
前言
本题是在栈与队列的基础上,为巩固两者而出的题,所以基本是在实现了栈与队列的基础上做的,如果没有栈与队列的基础,请看我之前的文章,数据结构之栈与队列详解
一、用队列实现栈
1.题目介绍
题目在225. 用队列实现栈

2.思路
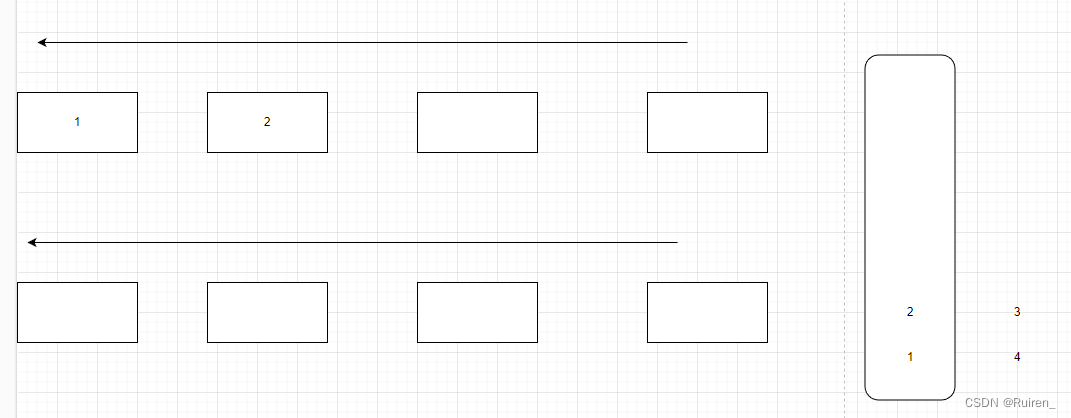
1️⃣将不为空的队列的数据导入为空的队列中至数据只剩余一个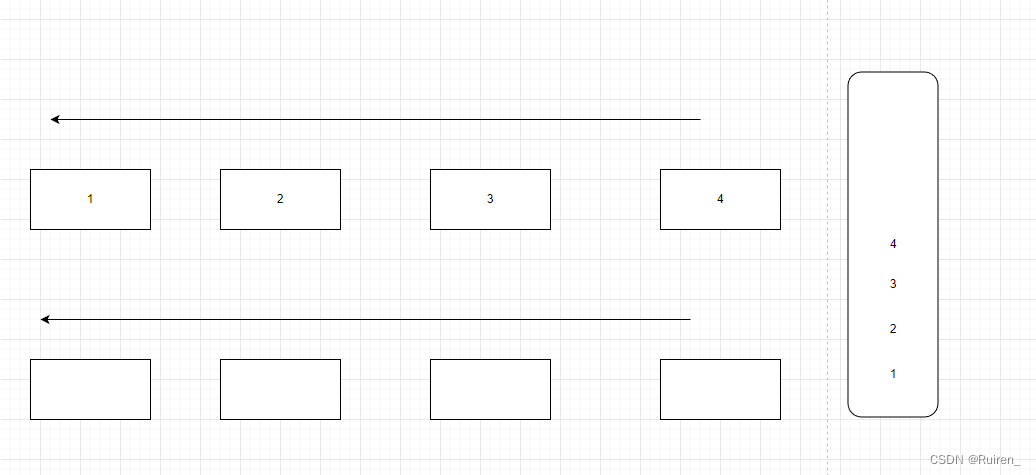
2️⃣队列出掉4,对于栈来说,就是4出栈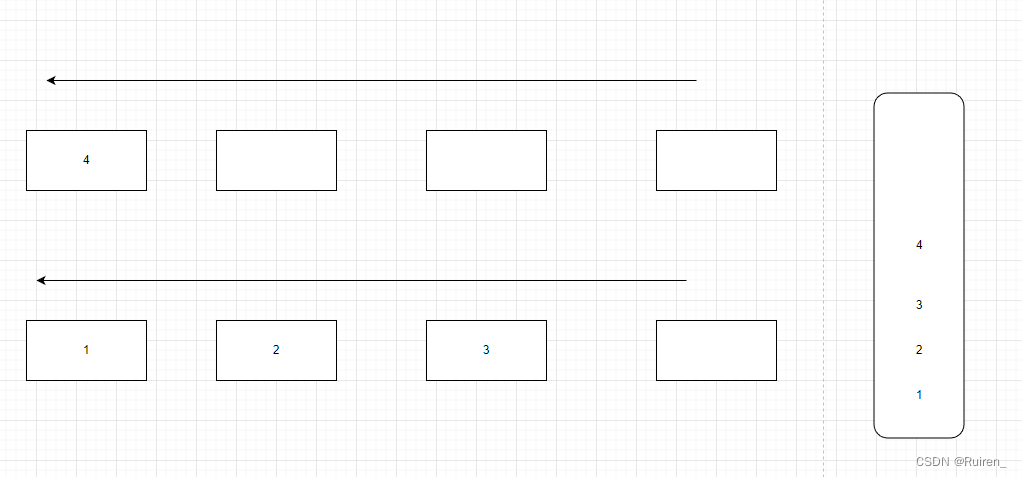
3️⃣
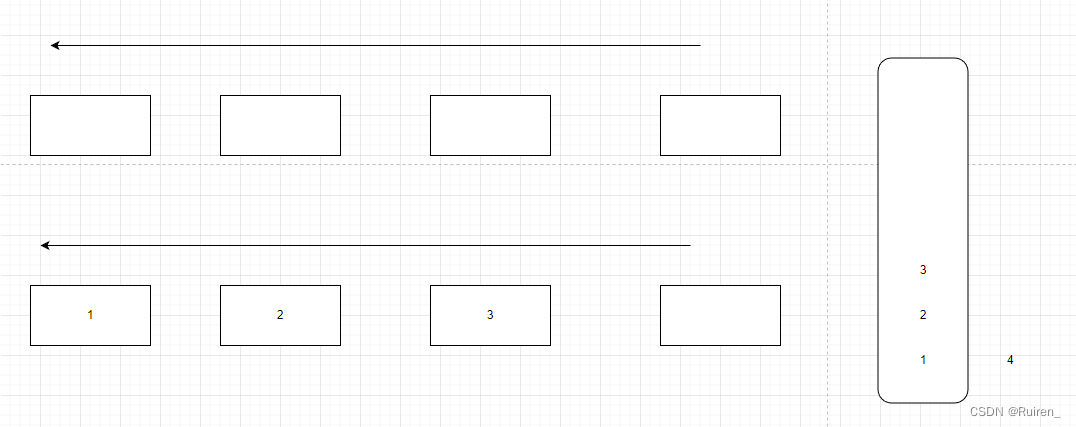
4️⃣当其中一个队列为空时,将不为空的队列的数据导入为空的队列中至数据只剩余一个
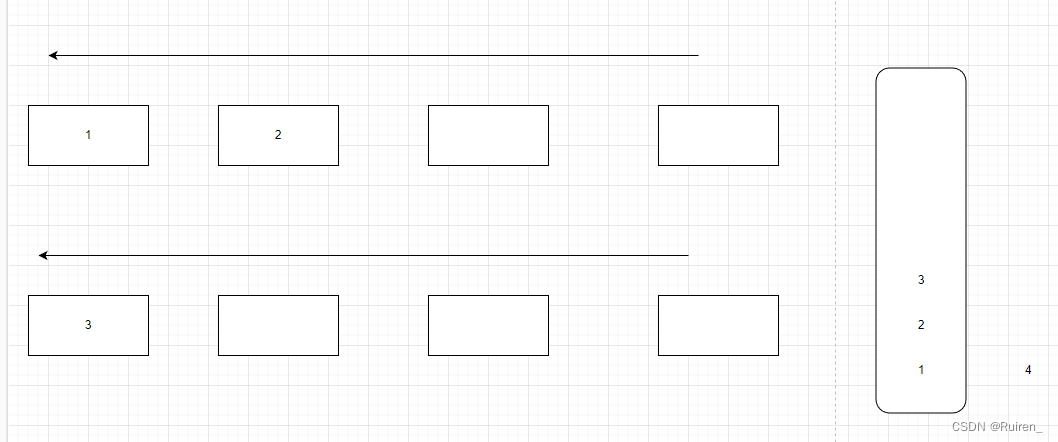
5️⃣重复上述操作
3.代码
typedef char QDatatype;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDatatype Data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
int size;
}Queue;
typedef struct
{
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
}MyStack;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->Data = x;
newnode->next=NULL;
if (pq->size == 0)
{
pq->head =pq->tail= newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->size);
if (pq->head->next==NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head =pq->tail= NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size==0;
}
QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->Data;
