DoubleListNode {
public int key;
public int value;
public DoubleListNode pre;
public DoubleListNode next;
public DoubleListNode() {}
public DoubleListNode(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}206. 反转链表(⭐️⭐️)
思路
递归实现反转链表常常用来考察递归思想,我这里就用纯递归来翻转链表。对于递归算法,最重要的就是明确递归函数的定义。具体来说,我们的 reverse 函数定义是这样的:输入一个节点 head,将「以 head 为起点」的链表反转,并返回反转之后的头结点。明白了函数的定义,再来看这个问题。比如说我们想反转这个链表:
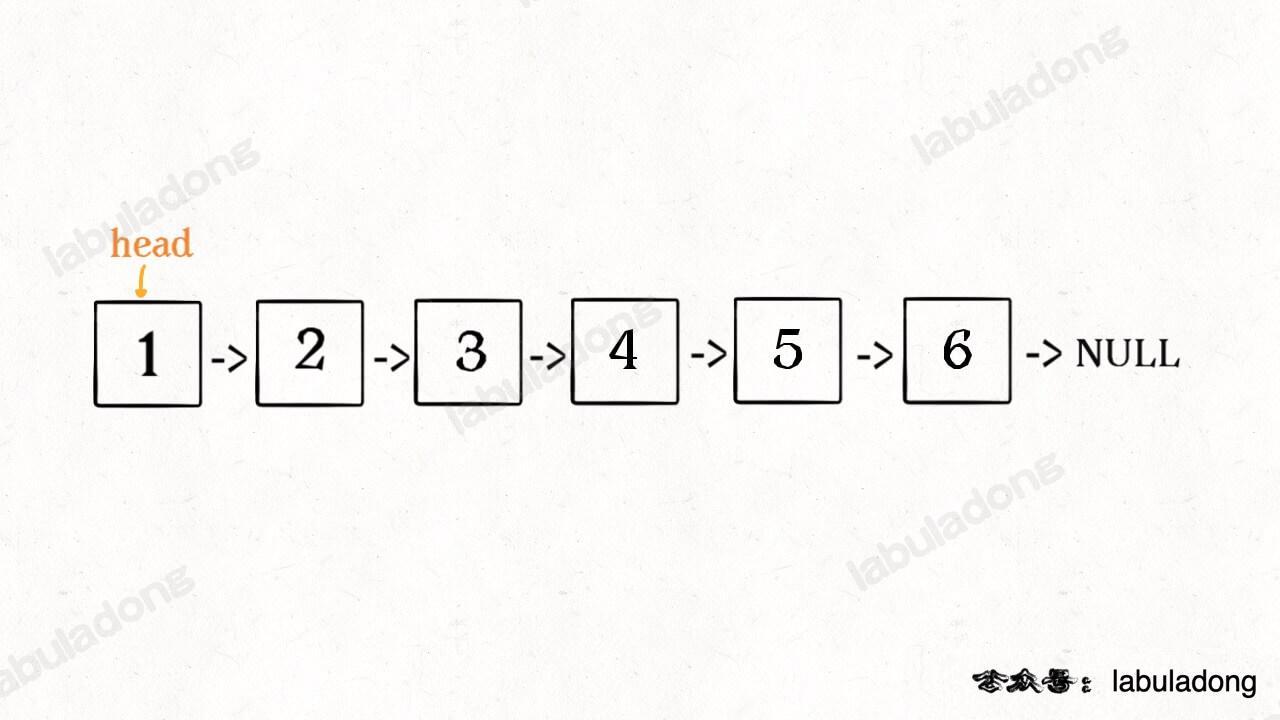
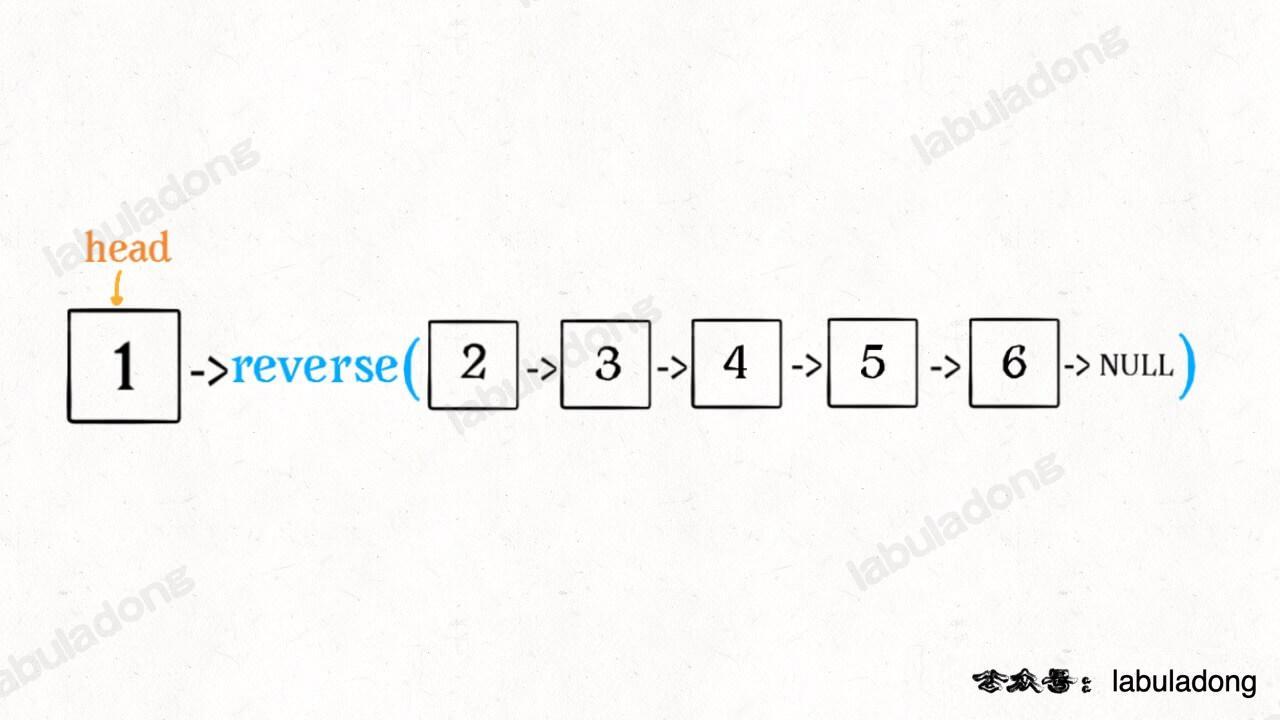
那么输入 reverse(head) 后,会在这里进行递归:
ListNode last = reverse(head.next);不要跳进递归(你的脑袋能压几个栈呀?),而是要根据刚才的函数定义,来弄清楚这段代码会产生什么结果:
这个 reverse(head.next) 执行完成后,整个链表就成了这样:
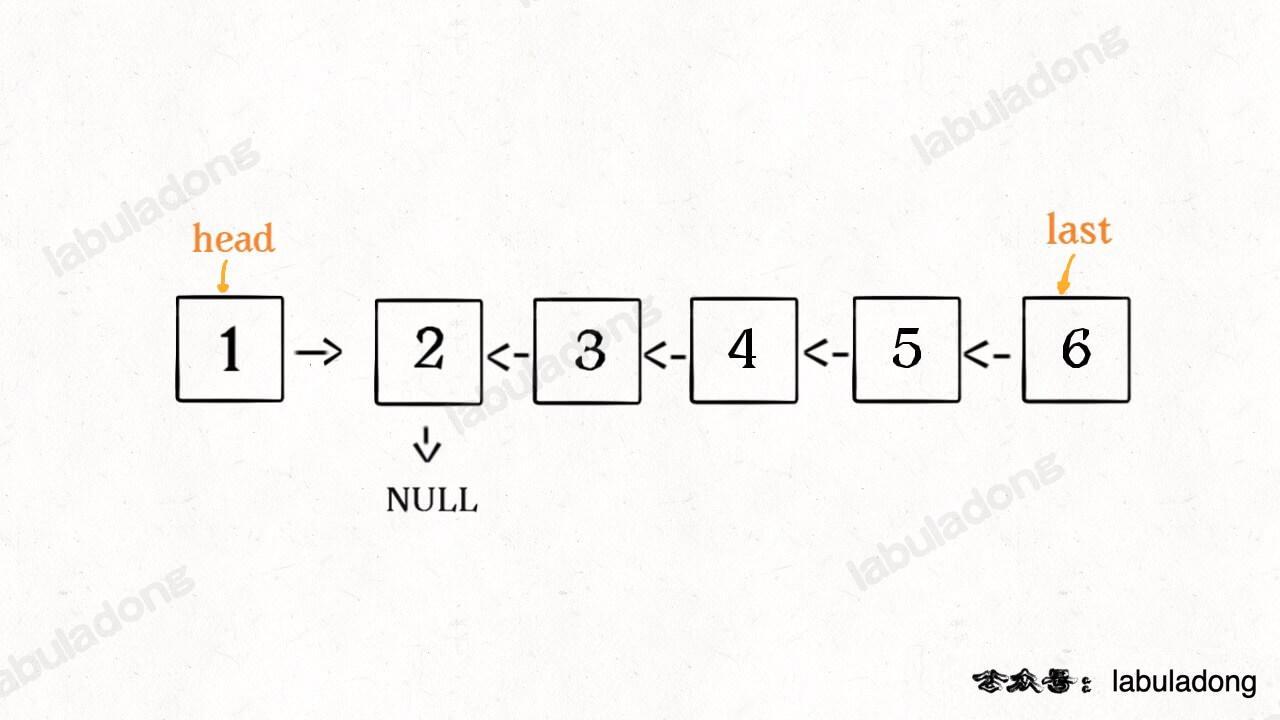
并且根据函数定义,reverse 函数会返回反转之后的头结点,我们用变量 last 接收了。
现在再来看下面的代码:
head.next.next = head;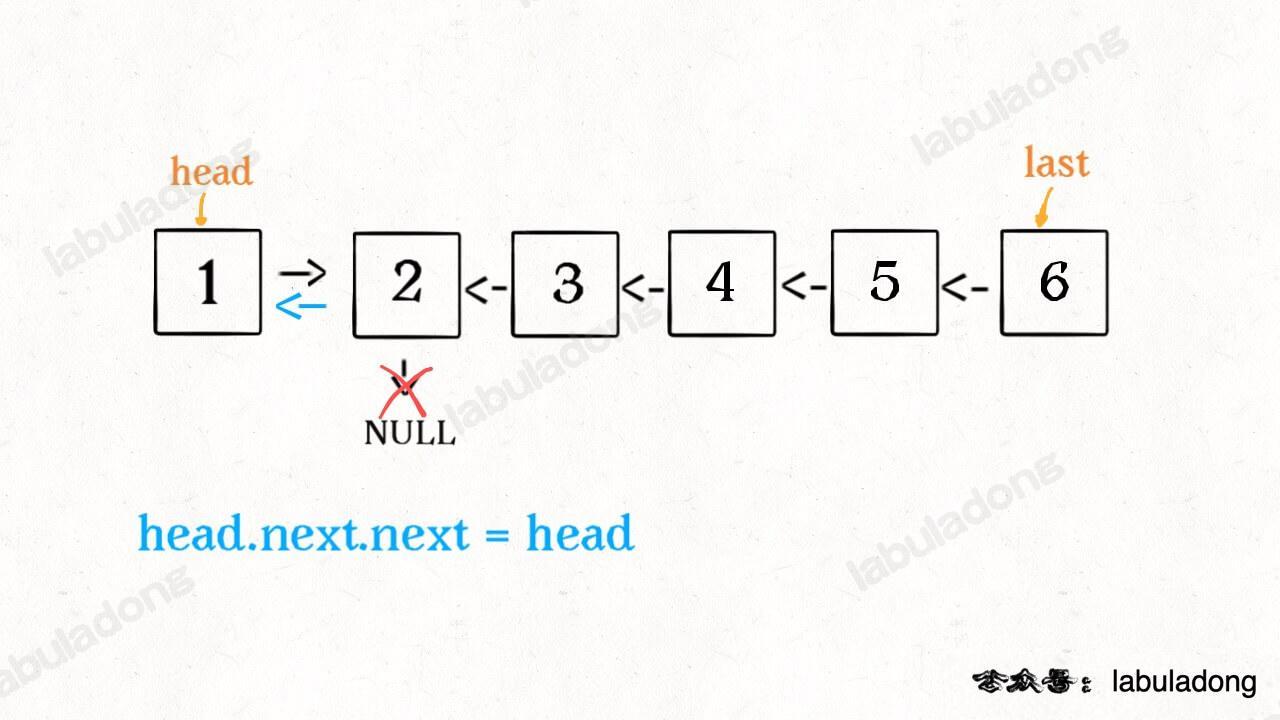
接下来:
head.next = null;
return last;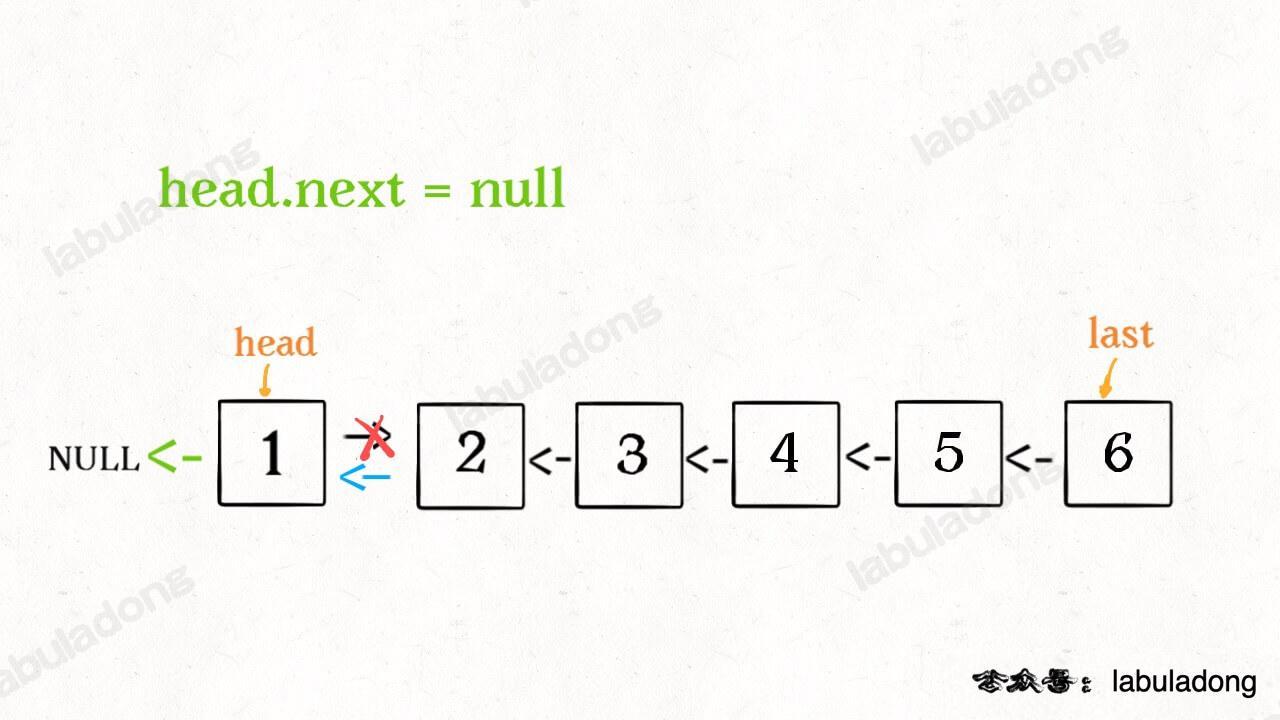
代码
public class ReverseList {
public ListNode reverseListIterationVersion(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode newHead = null;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return head;
}
public ListNode reverseListRecursionVersion(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode last = reverseListRecursionVersion(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:迭代:O(1),递归: O(N)
146. LRU 缓存(⭐️⭐️)
思路
LRU 缓存机制可以通过哈希表辅以双向链表实现,我们用一个哈希表和一个双向链表维护所有在缓存中的键值对。双向链表按照被使用的顺序存储了这些键值对,靠近头部的键值对是最近使用的,而靠近尾部的键值对是最久未使用的。哈希表即为普通的哈希映射(HashMap),通过缓存数据的键快速映射到其在双向链表中的位置。
