display的使用
.c1{
background: pink;
display: inline-block;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
}
.c2{
background: pink;
display: block;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
}
.u1{
display: inline;
}
.div2{
display: none;
}
/* .div1:hover .div2{
display: block;
} */
.c3:hover + .div2{
display: block;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/index13.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 对于行内标签,必须要设置为块标签,才能改变宽度和高度 -->
<span class="c1">行内标签转为块标签</span>
<span class="c1">222222222</span>
<span class="c1">333333333</span>
<span class="c2">111111111</span>
<span class="c2">222222222</span>
<span class="c2">333333333</span>
<ul >
<li class="u1">块标签转为行内标签</li>
<li class="u1">22222222</li>
<li class="u1">33333333</li>
</ul>
<div class="div1">
<span class="c3">鼠标经过下拉列表</span>
<div class="div2">
列表1
列表2
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
盒模型
.div1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
.div2{
width: 100px;/*可以存放的内容的宽度,不包含padding*/
height: 100px;
border: 10px solid red;/*边框*/
padding-left: 10px;/*内间距*/
margin-left: 10px;/*外间距*/
margin-top: 10px ;
}
/*div2的实际宽度为100+10+10+10+10=140px*/
.ul1{
width: 400px;
height: 30px;
border-top: 5px solid green;
border-bottom: 1px solid gray;
border-left: 1px solid gray;
border-right: 1px solid gray;
}
.input1{
border: 2px solid red;
width: 100px;
height: 30px;
border-radius: 0px;/*角度*/
border-top-left-radius: 30px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 30px;
}
.input2{
border: 2px solid red;
width: 100px;
height: 30px;
border-radius: 10px 20px;/*角度 左上右下 右上左下*/
/* border-top-left-radius: 30px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 30px; */
}
.input3{
border: 2px solid red;
width: 100px;
height: 30px;
border-radius: 30px 20px 10px 5px;/*角度 左上 右上 右下 左下*/
padding: 5px 10px 5px 10px;上 右 下 左
/* border-top-left-radius: 30px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 30px; */
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/index14.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1">
11
</div>
<div class="div2">
222
</div>
<ul class="ul1">
</ul>
<input type="text" class="input1"/>
<input type="text" class="input2"/>
<input type="text" class="input3" value="1111111111111111"/>
</body>
</html>
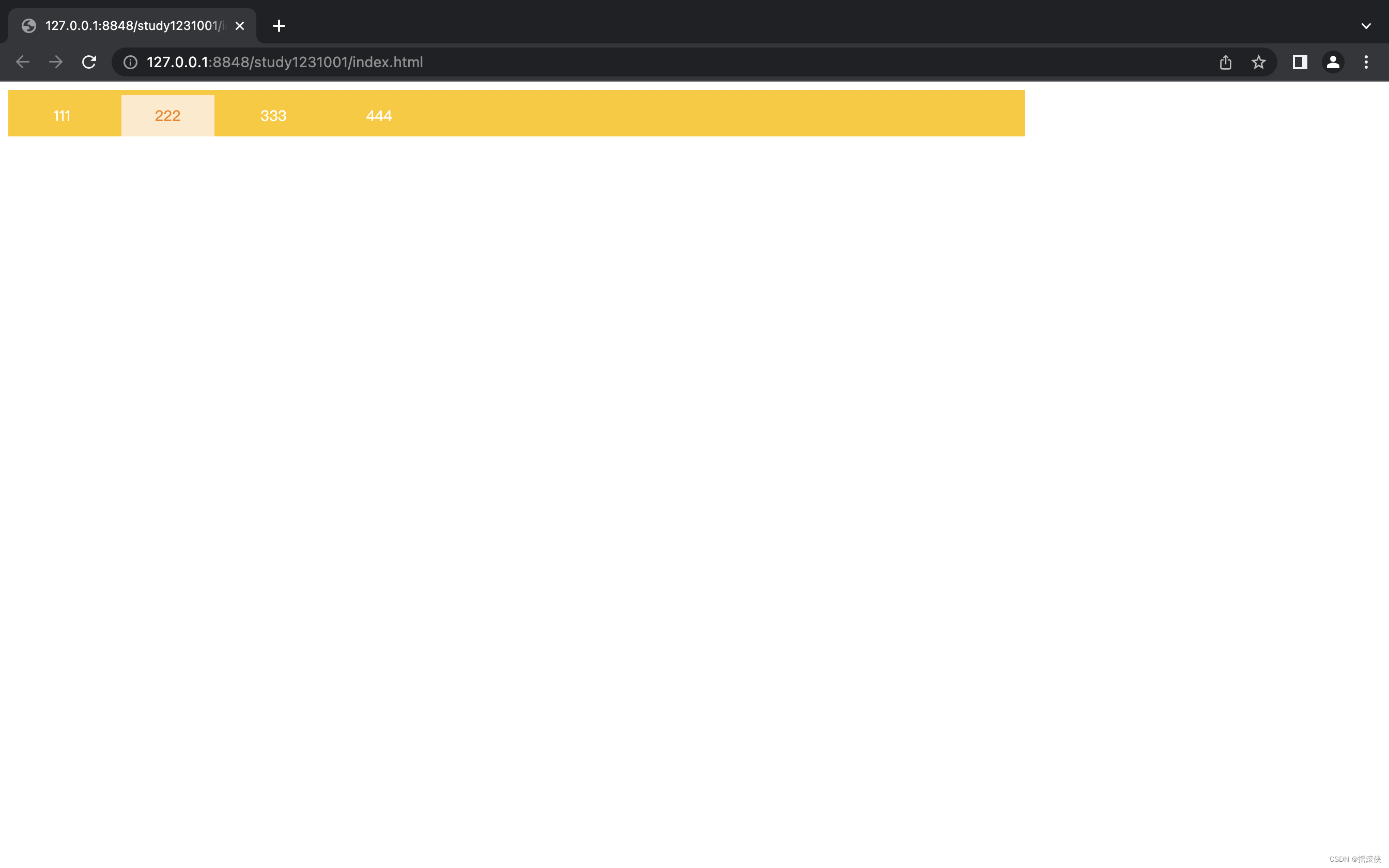
导航条
.nav{
width: 984px;
height: 45px;
background: url(../img/bmg1.png);
}
.nav>a{
display: inline-block;
