原理
sample将RDD这个集合内的元素进行采样,获取所有元素的子集。用户可以设定是否有放回的抽样、百分比、随机种子,进而决定采样方式。
参数说明:
withReplacement=true, 表示有放回的抽样;
withReplacement=false, 表示无放回的抽样。
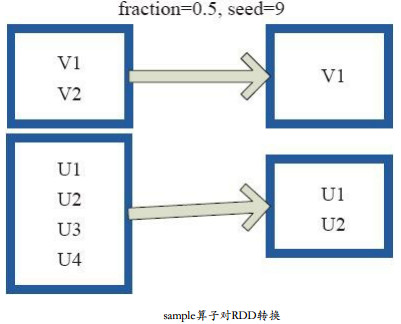
每个方框是一个RDD分区。通过sample函数,采样50%的数据。V1、V2、U1、U2、U3、U4采样出数据V1和U1、U2,形成新的RDD。
源码
/**
* Return a sampled subset of this RDD.
*/
def sample(withReplacement: Boolean,
fraction: Double,
seed: Long = Utils.random.nextLong): RDD[T] = {
require(fraction >= 0.0, "Negative fraction value: " + fraction)
if (withReplacement) {
new PartitionwiseSampledRDD[T, T](this, new PoissonSampler[T](fraction), true, seed)
} else {
new PartitionwiseSampledRDD[T, T](this, new BernoulliSampler[T](fraction), true, seed)
}
}上手使用
scala> val rdd = sc.makeRDD(1 to 100,2)
rdd: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Int] = ParallelCollectionRDD[2] at makeRDD at <console>:27
scala> rdd.sample(true,0.1,10).collect
res5: Array[Int] = Array(2, 4, 20, 20, 37, 70, 77)
scala> rdd.sample(true,0.1,10).collect
res6: Array[Int] = Array(2, 4, 20, 20, 37, 70, 77)
scala> rdd.sample(true,0.1,11).collect
res7: Array[Int] = Array(17, 19, 28, 35, 80, 94, 97)
scala> rdd.sample(true,0.1,131).collect
res8: Array[Int] = Array(7, 9, 10, 21, 29, 38, 41, 55, 57, 61, 72, 74, 74, 87, 91)
scala> rdd.sample(true,0.1,9).collect
res9: Array[Int] = Array(1, 19, 25, 28, 39, 60, 62, 77, 84, 88, 93,





















 2367
2367

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