}
QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->Data;
}
//此位置之上属于队列的实现代码,此下为题目所需完成的
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack *pst=( MyStack *)malloc(sizeof( MyStack));
QueueInit(&pst->q1);
QueueInit(&pst->q2);
return pst;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
while(QueueSize(&obj->q1)>1)
{
QDatatype front=QueueFront(&obj->q1);
QueuePop(&obj->q1);
QueuePush(&obj->q2,front);
}
QDatatype front=QueueFront(&obj->q1);
QueuePop(&obj->q1);
return front;
}
else
{
while(QueueSize(&obj->q2)>1)
{
QDatatype front=QueueFront(&obj->q2);
QueuePop(&obj->q2);
QueuePush(&obj->q1,front);
}
QDatatype front=QueueFront(&obj->q2);
QueuePop(&obj->q2);
return front;
}
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return (QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2));
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
二、用栈实现队列
1.题目介绍
题目在用栈实现队列

2.思路
这题我们需要仔细思考是否还需要像上面那样来回倒腾数据,比如我给个例子
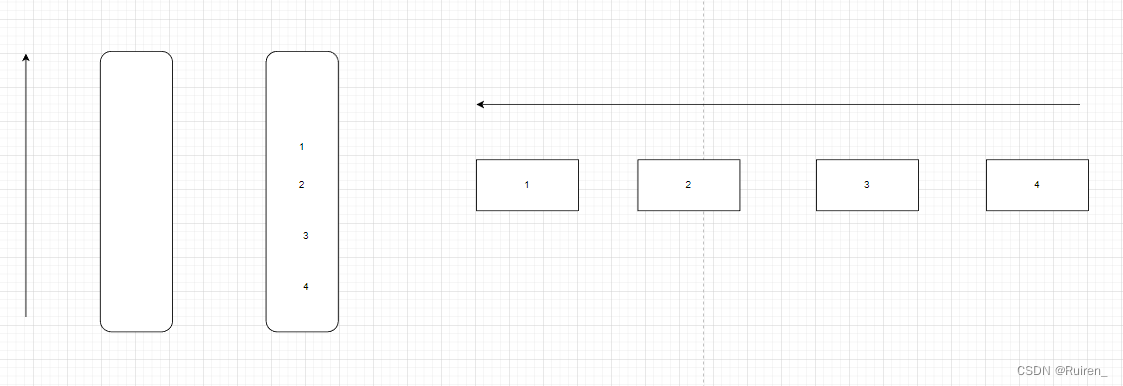
当我们出掉一个数据1后,发现我们不需要在来回倒腾了,
当我们在想出后面的时,我们一直只需要出另外一个
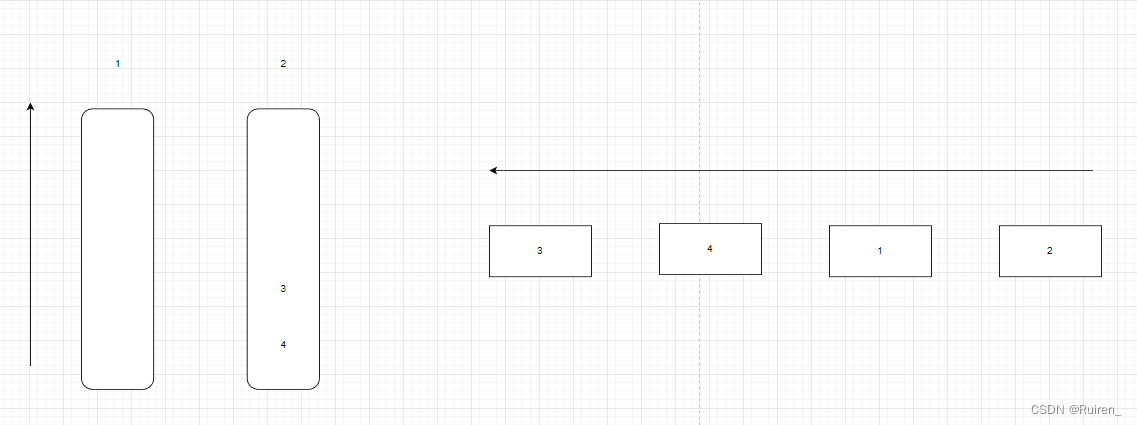