width: 90px;
height: 40px;
color: #fff;
font: 14px/40px "微软雅黑";
text-decoration: none;
text-align: center;
margin-top: 5px;
margin-left: 7px;
}
a:hover{
color: #f78102;
background-color: #ffeac9;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title></title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/index.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<nav class="nav">
<a>111</a>
<a>222</a>
<a>333</a>
<a>444</a>
</nav>
</body>
</html>
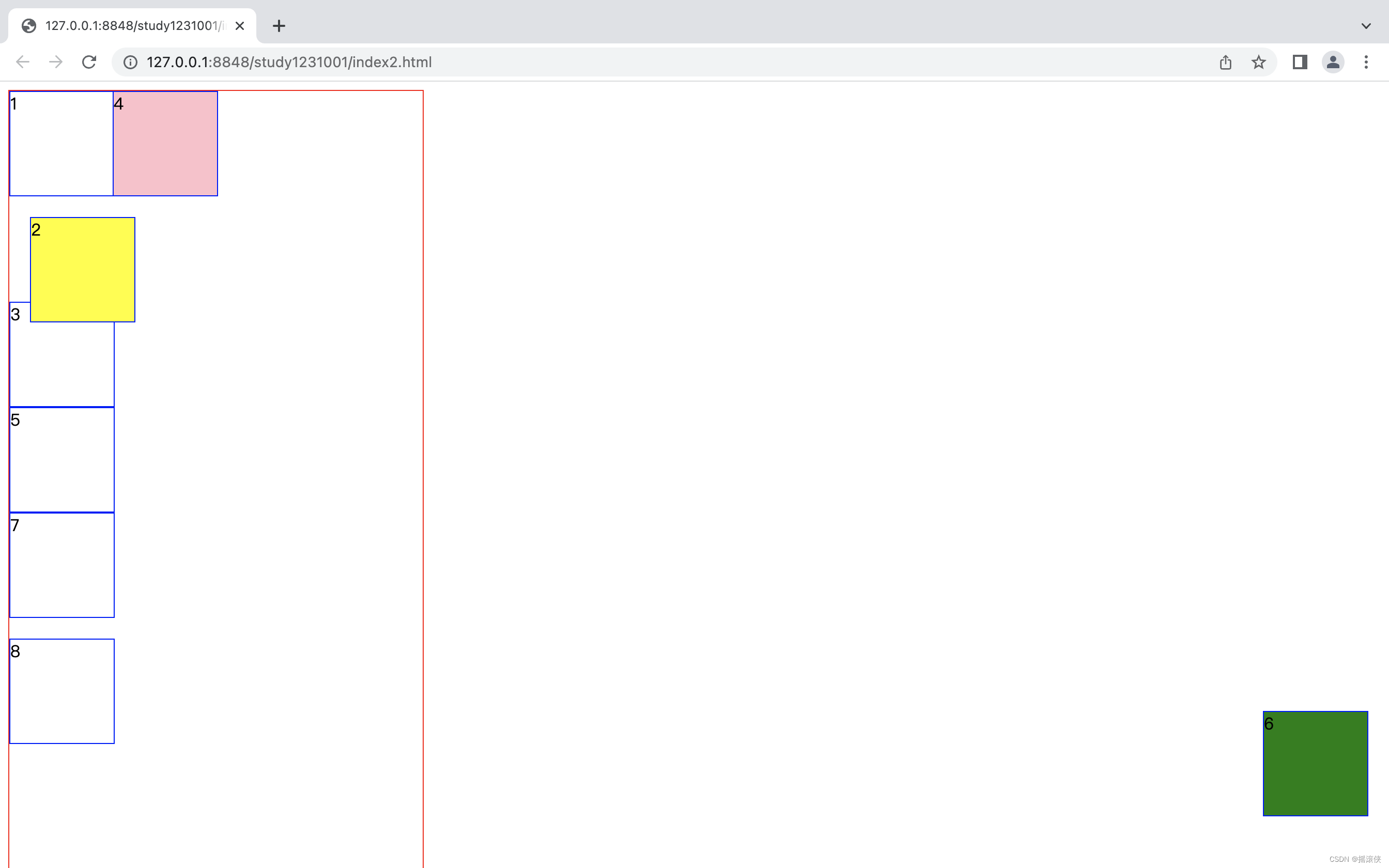
盒子如何定位
.parent{
width: 400px;
height: 800px;
border: 1px solid red;
position: relative;/*会影响到里层元素的绝对定位*/
}
.parent>div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid blue;
}
div.div2{
/* 相对定位,相对于自己本来的位置,在文档流中 */
position: relative;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
background-color: yellow;
}
div.div4{
/* 绝对定为,绝对于body,脱离正常文档流。如果外面的盒子做了相对定位,则它绝对于外面的盒子 */
position: absolute;
background-color: pink;
left:100px;
top:0px;
}
div.div6{
/*固定定位,脱离文档流,不会随着滚动条滚动*/
position: fixed;
bottom: 50px;
right: 20px;
background-color: green;
}
div.div7{
/* 默认定位,等于没有定位,会忽略top right bottom left */
position: static;
left: 20px;
top: 20px;
}
div.div8{
/* 继承父级元素的定位方式 */
position: inherit;