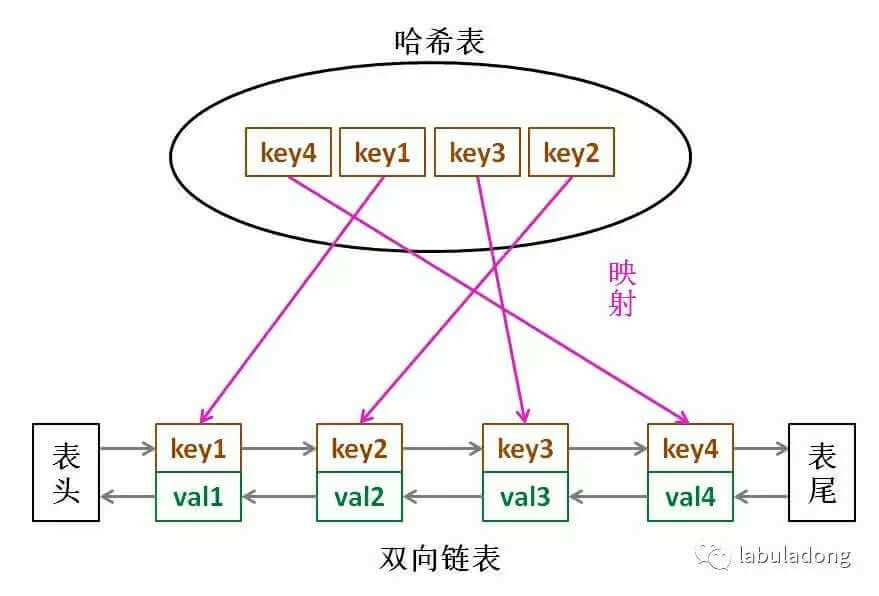
这是一个LRU(Least Recently Used)缓存的实现,用于缓存键值对,保持最近访问的数据在缓存中,并在缓存容量不足时淘汰最久未使用的数据。
构造方法:
- LRUCache(int capacity): 构造LRU缓存对象,传入缓存容量作为参数。
方法:
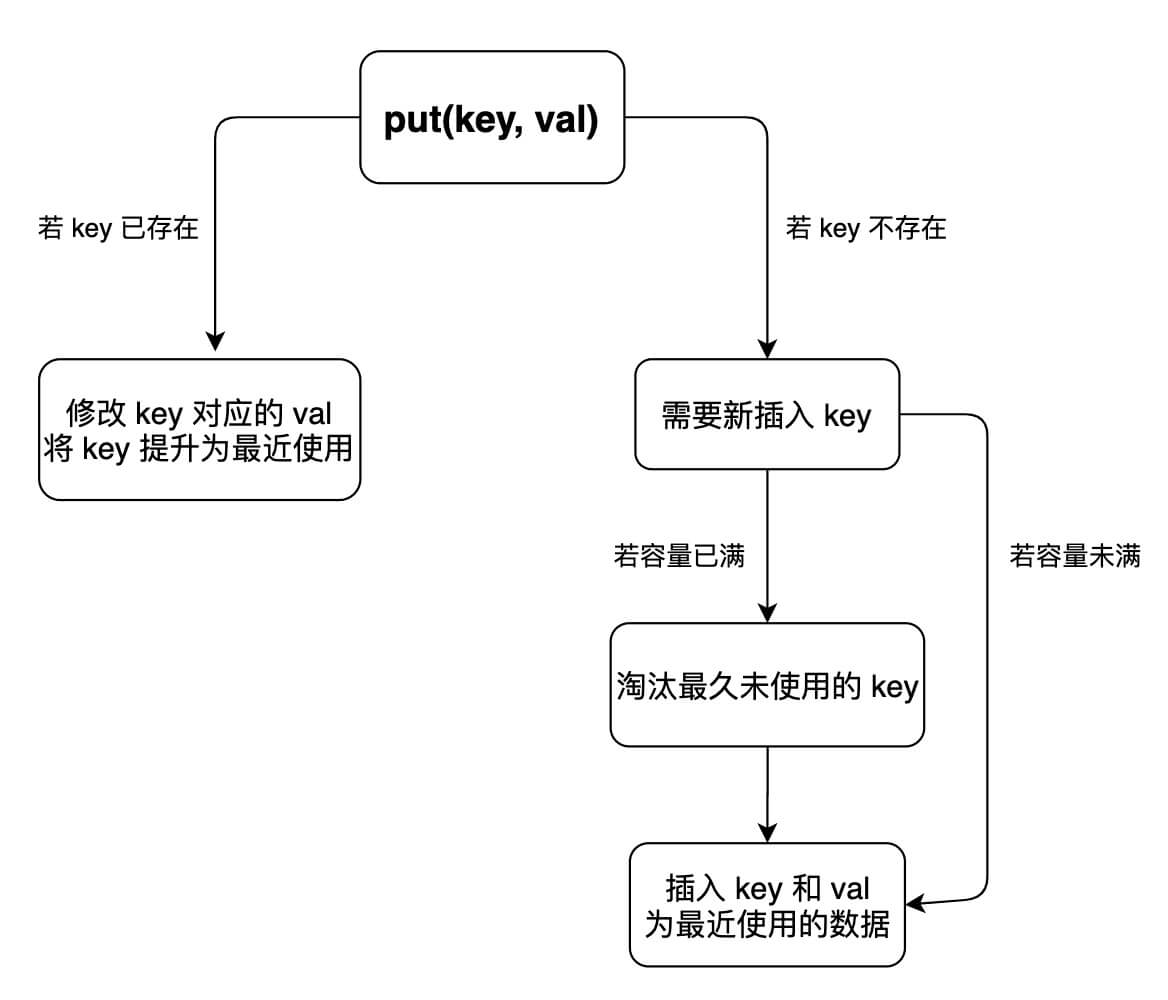
- int get(int key): 获取缓存中指定键的值,如果不存在则返回-1,存在则返回对应的值,并将该节点移到链表头部,表示最近使用。
- void put(int key, int value): 向缓存中插入或更新键值对。如果缓存中已存在该键,则更新对应值并将节点移到链表头部;如果不存在该键,则插入新节点到链表头部,并更新哈希表。如果插入节点后缓存容量超出限制,则移除链表尾部的节点,并从哈希表中删除对应键。
成员变量:
- HashMap<Integer, Node> cache: 哈希表用于快速查找缓存中的节点。
- int size: 当前缓存大小。
- int capacity: 缓存容量。
- Node head: 链表头部表示最近使用。
- Node tail: 链表尾部表示最久未使用。
私有方法:
- removeNode(Node node): 移除指定节点。
- addToHead(Node node): 将节点添加到链表头部。
- removeTail(): 移除链表尾部节点。
- moveToHead(Node node): 将节点移到链表头部,表示最近使用。
内部类:
- Node: 链表节点类,用于存储键值对及构建双向链表。包含键、值、前驱节点和后继节点。
代码
import java.util.HashMap;
public class LRUCache {
private HashMap<Integer, DoubleListNode> cache = new HashMap<>();
private int size = 0; // 当前缓存的大小
private int capacity = 0; // 当前缓存的容量
private DoubleListNode head = new DoubleListNode();
private DoubleListNode tail = new DoubleListNode();
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
DoubleListNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1;
} else {
moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
DoubleListNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
DoubleListNode newNode = new DoubleListNode(key, value);
cache.put(key, newNode);