那么如果我们在出一个后需要入数据呢,我们入到什么地方去呢,比如想下面这种情况,当我们出掉1和2后,我们在队列后面入1和2,那么我们在栈里面怎么入呢,因为3,和4的那个栈需要出掉其他数据,不能入,所以我们只能操作左边的栈
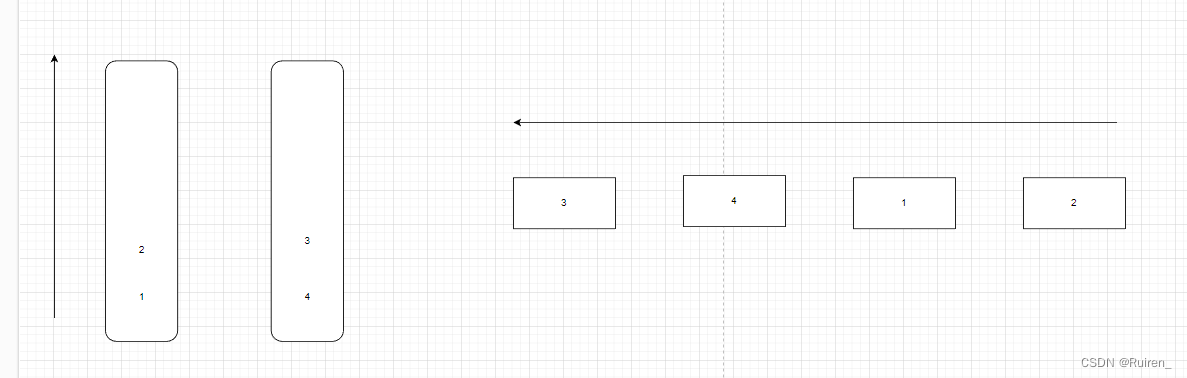
然后如果我们的右边的栈出完后,我们就重复上述操作
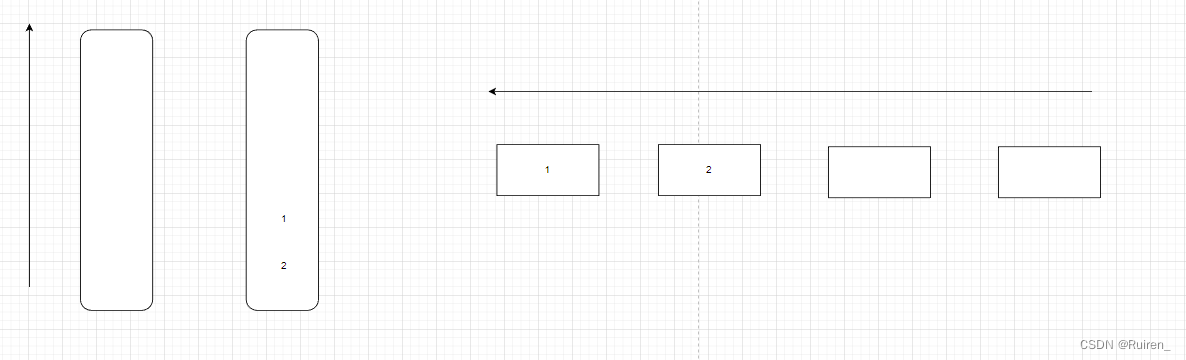
那么我们可以总结
1️⃣我们将一个栈只当作出数据的的,将一个栈只当入数据的(对于上图来说左边是入的,右边是出的)
2️⃣当出的栈为空时,我们就将入的栈的数据入到出的栈里面
3️⃣当出的栈不为空时,我们出数据就只向出栈出数据
3.代码
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;//初始化时如果top是0,即top指向栈顶上的后一位
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4: ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* temp = (STDataType * )realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType)*newcapacity);
if (temp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = temp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
return ps->top == 0;
}
void StackPrint(ST* ps)
{
while (ps->top)
{
printf("%d", StackTop(ps));
StackPop(ps);
}
}
typedef struct {
ST st1;//入的栈
ST st2;//出的栈
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* Queue=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
StackInit(&Queue->st1);
StackInit(&Queue->st2);
return Queue;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
StackPush(&obj->st1,x);
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if(StackEmpty(&obj->st2))
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->st1))
{
StackPush(&obj->st2,StackTop(&obj->st1));
StackPop(&obj->st1);
}
}
return StackTop(&obj->st2);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
int front=myQueuePeek(obj);
StackPop(&obj->st2);
return front;
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return (StackEmpty(&obj->st1)&&StackEmpty(&obj->st2));
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
StackDestroy(&obj->st2);
StackDestroy(&obj->st1);
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your MyQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();
* myQueuePush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myQueuePop(obj);
* int param_3 = myQueuePeek(obj);
* bool param_4 = myQueueEmpty(obj);
* myQueueFree(obj);
*/

























 189
189











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