top: 20px;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/index2.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<div class="parent">
<div class="div1">1</div>
<div class="div2">2</div>
<div class="div3">3</div>
<div class="div4">4</div>
<div class="div5">5</div>
<div class="div6">6</div>
<div class="div7">7</div>
<div class="div8">8</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
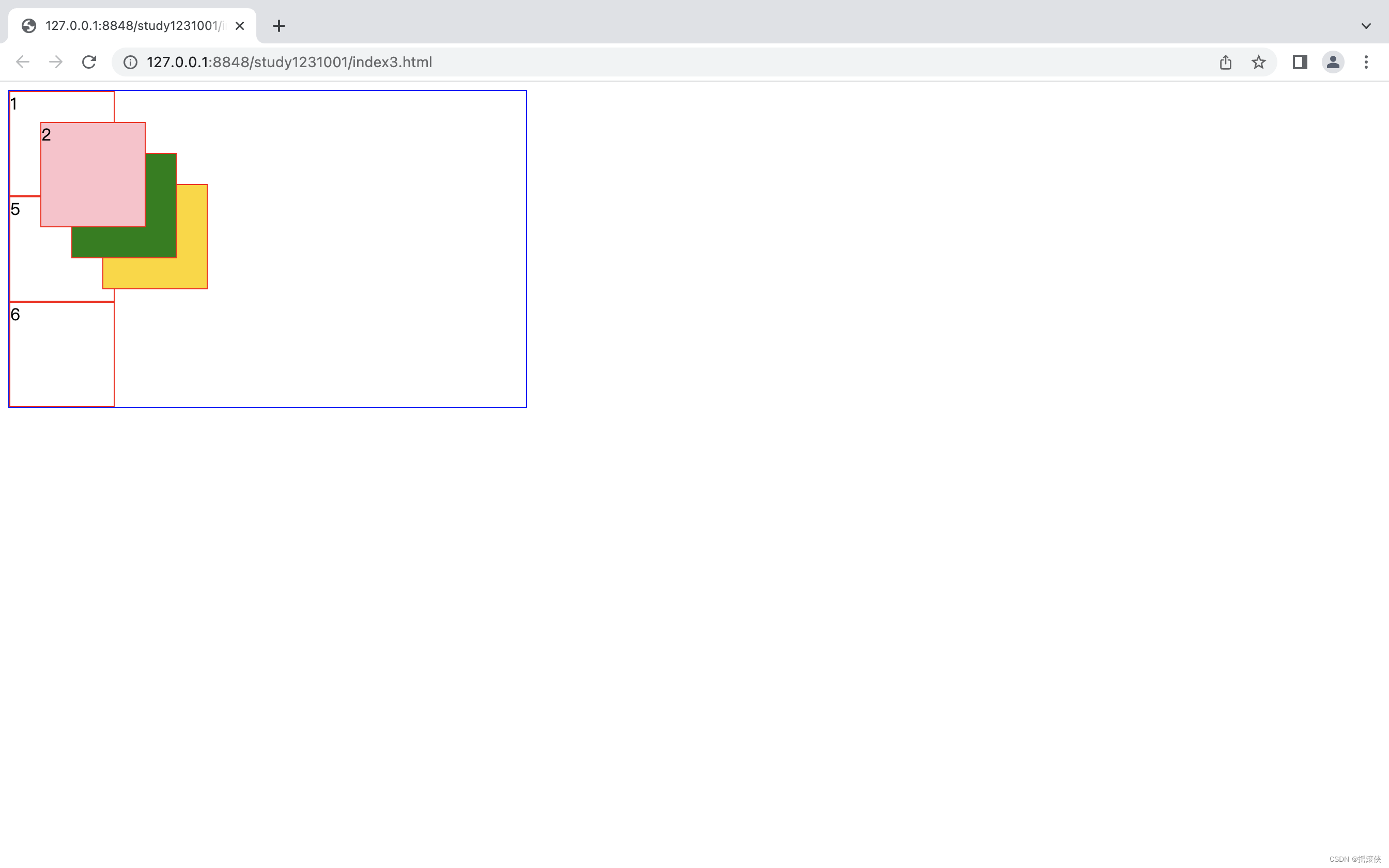
z-index
.parent{
width: 500px;
position: relative;
border: 1px solid blue;
}
.parent>div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
.div2{
position: absolute;
top: 30px;
left: 30px;
background-color: pink;
z-index: 4 ;
}
.div3 {
position: absolute;
top: 60px;
left: 60px;
background-color: green;
z-index: 3;
}
.div4 {
position: absolute;
top: 90px;
left: 90px;
background-color: gold;
}
.parent>div:hover{
z-index: 99;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/index3.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<div class="parent">
<div class="div1">1</div>
<div class="div2">2</div>
<div class="div3">3</div>
<div class="div4">4</div>
<div class="div5">5</div>
<div class="div6">6</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