addToHead(newNode);
size++;
if (size > capacity) {
cache.remove(tail.pre.key);
removeTail();
size--;
}
} else {
node.value = value;
moveToHead(node);
}
}
private void moveToHead(DoubleListNode node) {
removeNode(node);
addToHead(node);
}
private void addToHead(DoubleListNode node) {
// 先改变 node 的指针
node.pre = head;
node.next = head.next;
// 再从右到左改变节点的指针,避免断链
head.next.pre = node;
head.next = node;
}
private void removeTail() {
DoubleListNode node = tail.pre;
removeNode(node);
}
private void removeNode(DoubleListNode node) {
// 从右往左边改变指针,避免断链
node.next.pre = node.pre;
node.pre.next = node.next;
}
}复杂度
- 时间复杂度:对于 put 和 get 都是 O(1)
- 空间复杂度:O(capacity)
升级:过 x 秒之后没有操作的元素会自动过期删除(开一个定时任务)。
25. K 个一组翻转链表(⭐️⭐️)
思路
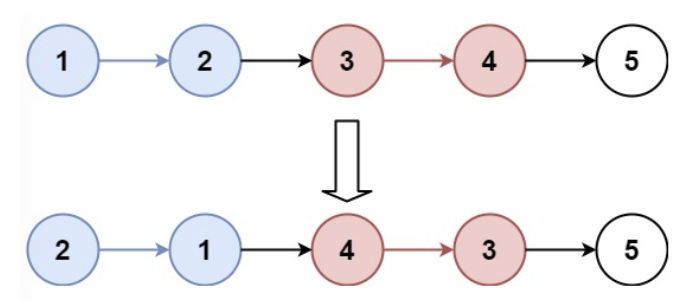
迭代:
两个关键的函数定义:
private ListNode findEnd(ListNode head, int k)
private void reverse(ListNode start, ListNode end)注意前后两个节点的 next 指针的处理。
递归:
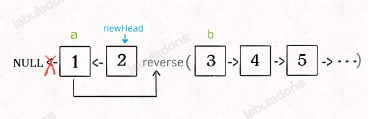
代码
public class ReverseKGroup {
// 解法一:迭代
public ListNode reverseKGroupIterationVersion(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode end = findEnd(head, k);
if (end == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode start = head;
reverseIterationVersion(start, end);
head = end;
ListNode preEnd = start;
while (preEnd.next != null) {
start = preEnd.next;
end = findEnd(start, k);
if (end == null) {
return head;
}
reverseIterationVersion(start, end);
preEnd.next = end;
preEnd = start;
