一、position属性
1、position: static
static为每个元素获得的默认值。即没有定位,意味着将元素放在文档流中的正常位置,其元素不会受到 top, bottom, left, right影响。
2、position: absolute
绝对定位的元素的位置相对于最近的已定位父元素,如果元素没有已定位的父元素,那么它的位置相对于<html>。
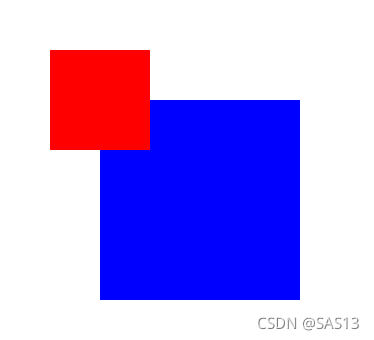
两色块原来的位置如下图:

对红色块设置绝对定位后,就会脱离原来的图层,往上面抬了一层。
这样蓝色色块就挤到了红色色块原来的位置,从而被红色色块盖住了。

position: absolute共有4个css属性:分别是上左下右top,left,bottom,right。
对红色色块设置 left: 100px;

这4个css元素相对于它的第一个position不为static的父元素,如果没有,就相对于body
上图的红色方块的定位就是相对于body的。
当我们把蓝方块宽高扩大100px,并将其设为红方块的父div,然后对红方块设置absolute, top、left:50px。此时红方块的是相对于body的,因为父元素蓝方块的position是默认值static。

接着将父元素蓝方块的position设为absolute,结果如下图所示。此时红方块的定位就是相对于蓝方块的。

3、position: relative
相对定位元素的定位是相对其正常位置。就是移动元素后,元素本来占有的位置会保留,然后会相对原来的位置定位。

<style>
* {
background: white;
margin: 0px;
}
.xm {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
margin: auto;
}
.xm-left {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
position:relative;
left:-20px;
margin: auto;
}
.xm-right {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
position:relative;
left:20px;
margin: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="xm">正常小明</div>
<div class="xm-left">左小明</div>
<div class="xm-right">右小明</div>
</body>4、position: fixed
元素的位置相对于浏览器窗口是固定位置。即使窗口是滚动的它也不会移动,可用于制作页面固定的导航栏。
.xm {
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
background: red;
position: fixed;
}








 本文详细介绍了CSS中的position属性,包括static、absolute、relative和fixed四种定位方式。通过实例解析了不同定位方式对元素位置的影响,帮助理解CSS布局原理。
本文详细介绍了CSS中的position属性,包括static、absolute、relative和fixed四种定位方式。通过实例解析了不同定位方式对元素位置的影响,帮助理解CSS布局原理。
















 730
730

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