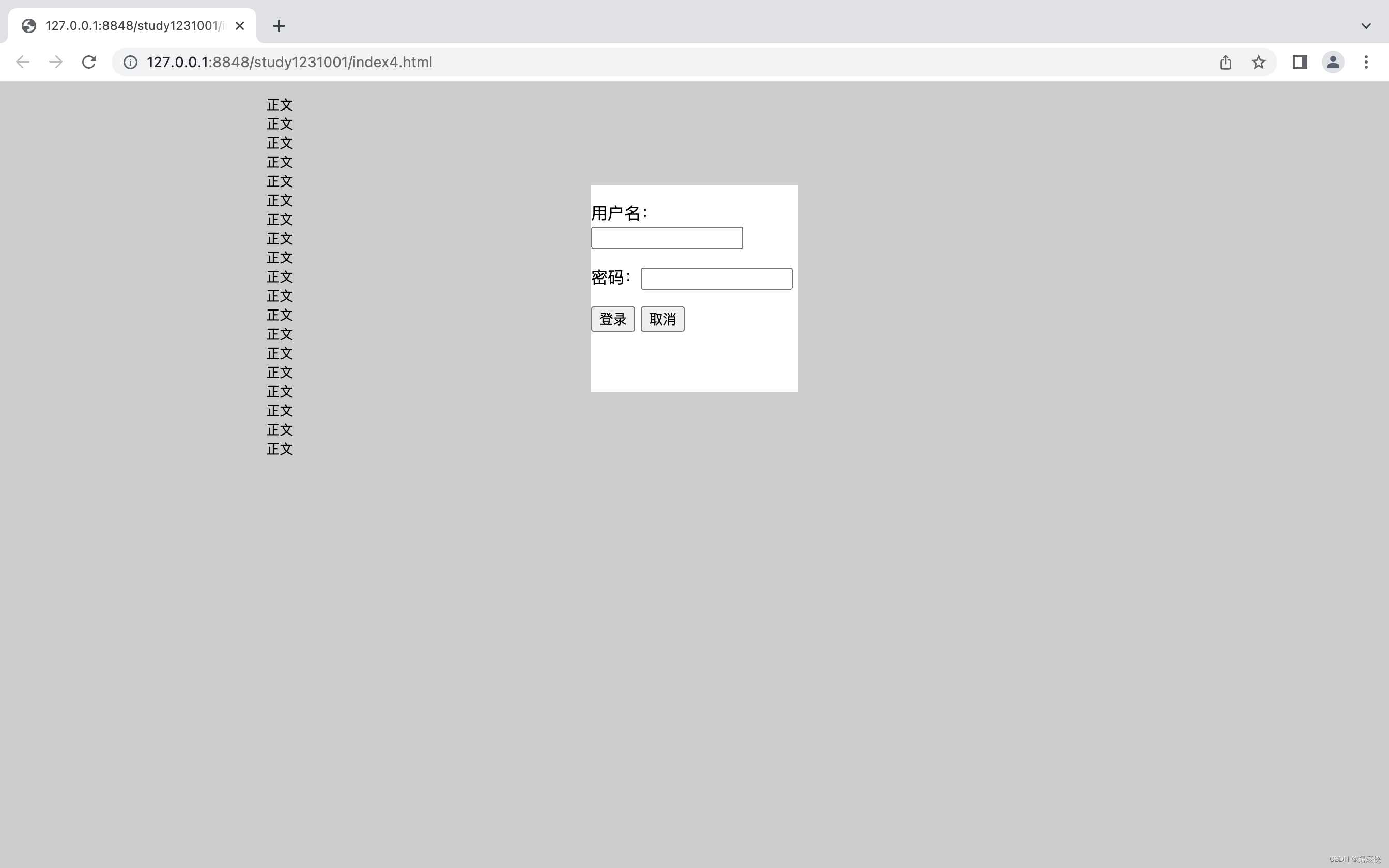
弹出登录窗口效果的实现
.bg{
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
}
.login{
position: fixed;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
top: 100px;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -100px;
background-color: white;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/index4.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<div class="bg"></div>
<div class="login">
<form action="" method="post">
<p>用户名:<input type="text"/></p>
<p>密码:<input type="password"/></p>
<p>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/>
<input type="reset" value="取消"/>
</p>
</form>
</div>
<div class="content">
<pre>
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
正文
</pre>
</div>
</body>
</html>








 文章详细介绍了CSS中的display属性,展示了如何将行内元素转换为块元素以及块元素转换为行内元素。同时,探讨了盒模型,包括width、height、padding、margin和border的计算方式,以及如何影响元素的尺寸。此外,还讨论了定位技术,如相对定位、绝对定位、固定定位,以及z-index在确定元素堆叠顺序中的作用。最后,提到了通过CSS实现弹出登录窗口的效果。
文章详细介绍了CSS中的display属性,展示了如何将行内元素转换为块元素以及块元素转换为行内元素。同时,探讨了盒模型,包括width、height、padding、margin和border的计算方式,以及如何影响元素的尺寸。此外,还讨论了定位技术,如相对定位、绝对定位、固定定位,以及z-index在确定元素堆叠顺序中的作用。最后,提到了通过CSS实现弹出登录窗口的效果。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