}
return head;
}
private ListNode findEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode end = head;
while (--k > 0 && end != null) {
end = end.next;
}
return end;
}
private void reverseIterationVersion(ListNode start, ListNode end) {
ListNode subStart = end.next;
ListNode newHead = null;
ListNode cur = start;
ListNode next = null;
while (cur != subStart) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
cur = next;
}
start.next = subStart;
}
// 解法二:递归
public ListNode reverseKGroupRecursionVersion(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// 区间[a, b),包含 k 个待反转的元素
ListNode a = head;
ListNode b = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
// 不足 k 个,不需要反转
if (b == null) {
return head;
}
b = b.next;
}
ListNode newHead = reverseRecursionVersion(a, b);
a.next = reverseKGroupRecursionVersion(b, k);
return newHead;
}
private ListNode reverseRecursionVersion(ListNode a, ListNode b) {
ListNode newHead = null;
ListNode cur = a;
ListNode next = null;
while (cur != b) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newHead;
}
}复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
21. 合并两个有序链表(⭐️⭐)
思路
代码
public class MergeTwoLists {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode p = dummyHead;
ListNode p1 = l1;
ListNode p2 = l2;
while (p1 != null && p2 != null) {
if (p1.val < p2.val) {
p.next = p1;
p1 = p1.next;
} else {
p.next = p2;
p2 = p2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
