Apollo配置中心动态生效原理
Spring中的重要概念
在了解Apollo配置中心实现原理之前,我们需要先熟悉一下Spring框架中的几个重要的概念:
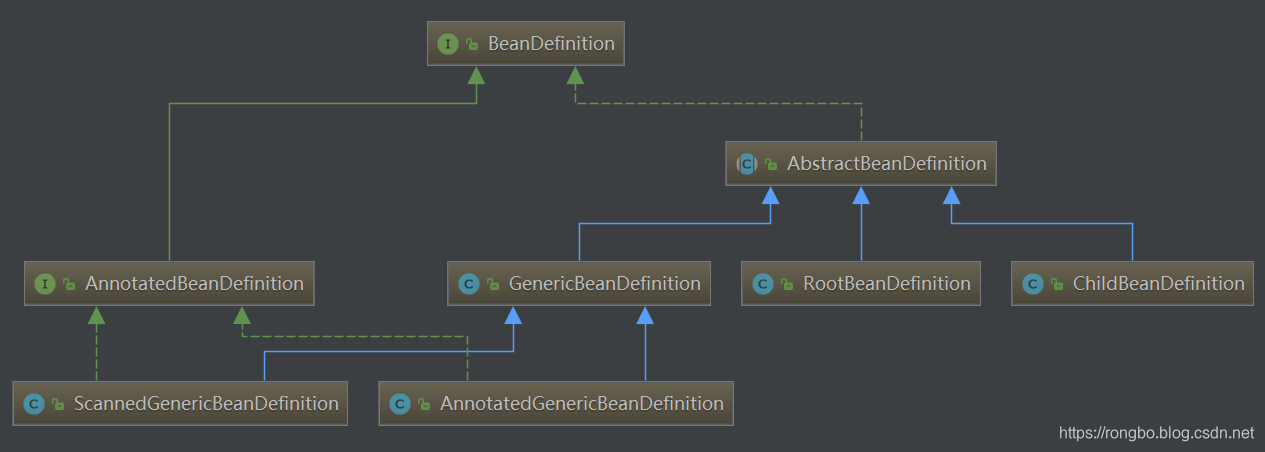
1、BeanDefinition
用于描述Bean的配置信息,Bean配置一般有三种方式:
(1)XML配置文件
(2)@Service、@Component等注解
(3)Java Config方式
对应的BeanDefinition实现类如下图,Spring容器启动时,会把所有的Bean配置信息转换为BeanDefinition对象。
2、BeanDefinitionRegistry
BeanDefinition容器,所有的Bean定义都注册在BeanDefinitionRegistry对象中。
3、PropertySource
用于存放Spring配置资源信息,例如spring项目中properties或者yaml文件配置信息均会保存在PropertySource对象中。Spring支持使用@PropertySource注解,將配置信息加载到Environment对象中。
4、ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar是一个接口,该接口的实现类作用于在Spring解析Bean配置生成BeanDefinition对象阶段。
在Spring解析Configuration注解时,向Spring容器中增加额外的BeanDefinition。
5、BeanFactoryPostProcessor
Bean工厂后置处理器,用于在BeanDefinition对象注册完成后,修改Bean工厂信息,例如增加或者修改BeanDefinition对象。
6、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
它是一个特殊的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,用于在BeanDefinition对象注册完成后,访问、新增或者修改BeanDefinition信息。
7、PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
它是一个特殊的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,用于解析Bean配置中的${…}参数占位符。
8、BeanPostProcessor
Bean后置处理器,bean初始化方法调用前后,执行拦截逻辑,可以对原有的Bean进行包装或者根据标记接口创建代理对象。
Spring框架启动过程回顾
Spring框架启动大致会经过以下几个阶段:
1、解析Bean配置信息,將配置信息转换为BeanDefinition对象,注册到BeanDefinitionRegistry中。
2、执行所有的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory()方法对Bean工厂信息进行修改,包括修改或新增BeanDefinition对象。
注意:如果需要控制BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行顺序需要实现PriorityOrdered接口,getOrder()方法返回的值越小,执行优先级越高。
3、通过BeanDefinition对象实例化所有Bean,注入依赖。
4、执行所有BeanPostProcessor对象的postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法。
5、执行Bean的初始化方法,例如InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet方法,或init-method属性指定的方法。
执行所有BeanPostProcessor对象的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法
Apollo原理解析
Apollo框架使用非常简单,如果是Spring Boot项目,只需要在启动类上增加@EnableApolloConfig注解即可。例如:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableApolloConfig
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true);
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
那么@EnableApolloConfig注解到底做了什么事情了,我们可以看下EnableApolloConfig注解的定义,代码如下:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(ApolloConfigRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableApolloConfig {
/**
* Apollo namespaces to inject configuration into Spring Property Sources.
*/
String[] value() default {ConfigConsts.NAMESPACE_APPLICATION};
/**
* The order of the apollo config, default is {@link Ordered#LOWEST_PRECEDENCE}, which is Integer.MAX_VALUE.