if (p1 != null) {
p.next = p1;
}
if (p2 != null) {
p.next = p2;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(M + N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
141. 环形链表(⭐️⭐️)
思路
代码
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 如果链表为空或只有一个节点,肯定不存在循环,直接返回false
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
142. 环形链表 II(⭐️⭐️)
思路
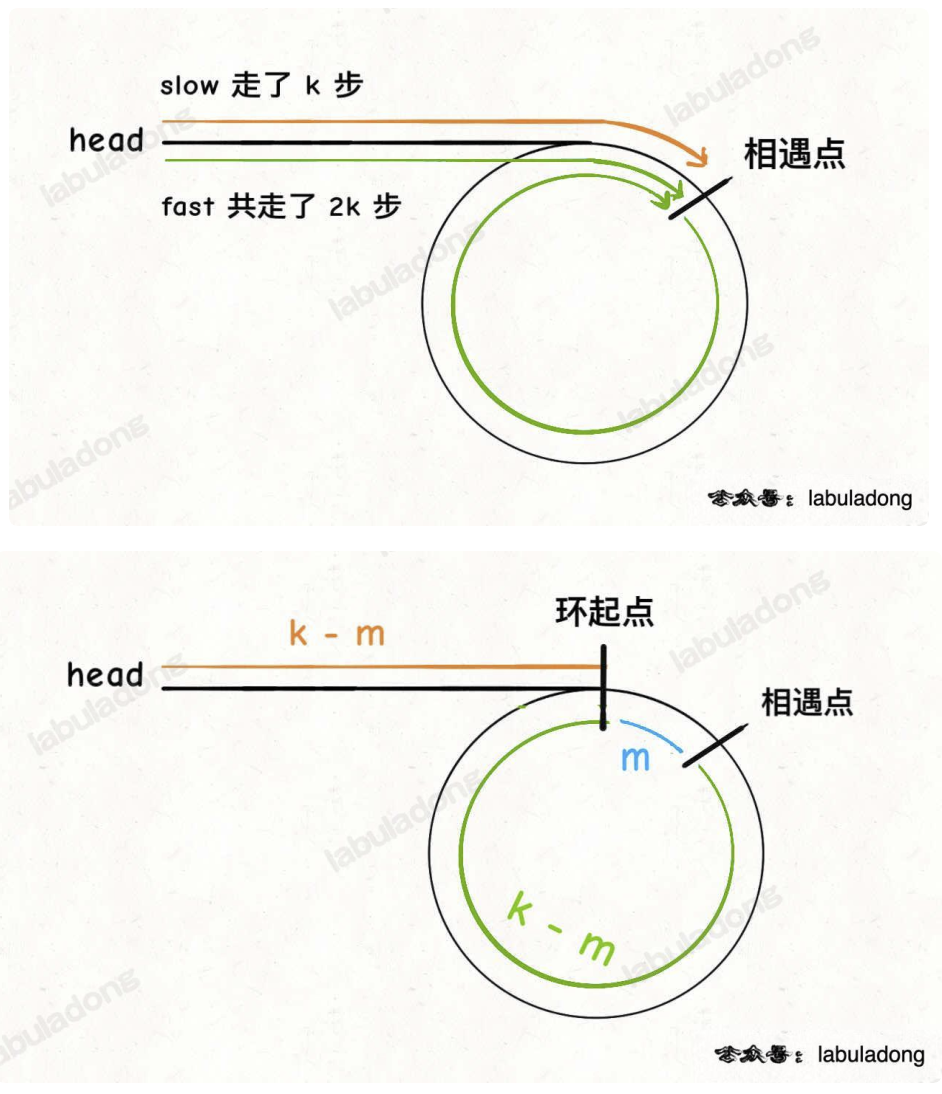
代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
break;
}
}
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return fast;
}
}复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
23. 合并 K 个升序链表(⭐️⭐️)
思路
代码
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class MergeKLists {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) {
return null;
}
PriorityQueue<ListNode> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(
Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.val)
);
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
for (ListNode list : lists) {
if (list == null) {
continue;
}
priorityQueue.add(list);
}
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
ListNode node = priorityQueue.poll();
cur.next = node;
cur = cur.next;
if (node.next != null) {
priorityQueue.add(node.next);
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(K * N * log K),其中 K 为最小堆的最大的元素数量
- 空间复杂度:O(K)
160. 相交链表(⭐️⭐️)
思路
pA 和 pB一同走过 a + b + c 路径长度时相遇在相交点。
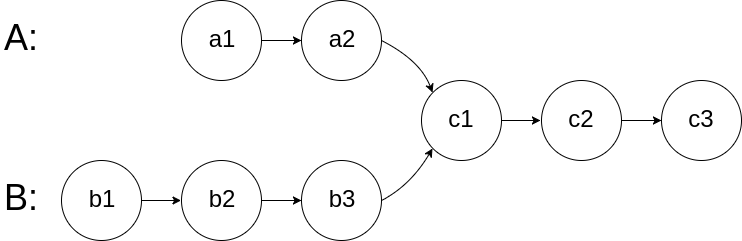
代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pA = headA;
ListNode pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(M + N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
143. 重排链表(⭐️⭐️)
思路
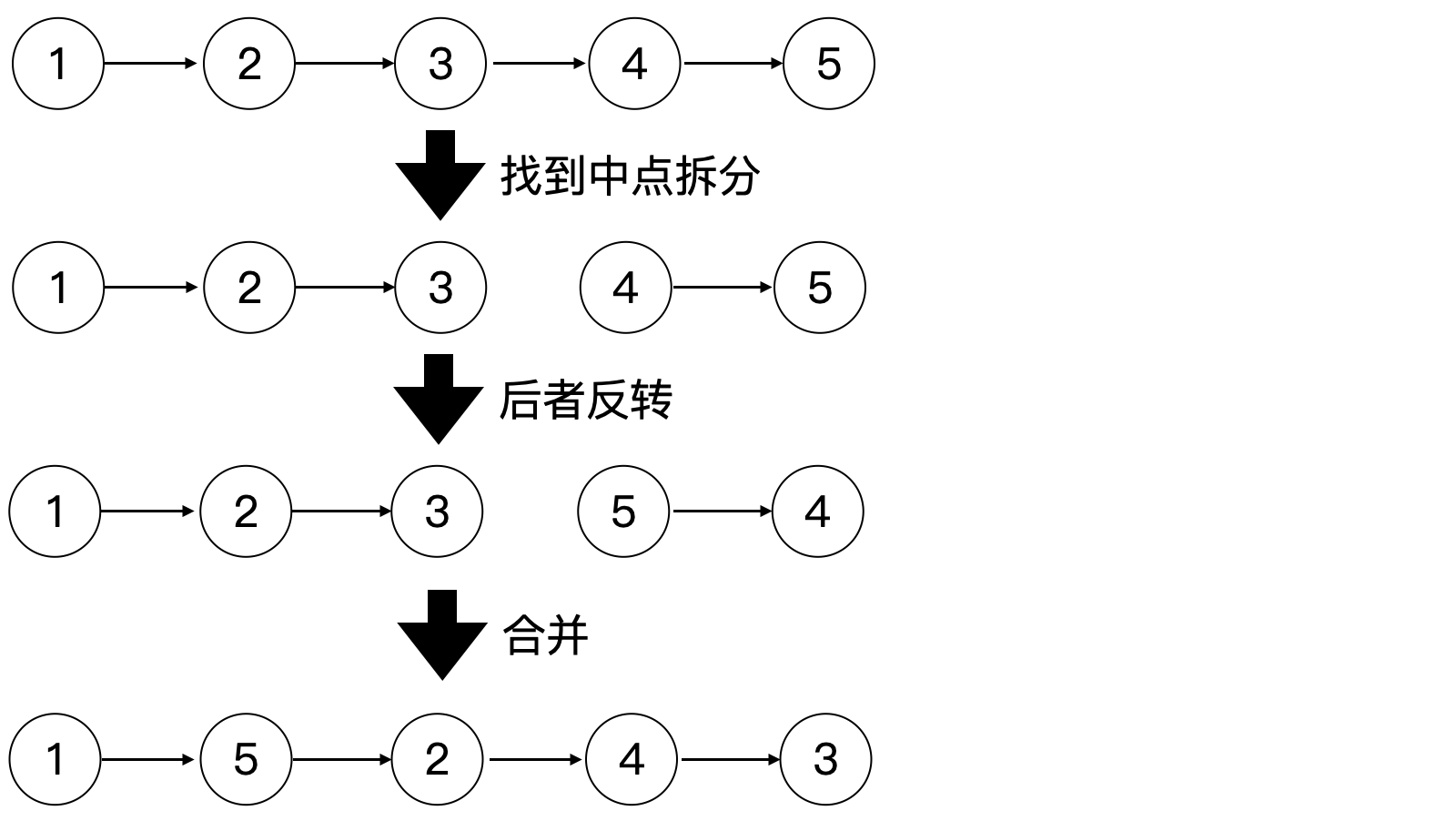
代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ReorderList {
// 方法一:利用线性表,双指针遍历
public void reorderListVerison1(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
ArrayList<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
list.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
int left = 0;
int right = list.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
list.get(left).next = list.get(right);
left++;
if (left == right) {
break;
}
list.get(right).next = list.get(left);
right--;
}
list.get(right).next = null;
}
// 方法二:快慢指针找到中间节点,再将后面半个链表反转,然后再插入
public void reorderListVersion2(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
ListNode mid = findMiddleNode(head);
ListNode l1 = head;
ListNode l2 = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
l2 = reverseList(l2);
mergeList(l1, l2);
}
private void mergeList(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode l1Next = null;
ListNode l2Next = null;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
l1Next = l1.next;
l2Next = l2.next;
l1.next = l2;
l1 = l1Next;
l2.next = l1;
l2 = l2Next;
}
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode newHead = null;