* If there are properties with the same name in different apollo configs, the apollo config with smaller order wins.
* @return
*/
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
如上面代码所示,在EnableApolloConfig注解中,通过@Import注解导入了一个ApolloConfigRegistrar,接下来我们就来看一下ApolloConfigRegistrar的实现:
public class ApolloConfigRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(importingClassMetadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableApolloConfig.class.getName()));
String[] namespaces = attributes.getStringArray("value");
int order = attributes.getNumber("order");
PropertySourcesProcessor.addNamespaces(Lists.newArrayList(namespaces), order);
Map<String, Object> propertySourcesPlaceholderPropertyValues = new HashMap<>();
// to make sure the default PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer's priority is higher than PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
propertySourcesPlaceholderPropertyValues.put("order", 0);
BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.class.getName(),
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.class, propertySourcesPlaceholderPropertyValues);
BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, PropertySourcesProcessor.class.getName(),
PropertySourcesProcessor.class);
BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, ApolloAnnotationProcessor.class.getName(),
ApolloAnnotationProcessor.class);
BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, SpringValueProcessor.class.getName(), SpringValueProcessor.class);
BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, SpringValueDefinitionProcessor.class.getName(), SpringValueDefinitionProcessor.class);
BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, ApolloJsonValueProcessor.class.getName(),
ApolloJsonValueProcessor.class);
}
}
如上面代码所示,ApolloConfigRegistrar实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,前面有提到过,ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口的实现类作用于在Spring解析Bean配置生成BeanDefinition对象阶段,在Spring解析Configuration注解时,向Spring容器中增加额外的BeanDefinition。
ApolloConfigRegistrar中注册了几个BeanDefinition,具体如下:
1、PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer -------->BeanFactoryPostProcessor
2、PropertySourcesProcessor -------->BeanFactoryPostProcessor
3、ApolloAnnotationProcessor -------->BeanPostProcessor
4、SpringValueProcessor -------->BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor
5、SpringValueDefinitionProcessor-------->BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
(即BeanFactoryPostProcessor)
6、ApolloJsonValueProcessor -------->BeanPostProcessor
这些类要么实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,要么实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,前面有提到过BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor是Spring提供的扩展机制,BeanFactoryPostProcessor一定是在BeanPostProcessor之前执行。
接下来我们就来看一下这些自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor的执行顺序,以及它们具体做了什么事情。
自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor
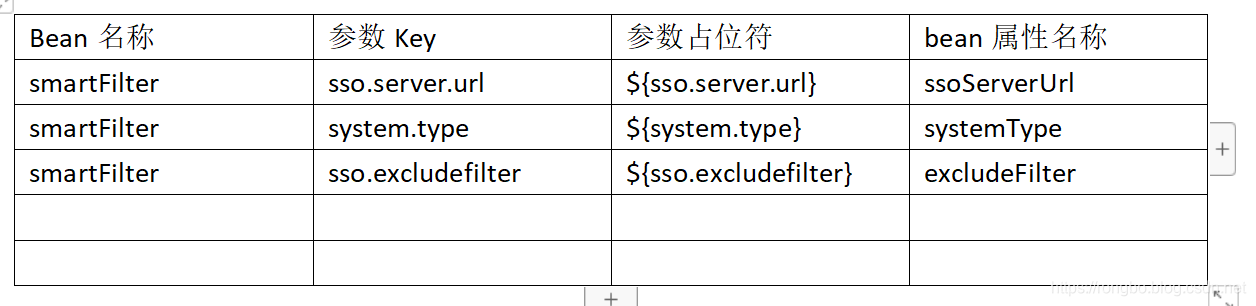
1、SpringValueDefinitionProcessor
对所有的BeanDefinition进行遍历,將属性中包含${…}参数占位符的属性添加到Apollo 属性注册表。Apollo 属性注册表具体结构如下:
2、PropertySourcesProcessor
(1)根据命名空间从配置中心获取配置信息,创建RemoteConfigRepository和LocalFileConfigRepository对象。RemoteConfigRepository表示远程配置中心资源,LocalFileConfigRepository表示本地缓存配置资源。
(2)LocalFileConfigRepository对象缓存配置信息到C:\opt\data 或者/opt/data目录。
(3)RemoteConfigRepository开启HTTP长轮询请求定时任务,默认2s请求一次。
(4)將本地缓存配置信息转换为PropertySource对象(Apollo自定义了Spring的PropertySource),加载到Spring的Environment对象中。
(5)將自定义的ConfigPropertySource注册为观察者。一旦RemoteConfigRepository发现远程配置中心信息发生变化,ConfigPropertySource对象会得到通知。
3、PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
加载本地Properties文件,將${…}参数占位符替换为具体的值。
4、SpringValueProcessor
仅仅是为了获取SpringValueDefinitionProcessor中获取的 包含${…}参数占位符的BeanDefinition。(从面向对象设计原则的角度,不符合单一责任原则,可以注册到Guice容器里,然后从Guice容器获取。)
自定义BeanPostProcessor
5、ApolloJsonValueProcessor
处理ApolloJsonValue注解,属性或者方法中包含ApolloJsonValue注解的Bean,属性值也会根据配置中心配置的修改发生变化,因此也需要添加到配置中心可配的容器中
6、ApolloAnnotationProcessor
处理ApolloConfigChangeListener注解,ApolloConfigChangeListener注解用于注册一个配置变化监听器。
7、SpringValueProcessor
处理Spring中的Value注解,將属性或者方法中包含Value注解的Bean信息添加到Apollo属性注册表。
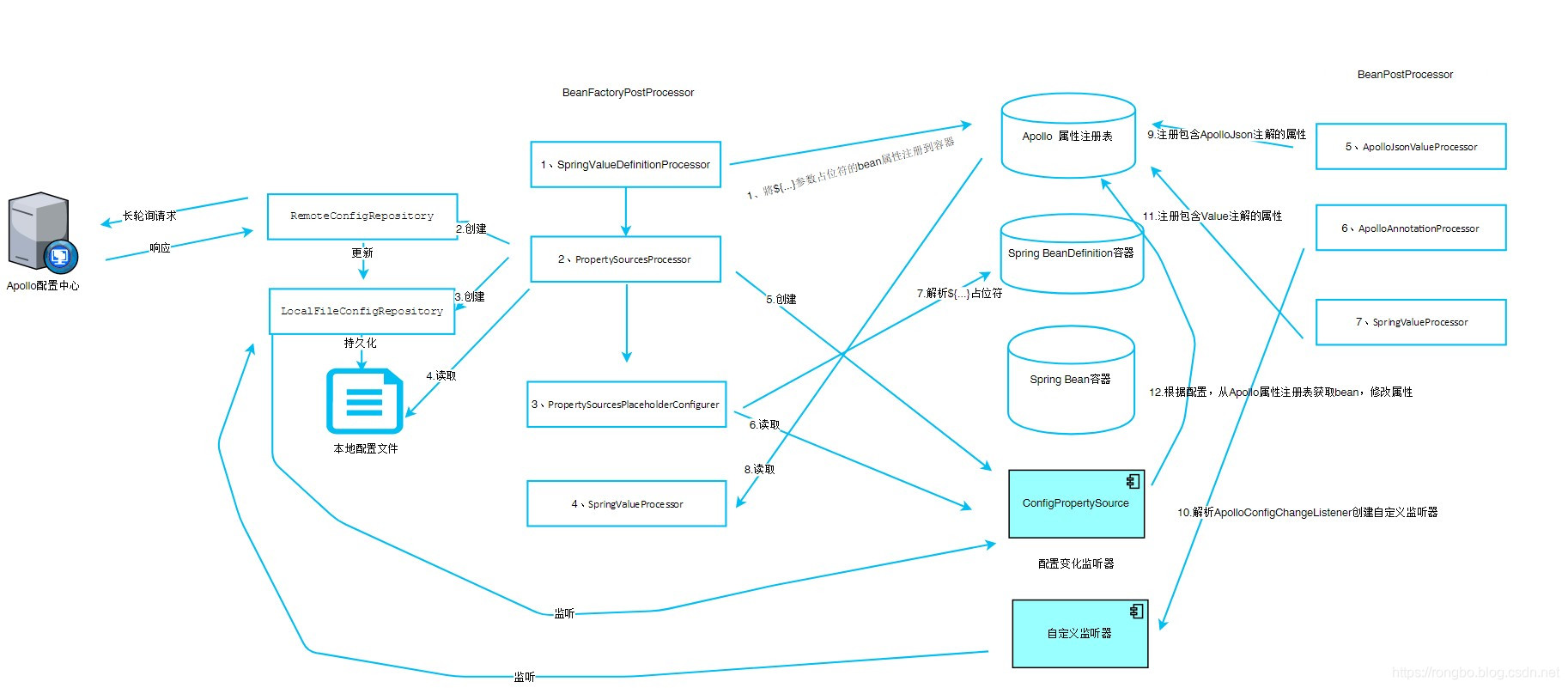
整个过程如下图所示:
总结
Apollo配置中心动态生效机制,是基于Http长轮询请求和Spring扩展机制实现的,在Spring容器启动过程中,Apollo通过自定义的BeanPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor將参数中包含${…}占位符和@Value注解的Bean注册到Apollo框架中定义的注册表中。然后通过Http长轮询不断的去获取服务端的配置信息,一旦配置发生变化,Apollo会根据变化的配置的Key找到对应的Bean,然后修改Bean的属性,从而实现了配置动态生效的特性。
需要注意的是,Apollo在配置变化后,只能修改Bean的属性,例如我们数据源的属性发生变化,新创建的Connection对象是没问题的,但是连接池中已经创建的Connection对象相关信息是不能动态修改的,所以依然需要重启应用。
























 1155
1155











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