ListNode cur = null;
ListNode next = null;
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newHead;
}
private ListNode findMiddleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
}复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:方法一:O(N),方法二:O(1)
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点(⭐️⭐️)
思路
双指针。
代码
public class RemoveNthFromEnd {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode x = findFromEnd(dummyHead, n + 1);
x.next = x.next.next;
return dummyHead.next;
}
// 双指针找到倒数第 n 个节点
private ListNode findFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode p1 = head;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
p1 = p1.next;
}
ListNode p2 = head;
while (p1 != null) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
return p2;
}
}
复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II(⭐️⭐️)
思路
代码
public class DeleteDuplicates {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val) {
int x = cur.next.val;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == x) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
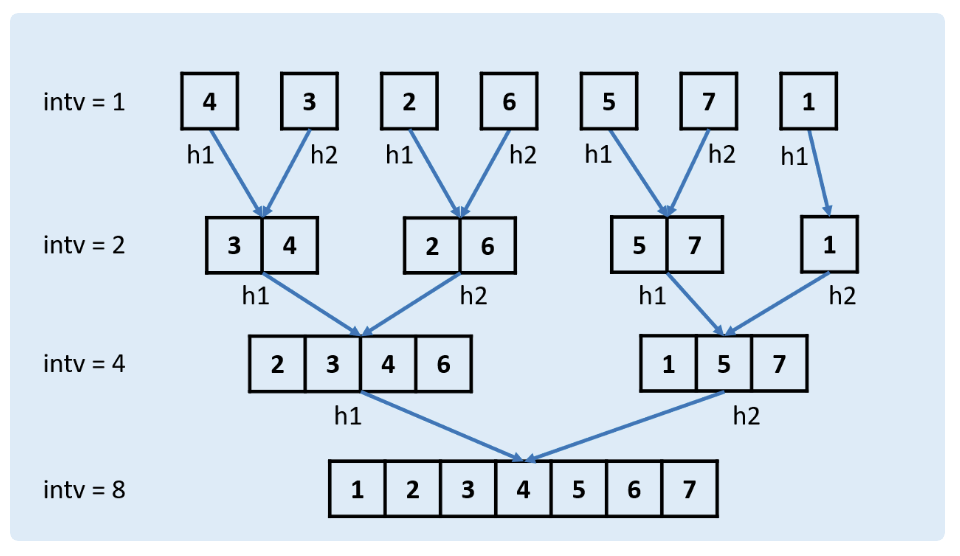
148. 排序链表(⭐️⭐️)
思路
方法一:自顶向下归并排序
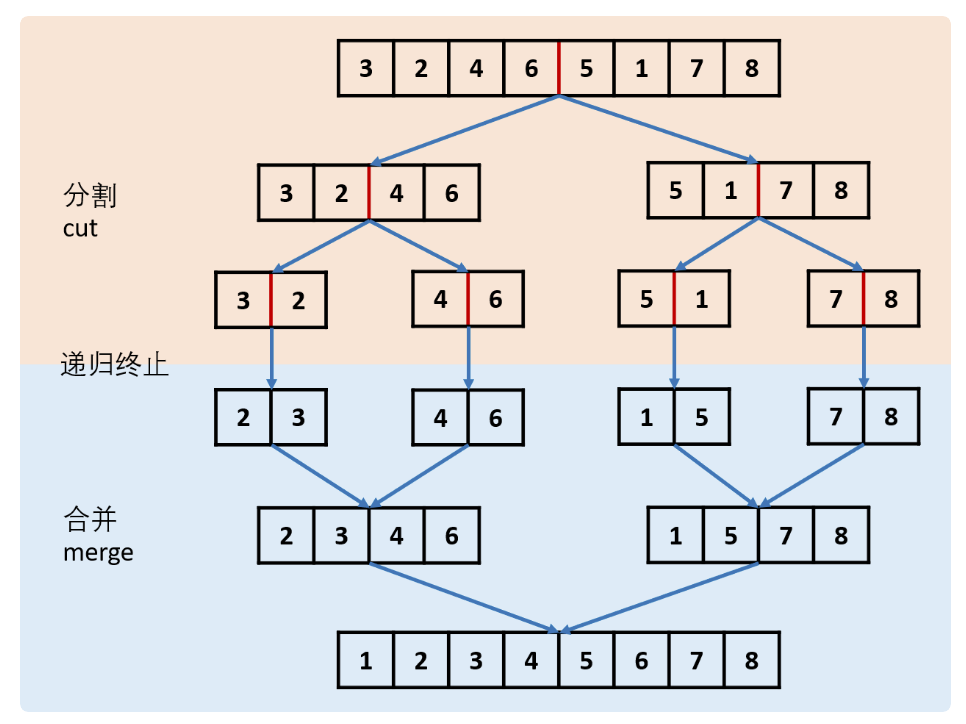
方法二:自底向上归并排序
代码
public class SortList {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 使用快慢指针找到链表中点,分为左右两个部分
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode mid = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(mid);
// 合并左右两个有序链表
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
while (left != null && right != null) {
if (left.val < right.val) {
cur.next = left;
left = left.next;
} else {
cur.next = right;
right = right.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = left == null ? right :left;
return dummyHead.next;
}
}在这个代码片段中,快指针 (fast) 需要先走一步的原因是为了确保链表在长度为偶数时,slow 指针能够准确地指向链表的中间节点。
具体来说,如果 fast 和 slow 指针都从链表头开始同步移动,每次 fast 移动两步,slow 移动一步,那么当 fast 到达链表末尾时,slow 指针会停在整个链表长度的中间位置(无论链表长度是奇数还是偶数)。
但是,如果不先让 fast 走一步,对于偶数长度的链表,slow 指针会在中间偏后的位置。通过让 fast 指针先走一步,当链表长度为偶数时,slow 指针会正好停在中间节点的前一个位置,从而使链表能够正确地分成两个部分。
复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(N * log(N))
- 空间复杂度:O(log(N))
2. 两数相加(⭐️⭐)
思路
代码
public class AddTwoNumbers {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
int carry = 0; // 进位
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int l1Value = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val;
int l2Value = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val;
int sum = l1Value + l2Value + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(sum);
cur = cur.next;
if (l1 != null) {
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l2 != null) {
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
if (carry == 1) {
cur.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)






















 1713
1713

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








